NASA to Launch World's Largest Solar Sail in 2014
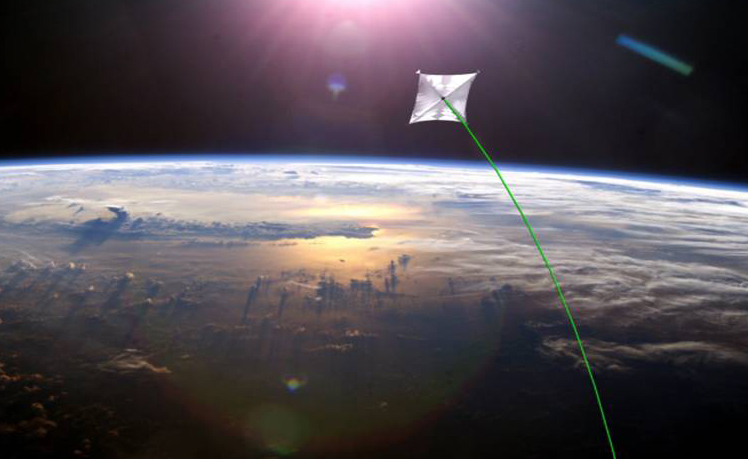

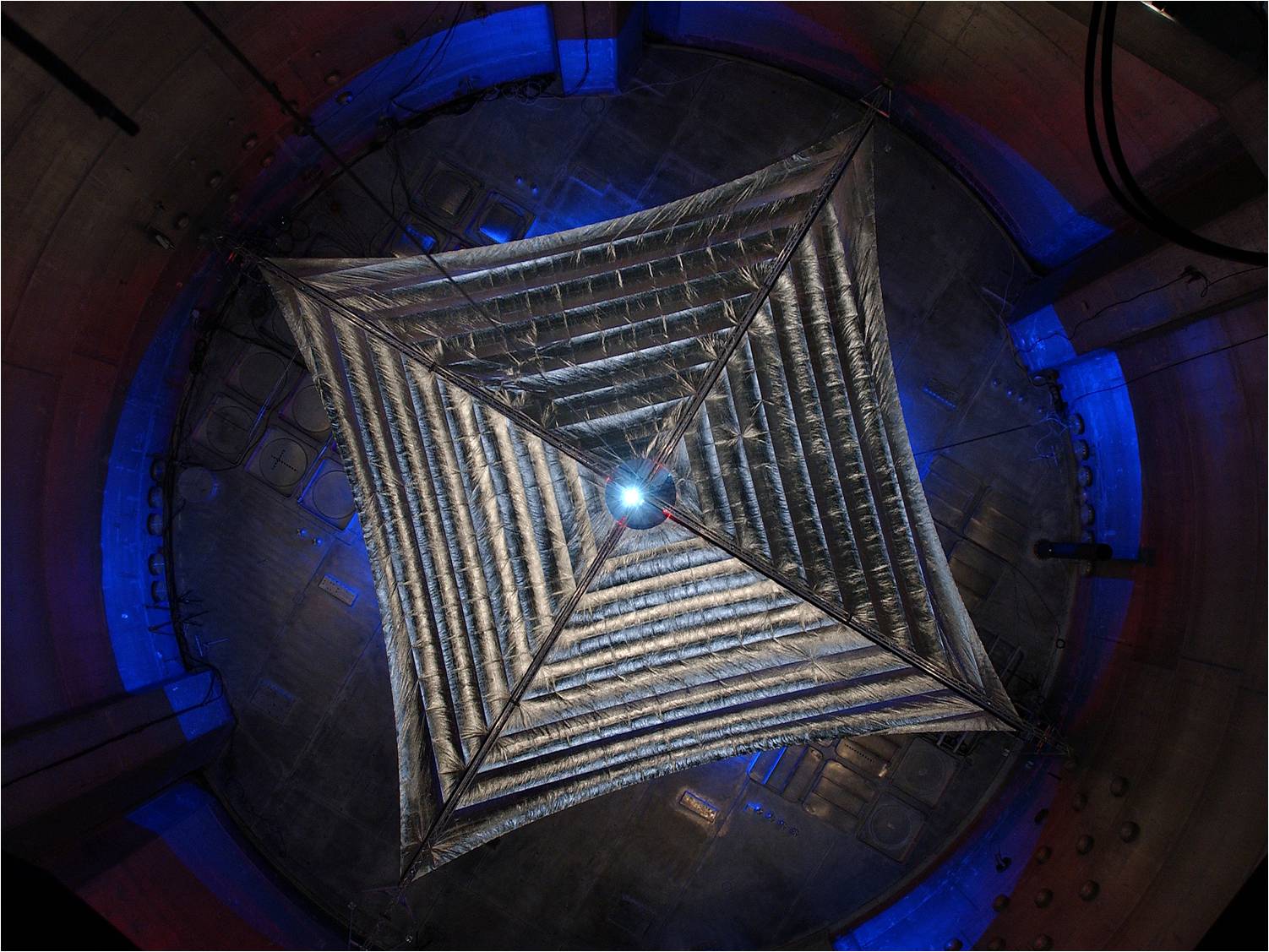
The largest solar sail ever constructed is headed for the launch pad in 2014 on a mission to demonstrate the value of "propellantless propulsion"— the act of using photons from the sun to push a craft through space.
Dubbed Sunjammer, the giant solar sail measures about 124 feet (38 meters) on a side and boasts a total surface area of nearly 13,000 square feet (1,208 square m, or one-third of an acre). The project is under the wing of NASA's Space Technology Program, within the agency's Office of the Chief Technologist.
NASA has contracted with a team of high-tech "solar sailors" at L'Garde Inc. of Tustin, Calif., to build Sunjammer.
L'Garde is no newcomer to novel space structures. The company has worked with the space agency on several projects, including the creation of inflatable structures for radio frequency antennas and solar arrays. In 1996, the company flew the Inflatable Antenna Experiment (IAE) aboard the space shuttle Endeavour's STS-77 mission. [Photos: Solar Sail Evolution for Space Travel]
Programmatic milestone
"We took the name Sunjammer from an Arthur C. Clarke short story, a fictional yacht race in the heavens using solar sails," said Nathan Barnes, L'Garde's chief operating officer and executive vice president, as well as Sunjammer's project manager. Permission to use the name came from the Clarke estate, he told SPACE.com.
Work on Sunjammer this year includes a programmatic milestone — a critical design review — along with a variety of ground demonstration tests and qualification of components, Barnes said. The flight of the solar sail, he said, is set for the end of 2014, to be sent spaceward atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"With this sail, we’re targeting our end goal somewhere in the neighborhood of 1,864,114 miles (3 million kilometers) distance from the Earth," Barnes said.
