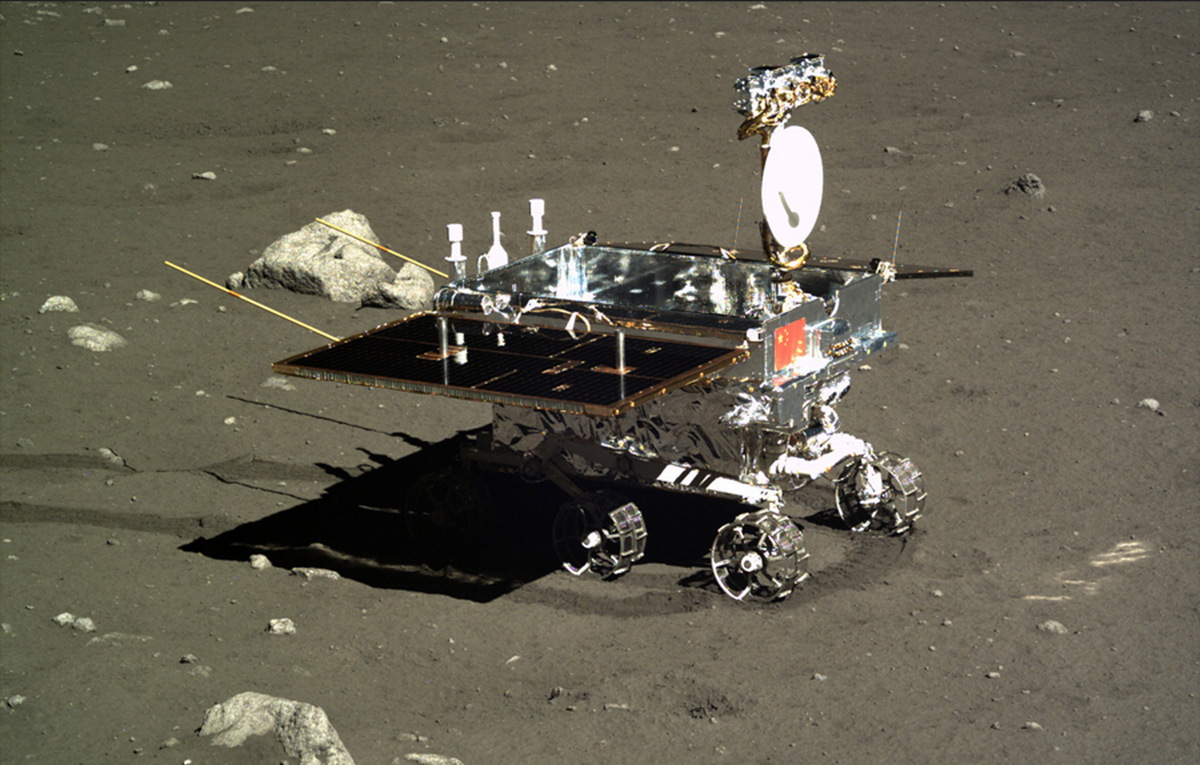
The moon's past was livelier and more complex than scientists had thought, new results from China's first lunar rover suggest.
China's Yutu moon rover found evidence of at least nine distinct rock layers deep beneath its wheels, indicating that the area has been surprisingly geologically active over the past 3.3 billion years.
"Two things are most interesting," said Long Xiao, a researcher at the China University of Geosciences in Wuhan, who is the lead author of the study detailing the new findings. "One is [that] more volcanic events have been defined in the late volcanism history of the moon," Xiao told Space.com via email. [The Moon: 10 Surprising Lunar Facts]
"Another is the lunar mare [volcanic plain] area is not only composed of basaltic lavas, but also explosive eruption-formed pyroclastic rocks," Xiao added. "The latter finding may shed light on … the volatile contents in the lunar mantle."


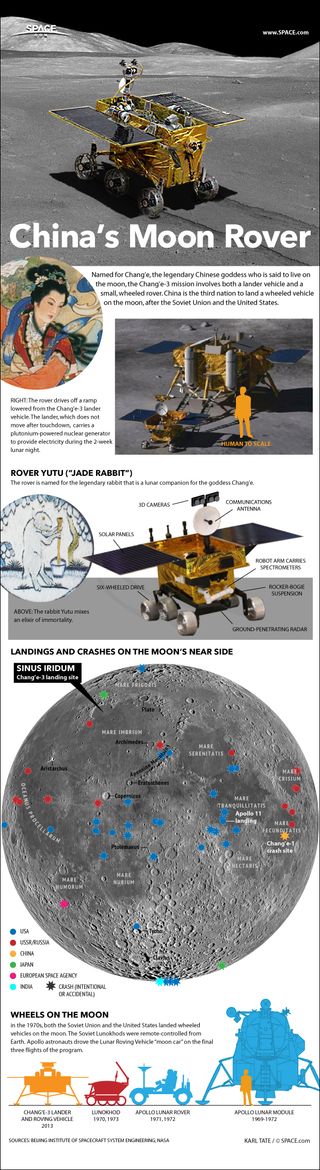
Yutu (whose name means "jade rabbit") is part of China's Chang'e 3 moon mission. Chang'e 3 delivered Yutu and a stationary lander to the lunar surface on Dec. 14, 2013 — the first soft touchdown on the moon since the Soviet Union's Luna 24 mission in 1976.
Yutu traveled 374 feet (114 meters) on the moon in a zigzag fashion before a glitch ended its travels in January 2014.
The rover was equipped with cameras and three main scientific instruments — the Lunar Penetrating Radar (LPR), the Visible Near-Infrared Spectrometer (VNIS) and the Active Particle-Induced X-ray Spectrometer (APXS). The new study, which was published online today (March 12) in the journal Science, reports results from the camera and the LPR, which can probe about 1,300 feet (400 m) beneath the moon's surface.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Those data paint a detailed portrait of the Chang'e 3 landing site, which sits just 165 feet (50 m) away from a 1,475-foot-wide (450 m) crater known as C1. C1 was gouged out by a cosmic impact that occurred sometime between 80 million and 27 million years ago, the study authors said.
Yutu studied the ground it rolled over, characterized the craters it cruised past and investigated an oddly coarse-textured rock dubbed Loong, which measures about 13 feet long by 5 feet high (4 by 1.5 m). Overall, the rover's observations suggest that the composition of its landing site is quite different from that of the places visited by NASA's Apollo missions and the Soviet Union's Luna program.
While Yutu isn't beaming home any new data these days, the scientific community can expect to hear about more discoveries from the mission shortly, Xiao said.
"Unfortunately, Yutu encountered mechanical problems and has ended its mission," he told Space.com. "No more data will come. However, our report only provides the scientific results based on imagery and radar data. More results from NIS and APXS for composition study will come out soon."
Follow Mike Wall on Twitter @michaeldwall and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook or Google+. Originally published on Space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.