Problem Detected with Voyager 2 Spacecraft at Edge of Solar System
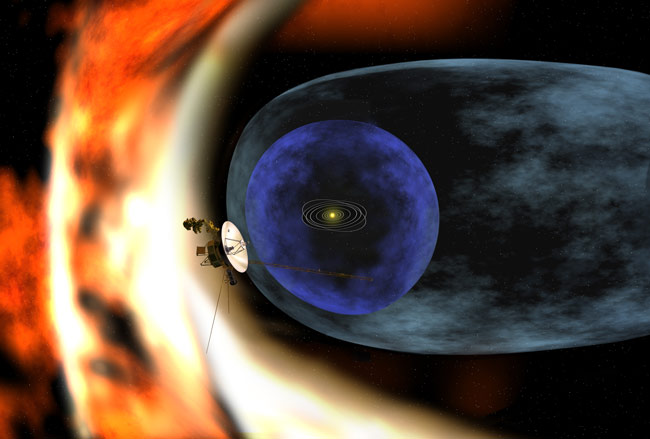
NASA has commanded the famed Voyager 2 probe to send only information on its health and status after spotting a puzzling change in the spacecraft's pattern of communication from the edge of the solar system.
The 33-year-old Voyager 2 spacecraft, which is currently 8.6 billion miles (13.8 billion km) from Earth, is apparently still in good health, according to the latest engineering data received on May 1. But Voyager 2's flight data system, which formats information before beaming it back to Earth, has experienced a hiccup that altered the pattern in which it sends updates home.
Because of that pattern change, mission managers can no longer decode the science data beamed to Earth from Voyager 2. The space probe and its twin Voyager 1 are flying through the bubble-like heliosphere, created by the sun, which surrounds our solar system.
The first hint of a problem came on April 22, when engineers first spotted the data pattern change. Since then, they've been working to fix the glitch and began sending commands back to Voyager 2 on April 30.
Because Voyager 2 is so far from Earth, it takes 13 hours for a message to reach the spacecraft and another 13 hours for responses to come back to NASA's Deep Space Network of listening antennas around the world.
"Voyager 2's initial mission was a four-year journey to Saturn, but it is still returning data 33 years later," said Voyager project scientist Ed Stone of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. "It has already given us remarkable views of Uranus and Neptune, planets we had never seen close-up before. We will know soon what it will take for it to continue its epic journey of discovery."
Voyager 2 took a so-called "grand tour" of the solar system when it visited the gas giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune in the 1980s by taking advantage of a rare planetary alignment that occurs once every 176 years.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The two space probes were built primarily to study Jupiter and Saturn, but Voyager 2 also swing by Uranus in 1986 and Neptune in 1989 during its extended mission.
NASA launched Voyager 2 on Aug. 20,1977, just two weeks before Voyager 1. Together, the two spacecraft are the most distant human-built objects in space. Voyager 1 is about 10.5 billion miles (16.9 billion km) away from Earth and in perfect health, mission managers said.
- Gallery: Voyager's Photo Legacy
- Top 10 Voyager Facts
- Voyager Spacecraft Reveals Solar System Edge

Tariq is the award-winning Editor-in-Chief of Space.com and joined the team in 2001. He covers human spaceflight, as well as skywatching and entertainment. He became Space.com's Editor-in-Chief in 2019. Before joining Space.com, Tariq was a staff reporter for The Los Angeles Times covering education and city beats in La Habra, Fullerton and Huntington Beach. He's a recipient of the 2022 Harry Kolcum Award for excellence in space reporting and the 2025 Space Pioneer Award from the National Space Society. He is an Eagle Scout and Space Camp alum with journalism degrees from the USC and NYU. You can find Tariq at Space.com and as the co-host to the This Week In Space podcast on the TWiT network. To see his latest project, you can follow Tariq on Twitter @tariqjmalik.
