Mars Craters Tell Story of Water and Ice
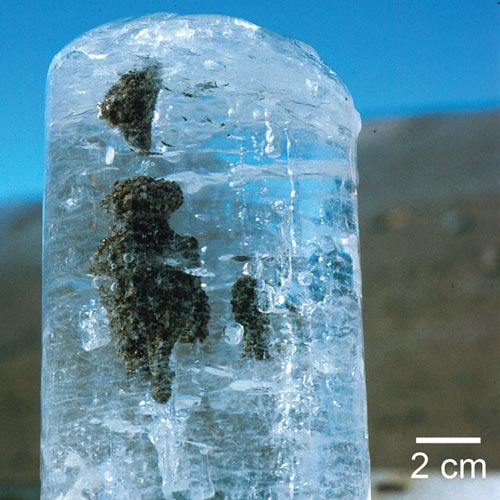

Enigmatic 'Meridiani Planum' deposits on Mars -- deep salty areas found by NASA's Opportunity rover -- have attracted several theories to explain their existence in recent years.
Add another one to the list: the Martian deposits could be remnants of a massive ancient ice-field, a new study suggests.
This new icy theory better explains some of the odd signatures of the deposits, its authors say. The finding, detailed in the Feb. 15 online version of the journal Nature Geoscience, "advances a new idea for how the sedimentology of Mars developed," said study co-author Paul Niles of NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston.
Evaporating ocean, bubbling groundwater
Opportunity discovered the deposits, which are nearly half-a-mile deep in places, when it landed on Mars in 2004. Similar layers are seen scattered across the planet, but are concentrated around Meridiani, an area that covers several hundred square miles.
The deposits feature thick layers of salty minerals, including calcium and magnesium sulfates.
Previous theories on the origin of the deposits include evaporation of a giant ocean that once covered the northern plains of Mars, and, as described in a 2007 study, and the evaporation of shallow pools created by groundwater bubbling up from below the surface.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
On Earth, similar salty deposits, such as those in White Sands, New Mexico, are known to have come from the evaporation of lakes.
But lake and oceans require an enclosed space to hold the water, which Meridiani does not have. The 2007 study used a model to show the area was suited to groundwater upwelling, but Niles says it still leaves some of the chemistry of the deposits unexplained.
On Earth, ocean evaporate deposits are purely calcium sulfates, because magnesium stays dissolved in the water. But on Mars, there are "mixtures of minerals that don't really seem to go together," Niles told Space.com. "It's an interesting thing to try to explain."
The theory put forward by Niles and his co-author Joseph Michalski, of the Université Paris Sud in France, provides an explanation for the discrepancy.
Ice and acid
The new theory draws on the mechanism that scientists think is responsible for forming the ice that currently tops Mars' polar caps.
It is thought that that ice forms from snow created in the atmosphere when water is sucked up by dust and aerosols, a process called nucleation (the same process is also responsible for the snow and rain on Earth). Much of the aerosol incorporated into the snow was likely sulfur dioxide from volcanic emissions, Niles said.
"It's kind of like acid rain on Earth," he said.
All that ice and dust and aerosol eventually gets incorporated into a large ice field. While the ice reflects incoming sunlight, the dust grains absorb it and "get warmer than the ice," Niles explained. The ice around the grains melts, creating little pockets where the trapped materials can react with the water.
The sulfur aerosols make the water acidic, and it stays very acidic because any excess water is frozen out by the extremely cold temperatures.
Because the acidic water is kept in small pockets, the minerals in the silicate dust grains don't separate out like they would in a larger space. Such aggregates of grains have been seen in Antarctic ice cores.
Changing climate
Niles and Michalski propose that the ice was able to form around the area of Meridiani, which is nowhere near the poles today, because the past climate of Mars was different. Either a natural wandering of the Martian poles or changes in its degree of tilt, which could put the equator in the position of the poles today, could have made the area colder in the past.
The climate later changed, and the ice sublimed, leaving behind the clumps of minerals. This dust could later have been blown from its original position, reworking it into the apparently windblown deposits observed today.
The case of how the deposits came to be still isn't closed though, and it may take a rover exploring these or similar deposits to nail their origin down.
"There's a lot more work to be done to figure out how this happened," Niles said.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Andrea Thompson is an associate editor at Scientific American, where she covers sustainability, energy and the environment. Prior to that, she was a senior writer covering climate science at Climate Central and a reporter and editor at Live Science, where she primarily covered Earth science and the environment. She holds a graduate degree in science health and environmental reporting from New York University, as well as a bachelor of science and and masters of science in atmospheric chemistry from the Georgia Institute of Technology.