Effects of Worst Satellite Breakups in History Still Felt Today
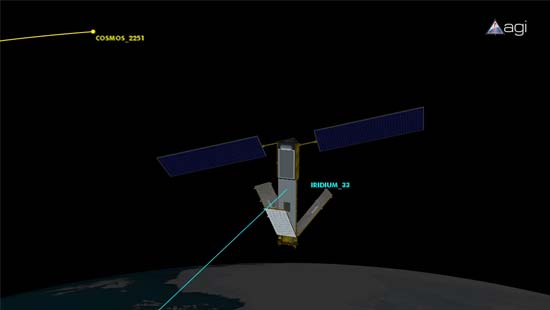
The anniversaries of two major space junk events — China's anti-satellite test on Jan. 11, 2007, and the destructive fender-bender between a defunct Soviet Union-era satellite with an operating U.S. spacecraft on Feb. 10, 2009 — are receiving special attention in orbital debris circles.
The Chinese anti-satellite test merited a nod by the Air Force Space Command (AFSPC) Public Affairs Office from Peterson Air Force Base in Colorado, labeling it an "Anniversary Milestone: Satellite Shootdown."
The Jan. 11 AFSPC release noted that the Chinese military used a ground-based missile to hit and destroy its aging Fengyun-1C weather satellite, which was orbiting more than 500 miles (805 kilometers) in space back in 2007.
"The test raised concerns about the vulnerability of U.S. satellites and a possible arms race in space," the press release stated.
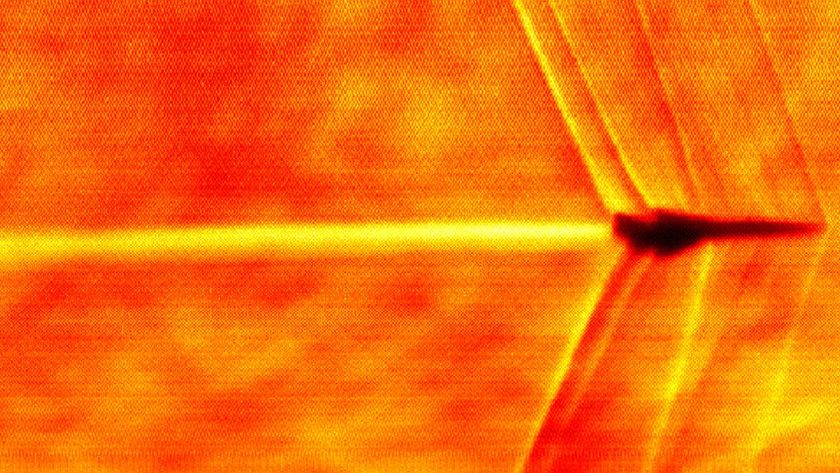
The anti-satellite test created more than 100,000 pieces of debris orbiting the planet, with about 2,600 of them more than 4 inches (10 centimeters) across, according to a NASA estimate.
"We carefully monitor those and the thousands of other bits of orbital debris to help provide for safe passage for those who traverse those orbits," the AFSPC statement concluded. [Worst Space Debris Events of All Time]
Debris count
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Similarly, NASA's "The Orbital Debris Quarterly News," a publication of the NASA Orbital Debris Program Office, spotlighted the two anniversaries in its January issue: China's ASAT test, as well as the upcoming fourth anniversary of the smashup between Russia's circa-1960s Cosmos 2251 spacecraft and the U.S. Iridium 33 communications satellite.
"The beginning of the year 2013 marks the sixth anniversary of the destruction of the Fengyun-1C (FY-1C) weather satellite as the result of an anti-satellite test conducted by China in January of 2007 and the fourth anniversary of the accidental collision between Cosmos 2251 and the operational Iridium 33 in February of 2009," the newsletter reported, adding, "These two events represent the worst satellite breakups in history."