A number of test objectives are to be checked off within the first couple months of flight, he added. These include deployment of the sail, demonstration of vector control using sail-tipped vanes, navigation with accuracy and, finally, maintenance of the spacecraft's position at a gravitationally stable location called Earth-Sun Lagrange Point 1.
Sunjammer won't be the world's first solar sail mission. NASA launched NanoSail-D, whose sail covered just 100 square feet (9.3 square m), in November 2010. And Japan's Ikaros probe deployed its solar sail in June 2010, becoming the first craft ever to cruise through space propelled only by sunlight.
Neat, clever, exotic orbits
Sunjammer is potentially applicable to an advanced space weather warning system, which could provide more timely and accurate notice of solar flare activity.
The U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration is collaborating with NASA and L’Garde on the upcoming demonstration flight, which will cruise to a spot that provides an interesting view of the sun.
"It will be us flying to a place that a customer actually wants to fly a solar sail to," Barnes said. "There are neat, clever, exotic orbits you can do with the solar sail that would permit viewing different portions of the sun that we can’t normally." [The Sun's Wrath: Worst Solar Storms in History]
One-quarter the size of a football field, Sunjammer will produce a whopping maximum thrust of approximately 0.01 newton, Barnes said — roughly equivalent to the weight of a sugar packet.
Thinner sail
Kapton is the solar sail material of choice. The mission team worked with chemical company DuPont to produce a special layer of Kapton for Sunjammer just 5 microns thick.
