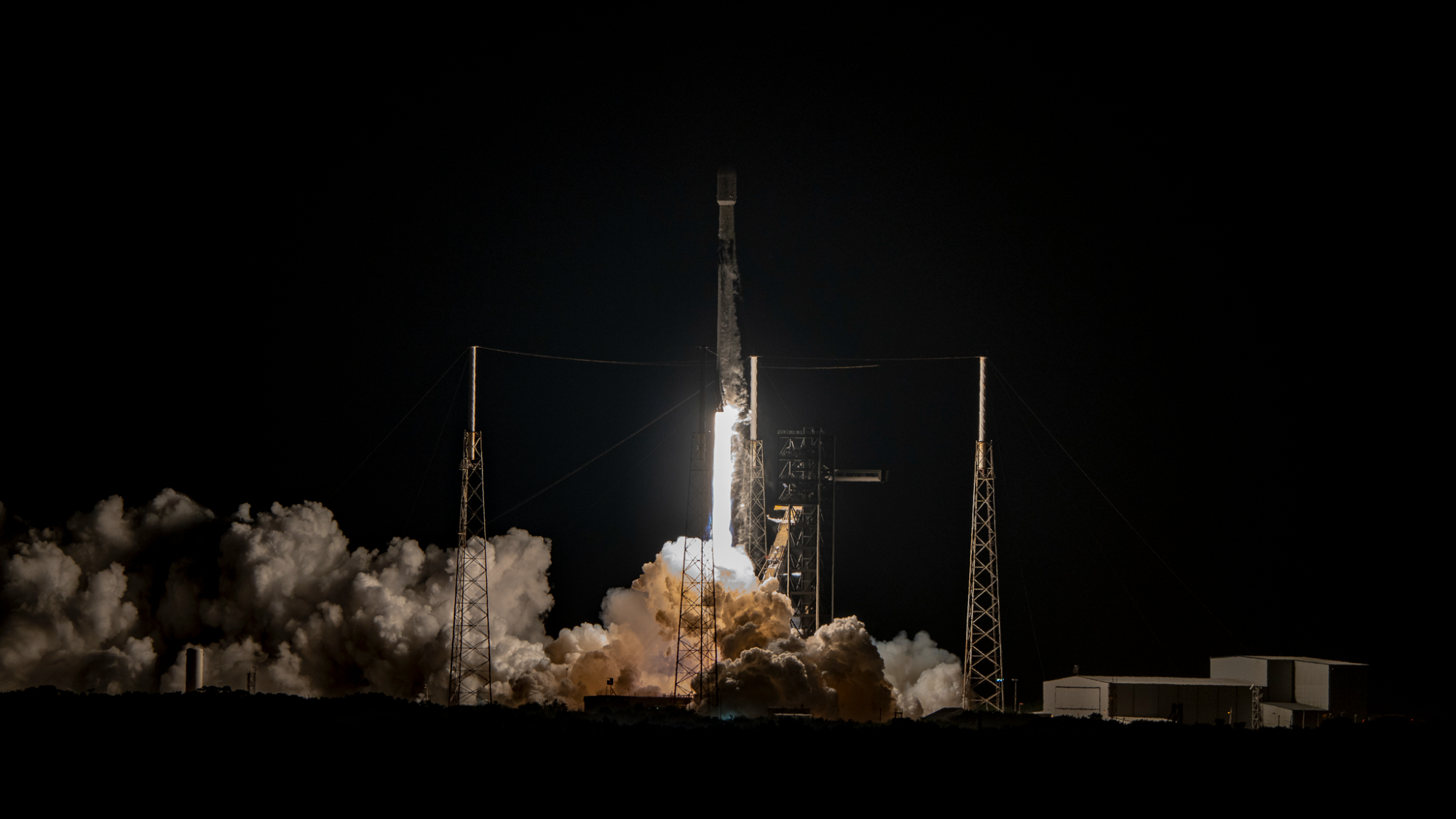
A robotic Russian spacecraft that launched on a mission to the Mars moon Phobos Tuesday (Nov. 8) is apparently stuck in Earth orbit, but hope for the probe is not lost yet, according to news reports.
The Phobos-Grunt spacecraft launched at 3:16 p.m. EST (2016 GMT) Tuesday and was supposed to be on its way to Phobos by now. The probe separated from its Zenit rocket properly, but its own thrusters then failed to fire in order to send the spacecraft streaking toward Mars, Russian officials said.
"It has been a tough night for us because we could not detect the spacecraft [after the separation]," Russian space agency chief Vladimir Popovkin said, Russian news agency RIA Novosti reported. "Now we know its coordinates and we found out that the [probe's] engine failed to start."
Popovkin added that engineers aren't yet sure why Phobos-Grunt's engine didn't ignite, according to RIA Novosti. It's possible the onboard computers didn't send the proper command, he said.
Whatever the cause, the malfunction dealt a serious blow to the $163 million Phobos-Grunt mission, which aims to grab bits of Phobos' surface and send them back to Earth by 2014. But there may still be hope for the spacecraft, Russia's first attempt at an interplanetary mission since 1996.
"We will attempt to reboot the program," RIA Novosti reported Popovkin as saying. "The spacecraft is currently on a support orbit, the fuel tanks have not been jettisoned, and the fuel has not been spent."
Engineers have about three days to figure out and fix the problem, Popovkin added. After that time, Phobos-Grunt's batteries will run out, and the spacecraft will likely turn into just another piece of space debris. [Photos: Russia's Phobos-Grunt Mission to Mars Moon]
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Phobos-Grunt is also carrying China's first Mars probe, a small spacecraft called Yinghuo 1, that is supposed to separate from Phobos-Grunt and enter orbit around the planet Mars.
If Phobos-Grunt cannot be salvaged, it would mark the fourth straight Mars failure for Russia.
The nation's Phobos 1 and Phobos 2 spacecraft, which launched in July 1988, suffered critical failures before their missions were complete. And the Mars 96 probe crashed into the Pacific Ocean shortly after liftoff in November 1996.
Russia is not alone in suffering setbacks with Mars missions. Historically, about half of all missions aimed at the Red Planet have failed, according to NASA records.
NASA also currently plans to launch a new U.S. mission to Mars this month. The $2.5 billion Mars Science Laboratory mission will send a car-size rover called Curiosity to explore the huge Gale crater on Mars.
Several spacecraft are actively studying Mars today. They include orbiting spacecraft operated by NASA and the European Space Agency, as well as NASA's Opportunity rover on the planet's surface.
You can follow SPACE.com senior writer Mike Wall on Twitter: @michaeldwall. Follow SPACE.com for the latest in space science and exploration news on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.