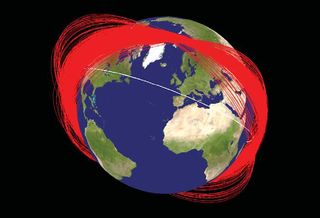
Altogether, the space junk created by these two events accounted for more than a third of the total cataloged satellite population in low-Earth orbit (LEO), where approximately 500 operational spacecraft reside or transit daily.
According to the NASA orbital debris office, a total of 5,579 fragments have been cataloged by the U.S. Space Surveillance Network (SSN) — a worldwide network of space surveillance radar and optical telescopes, both military and civilian — to observe the objects. Almost 5,000 of them still remain in orbit as of January 2013.
Changing the landscape
In addition to these cataloged objects, hundreds of thousands or more pieces of space litter, down to approximately a millimeter in size, were also generated during the breakups. These fragments are too tiny to be tracked by the SSN, but still large enough to be a safety concern for human space activities and robotic missions in low-Earth orbit — the region below 1,243 miles (2,000 km) altitude.
"Just like their cataloged siblings, many of them remain in orbit today. These two breakup events dramatically changed the landscape of the orbital debris environment in LEO," according to the NASA newsletter.
China's ASAT destruction of FY-1C and the mess produced, along with the Iridium 33 and Cosmos 2251 fragments, "will continue to be felt for decades to come," the newsletter points out.
In general, the Iridium 33 and Cosmos 2251 fragments will decay (in other words, be destroyed by falling through Earth's atmosphere) faster than the FY-1C fragments because of their lower altitudes. In the case of Iridium 33, that shorter lifetime is caused by the lightweight composite materials that were extensively used in the fabrication of the Iridium spacecraft.
Solar cycling
The enormous amounts of debris churned up by the fragmentations of Fengyun 1C, Cosmos 2251 and Iridium 33 will also be affected by our sun's 11-year cycle of activity, which is currently in what's called Solar Cycle 24, experts say.
Increased solar activity heats the Earth's atmosphere, causing it to expand. That expansion increases the density of the atmosphere at any given altitude. This, in turn, increases drag on space junk, as well as satellites, causing these objects to fall back to Earth more quickly.
By mid-2012, more than 570 (10 percent) of the cataloged debris from the ASAT test and the satellite collision had already fallen out of orbit and with an increasing rate. Many of the remaining cataloged bits of debris had also noticeably experienced the effects of atmospheric drag.
NASA predicts that Solar Cycle 24 will peak in early or mid-2013.
Future forecasting
However, Nicholas Johnson, chief scientist for orbital debris at the NASA Johnson Space Center in Houston, said the peak in solar activity expected in 2013 might be the lowest in 100 years.
"Hence, far fewer debris, both large and small, will fall back to Earth compared with a more normal solar cycle. This comes at a time of a record number of known orbital objects," Johnson said. "If solar activity does not return to normal levels during the next solar cycle (Solar Cycle 25), the rate of growth of the Earth orbital population will increase more rapidly than most forecasts now anticipate," he reported at last year's 63rd International Astronautical Congress in Naples, Italy.
Johnson also noted that by the end of Cycle 24 (estimated to come around 2020), about one-third of all debris from the two breakup events might have re-entered, depending upon the peak and duration of the forthcoming solar maximum.
Leonard David has been reporting on the space industry for more than five decades. He is former director of research for the National Commission on Space and a past editor-in-chief of the National Space Society's Ad Astra and Space World magazines. He has written for SPACE.com since 1999.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Leonard David is an award-winning space journalist who has been reporting on space activities for more than 50 years. Currently writing as Space.com's Space Insider Columnist among his other projects, Leonard has authored numerous books on space exploration, Mars missions and more, with his latest being "Moon Rush: The New Space Race" published in 2019 by National Geographic. He also wrote "Mars: Our Future on the Red Planet" released in 2016 by National Geographic. Leonard has served as a correspondent for SpaceNews, Scientific American and Aerospace America for the AIAA. He has received many awards, including the first Ordway Award for Sustained Excellence in Spaceflight History in 2015 at the AAS Wernher von Braun Memorial Symposium. You can find out Leonard's latest project at his website and on Twitter.