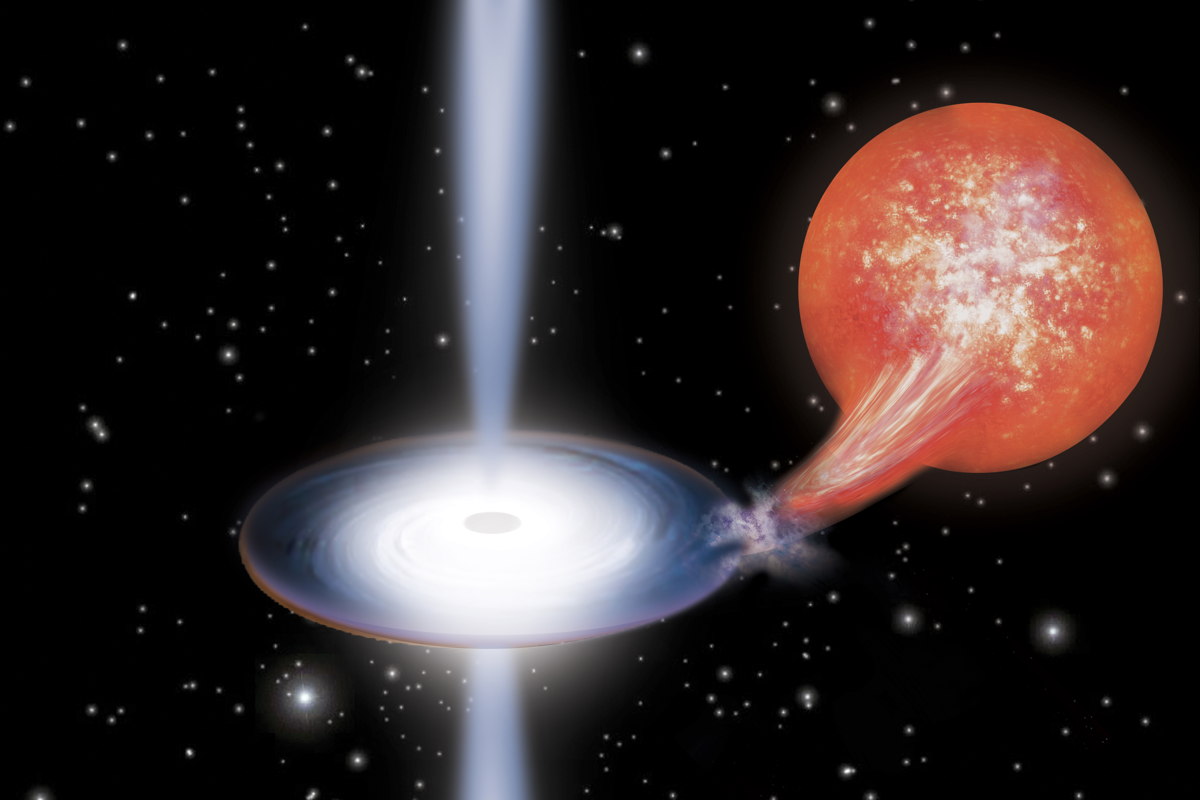

Astronomers have taken an unprecedented look at the superenergetic jets blasted out by black holes, and thus have answered a key question about the composition of these mysterious beams.
Scientists found evidence of nickel and iron in the jets emitted by a relatively small black hole, suggesting that "normal" matter plays a bigger role in these enigmatic structures than does exotic antimatter.
"We've known for a long time that jets contain electrons but haven't got an overall negative charge, so there must be something positively charged in them, too," study co-author James Miller-Jones, from the Curtin University node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research in Australia, said in a statement. [Images: Black Holes of the Universe]
"Until now, it wasn't clear whether the positive charge came from positrons, the antimatter 'opposite' of electrons, or positively charged atoms," Miller-Jones added. "Since our results found nickel and iron in these jets, we now know ordinary matter must be providing the positive charge."
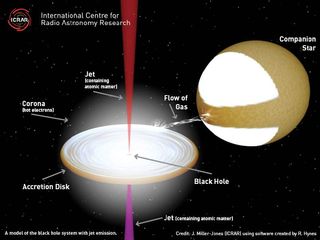
The researchers took the measure of 4U1630-47, a black-hole candidate just a few times more massive than the sun. They studied the object's X-ray emissions using the the European Space Agency's XMM-Newton satellite and analyzed the black hole in radio wavelengths using the Australia Telescope Compact Array system.
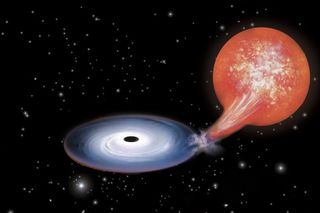
The radio observations keyed the team in to the sudden appearance of the jets, while XMM-Newton's data revealed emission lines in the jets' X-ray spectrum corresponding to iron and nickel. Further, these lines were shifted significantly, much as the sound from a siren changes pitch when a fire truck or ambulance approaches and then passes an observer, researchers said.
"It led us to conclude the particles were being accelerated to fast speeds in the jets — one directed towards Earth, and the other one in the opposite direction," co-author Simone Migliari, of the University of Barcelona, said in a statement.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The team calculated the mind-blowing velocity of the narrowly focused jets to be about 66 percent of the speed of light, or 440 million mph (708 million km/h).
Because positively charged atoms are much heavier than positrons, the jets are likely carrying a great deal more energy away from the black hole than previous studies had been able to confirm, researchers said.
The new findings also could help answer another long-standing mystery about black-hole jets: the location from which they are launched. Some astronomers think jets are powered by the spin of their host black holes, while others posit that they spring from the disk of material that surrounds and feeds these light-gobbling monsters.
"Our results suggest it's more likely the disk is responsible for channelling the matter into the jets, and we are planning further observations to try and confirm this," Miller-Jones said.
Follow Mike Wall on Twitter @michaeldwall and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook or Google+. Originally published on SPACE.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.