"Thinner is always better," Barnes said.
When collapsed, the Sunjammer solar sail is the size of a dishwasher and weighs just 70 pounds (32 kilograms).
There are a number of control techniques involved in successfully unfurling the sail, said Billy Derbes, L’Garde’s chief engineer for Sunjammer.
"The highest risk is in the deployment," Derbes said. A camera attached to the sail will capture the unfurling process.
Game-changing capabilities
NASA is keen to infuse solar sail technology into other potential game-changing mission capabilities.
Barnes said that possibilities include the collection and removal of orbital debris, deorbiting spent satellites, providing a direct communications link to Earth’s south pole, as well as for deep space propulsion.
Barnes said nongovernment, entertainment-oriented uses of solar sails are also being explored by L’Garde.
"All space travel right now is limited by expendables," Derbes said. "If you show a technology not limited by expendables — and Kapton is a long-lasting film material — what new applications will people think up? We’re opening up a whole new kind of thinking about how you do things in space."
'Star Trek' passengers
Also to fly onboard Sunjammer are the cremated remains of individuals, a service provided by Celestis, Inc., an affiliate company of Space Services, Inc., a Houston-based aerospace firm.
Celestis flight capsules and modules will be carried by Sunjammer on its voyage through deep space. Already part of that payload are the ashes of "Star Trek" creator Gene Roddenberry and his wife Majel Barrett Roddenberry, often called the "first lady" of the sci-fi series.
"Celestis is pleased to offer our first-ever Voyager deep space memorial spaceflight aboard the Sunjammer mission," said Celestis CEO Charles Chafer.
"Since 1997, Celestis has conducted a dozen memorial spaceflights, and this solar sail mission will mark our most ambitious flight ever. We are excited to be a part of the Sunjammer team," Chafer told SPACE.com.
'Green' space propulsion
Sunjammer’s success is the key to enabling several science and exploration missions that can only be accomplished with a solar sail, said Les Johnson, deputy manager of the Advanced Concepts Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala.
Along with better sun-watching and warning tasks, NASA recently studied the use of a solar-sail-propelled spacecraft for visiting multiple near-Earth asteroids (NEAs), Johnson said.
"We found that a Sunjammer-derived sail could visit up to six NEAs within six years of being launched. This would be impossible with chemical rockets and might not be achievable by electric propulsion. And it’s all because the sail uses no propellant … deriving its thrust from sunlight, making it a very ‘green’ space propulsion system," he said.
Johnson is co-editor with Jack McDevitt of "Going Interstellar" (Baen Books, 2012), a unique blend of science fact and science-fiction writings on interstellar voyaging.
"For me, I’m most excited about using a solar sail unfurled close to the sun, inside the orbit of Mercury, and using the increased solar pressure there to accelerate a large solar sail to speeds that will allow it to reach well beyond the edge of the solar system and into interstellar space within my lifetime," Johnson said.
Doing so, Johnson said, "would be the first ‘baby step’ in a series of increasingly large sails that might one day enable us to reach the stars. This is one of the few ways nature has provided for us to travel between the stars."
Leonard David has been reporting on the space industry for more than five decades. He is former director of research for the National Commission on Space and a past editor-in-chief of the National Space Society's Ad Astra and Space World magazines. He has written for SPACE.com since 1999. Follow SPACE.com on Twitter @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebook & Google+.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Leonard David is an award-winning space journalist who has been reporting on space activities for more than 50 years. Currently writing as Space.com's Space Insider Columnist among his other projects, Leonard has authored numerous books on space exploration, Mars missions and more, with his latest being "Moon Rush: The New Space Race" published in 2019 by National Geographic. He also wrote "Mars: Our Future on the Red Planet" released in 2016 by National Geographic. Leonard has served as a correspondent for SpaceNews, Scientific American and Aerospace America for the AIAA. He has received many awards, including the first Ordway Award for Sustained Excellence in Spaceflight History in 2015 at the AAS Wernher von Braun Memorial Symposium. You can find out Leonard's latest project at his website and on Twitter.