Future Spacesuit to Imitate Gravity on Long NASA Missions
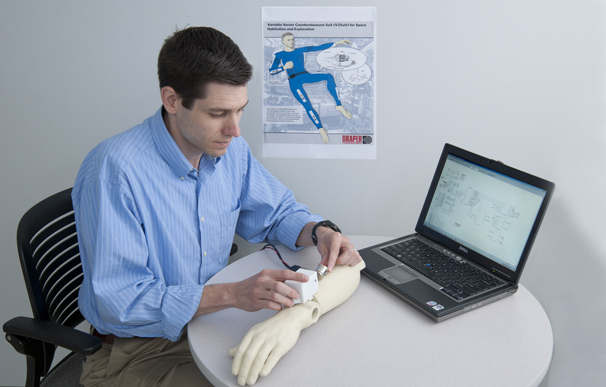
Just reaching for floating M&Ms aboard the space station can prove tricky for new astronauts whose bodies are accustomed to Earth's gravity. On long missions to other planets, they might not struggle so much if they had spacesuits designed to resist movement in an imitation of gravity.
Such a suit could help stabilize astronauts living in the microgravity environment of space stations and spaceships so that they avoid the body coordination mistakes that make even simple tasks difficult.
NASA commissioned work toward a suit for future space missions based on an idea by the Draper Laboratory.
"We would expect the resistance to simulate movements against a gravitational acceleration when in microgravity," said Kevin Duda, senior member of the technical staff in the Draper Laboratory's Human Centered Engineering Group, at Cambridge, Mass.
An inertial measurement unit would help the suit gauge an astronaut's movement. That in turn could allow flywheel gyroscopes — spinning devices that resist changes in angular momentum caused by motion — to raise or lower spacesuit resistance for every movement, by increasing speed or changing direction. [Infographic: Spacesuit Evolution Through the Years]
First-generation versions of the suit mainly would help astronauts working inside the protected habitat of a space station or spacecraft. But if the concept holds up, it might eventually help stabilize astronauts during spacewalks, as well as on low-gravity planets or asteroids.
"Sensing and adapting to exactly what an astronaut wants to do is difficult," Duda told InnovationNewsDaily. "We need to analyze the mechanics and prototype the concept before we can accurately quantify the type of performance we can expect."
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Wearing such a suit also might help astronauts ease back into life on Earth, because their muscle coordination would not have to readjust from the resistance-free motions in microgravity.
Another side benefit from the suit could take the form of a space technology spinoff that helps people go through physical rehabilitation. Patients suffering from stroke, spinal cord and brain injuries could make use of the device, as could older people.
"A wearable, full-motion device could be programmed to help you learn, or re-learn, specific movements," Duda explained.
Duda's Draper Lab group has partnered on the project with scientists at NASA's Johnson Space Center and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. They plan to first create a prototype for a spacesuit arm by 2012, with funding from the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts program.
If success attracts continued funds, Duda said, a full-body wearable suit could become a reality within a decade — easily within the time frame for NASA's plans targeting the asteroids, Mars and beyond.
You can follow InnovationNewsDaily senior writer Jeremy Hsu on Twitter @ScienceHsu. Follow InnovationNewsDaily on Twitter @News_Innovation, or on Facebook.
Jeremy Hsu is science writer based in New York City whose work has appeared in Scientific American, Discovery Magazine, Backchannel, Wired.com and IEEE Spectrum, among others. He joined the Space.com and Live Science teams in 2010 as a Senior Writer and is currently the Editor-in-Chief of Indicate Media. Jeremy studied history and sociology of science at the University of Pennsylvania, and earned a master's degree in journalism from the NYU Science, Health and Environmental Reporting Program. You can find Jeremy's latest project on Twitter.

