How Astronomers May Hunt for Life on Alien Planets
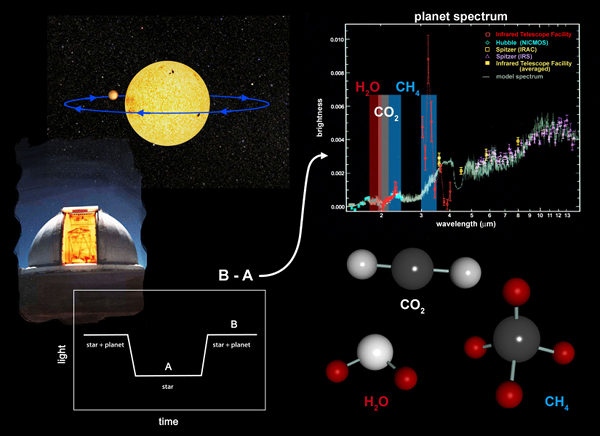
Any sulfurous molecules that astronomers spot on alien worlds might be a way to reveal whether or not those distant planets host life, researchers suggest.
On Earth, microbes can live off the energy available in sulfurous molecules that volcanoes release, essentially "breathing" these compounds the way humans breathe oxygen. If a similar kind of metabolism evolved on an extrasolar planet, the sulfurous molecules detected in the atmosphere of that world might help reveal the presence of alien life, said researcher Renyu Hu, a doctoral student in planetary science at MIT.
To see what telltale signs any sulfur-dependent life might generate, Hu and his colleagues modeled Earth-sized planets in the habitable zones of sun-like stars — that is, areas where worlds could have liquid water on their surfaces. These simulated planets possessed nitrogen-based atmospheres like Earth but 1,000 times more sulfur.

Sulfur-dependent life on Earth releases hydrogen sulfide as waste. The researchers found these microbes could increase hydrogen sulfide levels by nearly 10 times what they would be on a planet without such life. [Graphic: Sky Full of Alien Planets]
From interstellar distances, it would be hard to distinguish hydrogen sulfide (H2S) from water (H2O) on the surfaces of exoplanets. However, the researchers calculate that extra atmospheric hydrogen sulfide would in turn cause more pure sulfur aerosols to form in the air, which astronomers could detect based on their distinctive spectra or fingerprint in the visible and infrared wavelengths.
"Hydrogen sulfide emissions from the surface would have a large impact on the atmospheric composition of a planet," Hu said.
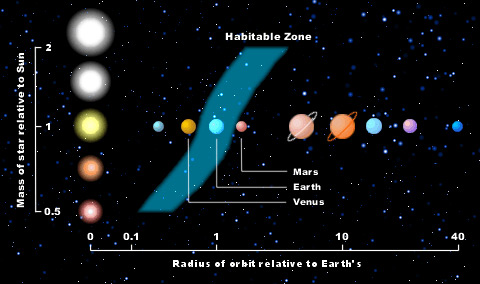
Still, no Earth-sized planets have been discovered yet in the habitable zones of sun-like stars. "Characterization of the atmospheres of exoplanets has been confined to close-in planets so far," Hu said.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Also, Hu cautioned that hydrogen sulfide is not a conclusive signature of life. "We need to test our assumptions thoroughly," he said. "It may be, for instance, that volcanism could produce tremendous amounts of that gas."
Hydrogen sulfide is not the only biosignature gas the researchers are investigating.
"We want to study as many as possible — look at many, many gases in Earth's atmosphere and see if they can be biosignatures as well," Hu said.
Hu, with his colleagues Sara Seager and William Baines, detailed their findings May 26 at the American Astronomical Society meeting in Boston.
This story was provided by Astrobiology Magazine, a web-based publication sponsored by the NASA astrobiology program.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Charles Q. Choi is a contributing writer for Space.com and Live Science. He covers all things human origins and astronomy as well as physics, animals and general science topics. Charles has a Master of Arts degree from the University of Missouri-Columbia, School of Journalism and a Bachelor of Arts degree from the University of South Florida. Charles has visited every continent on Earth, drinking rancid yak butter tea in Lhasa, snorkeling with sea lions in the Galapagos and even climbing an iceberg in Antarctica. Visit him at http://www.sciwriter.us










