Warp Drive May Be More Feasible Than Thought, Scientists Say
HOUSTON — A warp drive to achieve faster-than-light travel — a concept popularized in television's Star Trek — may not be as unrealistic as once thought, scientists say.
A warp drive would manipulate space-time itself to move a starship, taking advantage of a loophole in the laws of physics that prevent anything from moving faster than light. A concept for a real-life warp drive was suggested in 1994 by Mexican physicist Miguel Alcubierre; however, subsequent calculations found that such a device would require prohibitive amounts of energy.
Now physicists say that adjustments can be made to the proposed warp drive that would enable it to run on significantly less energy, potentially bringing the idea back from the realm of science fiction into science.
"There is hope," Harold "Sonny" White of NASA's Johnson Space Center said here Friday (Sept. 14) at the 100 Year Starship Symposium, a meeting to discuss the challenges of interstellar spaceflight.
Warping space-time
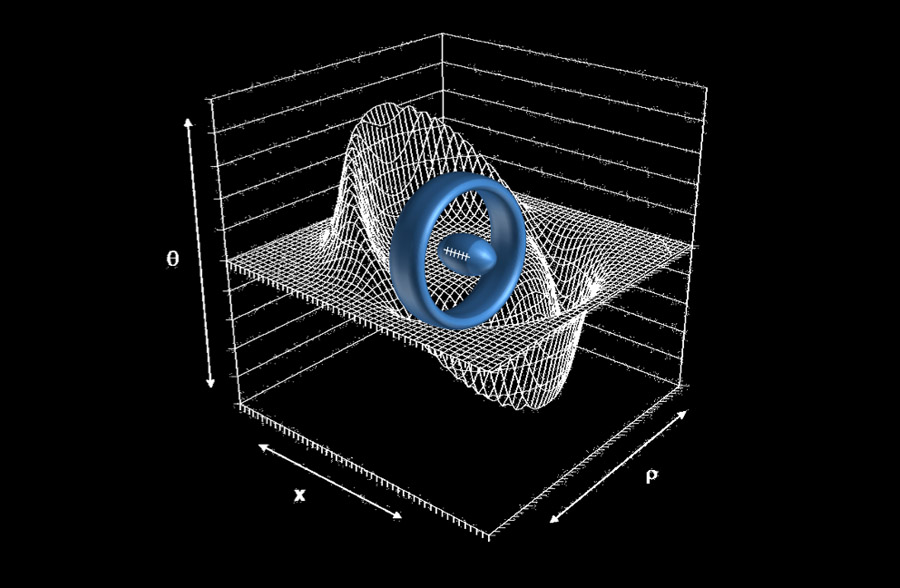
An Alcubierre warp drive would involve a football-shape spacecraft attached to a large ring encircling it. This ring, potentially made of exotic matter, would cause space-time to warp around the starship, creating a region of contracted space in front of it and expanded space behind. [Star Trek's Warp Drive: Are We There Yet? | Video]
Meanwhile, the starship itself would stay inside a bubble of flat space-time that wasn't being warped at all.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"Everything within space is restricted by the speed of light," explained Richard Obousy, president of Icarus Interstellar, a non-profit group of scientists and engineers devoted to pursuing interstellar spaceflight. "But the really cool thing is space-time, the fabric of space, is not limited by the speed of light."
With this concept, the spacecraft would be able to achieve an effective speed of about 10 times the speed of light, all without breaking the cosmic speed limit.
The only problem is, previous studies estimated the warp drive would require a minimum amount of energy about equal to the mass-energy of the planet Jupiter.
But recently White calculated what would happen if the shape of the ring encircling the spacecraft was adjusted into more of a rounded donut, as opposed to a flat ring. He found in that case, the warp drive could be powered by a mass about the size of a spacecraft like the Voyager 1 probe NASA launched in 1977.
Furthermore, if the intensity of the space warps can be oscillated over time, the energy required is reduced even more, White found.
"The findings I presented today change it from impractical to plausible and worth further investigation," White told SPACE.com. "The additional energy reduction realized by oscillating the bubble intensity is an interesting conjecture that we will enjoy looking at in the lab."
Laboratory tests
White and his colleagues have begun experimenting with a mini version of the warp drive in their laboratory.
They set up what they call the White-Juday Warp Field Interferometer at the Johnson Space Center, essentially creating a laser interferometer that instigates micro versions of space-time warps.
"We're trying to see if we can generate a very tiny instance of this in a tabletop experiment, to try to perturb space-time by one part in 10 million," White said.
He called the project a "humble experiment" compared to what would be needed for a real warp drive, but said it represents a promising first step.
And other scientists stressed that even outlandish-sounding ideas, such as the warp drive, need to be considered if humanity is serious about traveling to other stars.
"If we're ever going to become a true spacefaring civilization, we're going to have to think outside the box a little bit, we're going to have to be a little bit audacious," Obousy said.
You can follow SPACE.com assistant managing editor Clara Moskowitz on Twitter @ClaraMoskowitz. Follow SPACE.com on Twitter @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebook & Google+.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Clara Moskowitz is a science and space writer who joined the Space.com team in 2008 and served as Assistant Managing Editor from 2011 to 2013. Clara has a bachelor's degree in astronomy and physics from Wesleyan University, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. She covers everything from astronomy to human spaceflight and once aced a NASTAR suborbital spaceflight training program for space missions. Clara is currently Associate Editor of Scientific American. To see her latest project is, follow Clara on Twitter.