Tiny Japanese Satellite Will Write Morse Code Messages in the Sky

The robotic Japanese cargo vessel now en route to the International Space Station is loaded with food, clothes, equipment — and a set of tiny amateur radio satellites, including one that will write Morse code messages in the sky.
Japan's unmanned H-2 Transfer Vehicle-3 launched July 20 and is slated to arrive at the station Friday (July 27). The ultrasmall satellites it's carrying, which are known as cubesats, will likely remain on the orbiting lab until September, when they'll be deployed by Japanese astronaut Akihiko Hoshide using the Kibo module's robotic arm.
One of the cubesats, FITSAT-1, will write messages in the night sky with Morse code, helping researchers test out optical communication techniques for satellites, researchers said.
Artificial star
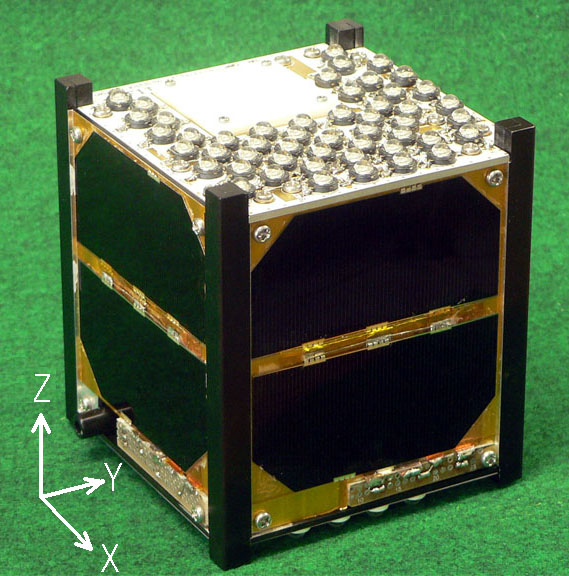
FITSAT-1 was developed at Japan’s Fukuoka Institute of Technology (FIT). It's nicknamed NIWAKA, which derives from "Hakata Niwaka," an improvised performance of traditional Japanese comedies with masks.
One of FITSAT-1's experimental duties is to twinkle as an artificial star, said project leader Takushi Tanaka, an FIT professor of computer science and engineering. Tanaka's research interests include artificial intelligence, language processing, logic programming and robot soccer, in addition to cubesats. [Video: Watch Robots Play Soccer]
Tipping the scales at just under 3 pounds (1.33 kilograms), FITSAT-1 carries high power light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that will produce extremely bright flashes.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"These, we hope, will be observable by the unaided eye or with small binoculars," Tanaka says on a FITSAT-1 website.
After its deployment from the orbiting lab, the cubesat's high-output LEDs will blink in flash mode, generating a Morse code beacon signal.
Morse code is a method of transmitting text information as a series of on-off tones, lights or clicks that can be understood by a skilled listener or observer.
"I am sure that FITSAT will work in space," Tanaka told SPACE.com, adding that the cubesat will likely be deployed Sept. 6.

Beaming with pride
FITSAT-1's orbit will take it between 51.6 degrees south latitude and 51.6 degrees north latitude, researchers said. The cubesat contains a neodymium magnet that forces it to always point to magnetic north, like a compass.

The flashing light from FITSAT-1 will be received by a Fukuoka Institute of Technology ground station that has a telescope and a photo-multiplier device linked to an antenna.
"When NIWAKA rises above the horizon, it will be to the south of the Fukuoka ground station," Tanaka said.
Both the ground gear and the LEDs will be aligned such that the ground station will be within the main beams, he added. Both high-speed and optical communication experiments will be performed for about three minutes as the satellite travels along its orbit.
The experiment will investigate the possibility of optical communication with satellites, Tanaka said.
Leonard David has been reporting on the space industry for more than five decades. He is a winner of last year's National Space Club Press Award and a past editor-in-chief of the National Space Society's Ad Astra and Space World magazines. He has written for SPACE.com since 1999.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Leonard David is an award-winning space journalist who has been reporting on space activities for more than 50 years. Currently writing as Space.com's Space Insider Columnist among his other projects, Leonard has authored numerous books on space exploration, Mars missions and more, with his latest being "Moon Rush: The New Space Race" published in 2019 by National Geographic. He also wrote "Mars: Our Future on the Red Planet" released in 2016 by National Geographic. Leonard has served as a correspondent for SpaceNews, Scientific American and Aerospace America for the AIAA. He has received many awards, including the first Ordway Award for Sustained Excellence in Spaceflight History in 2015 at the AAS Wernher von Braun Memorial Symposium. You can find out Leonard's latest project at his website and on Twitter.