This story was updated at 8:10 a.m. EST Saturday.
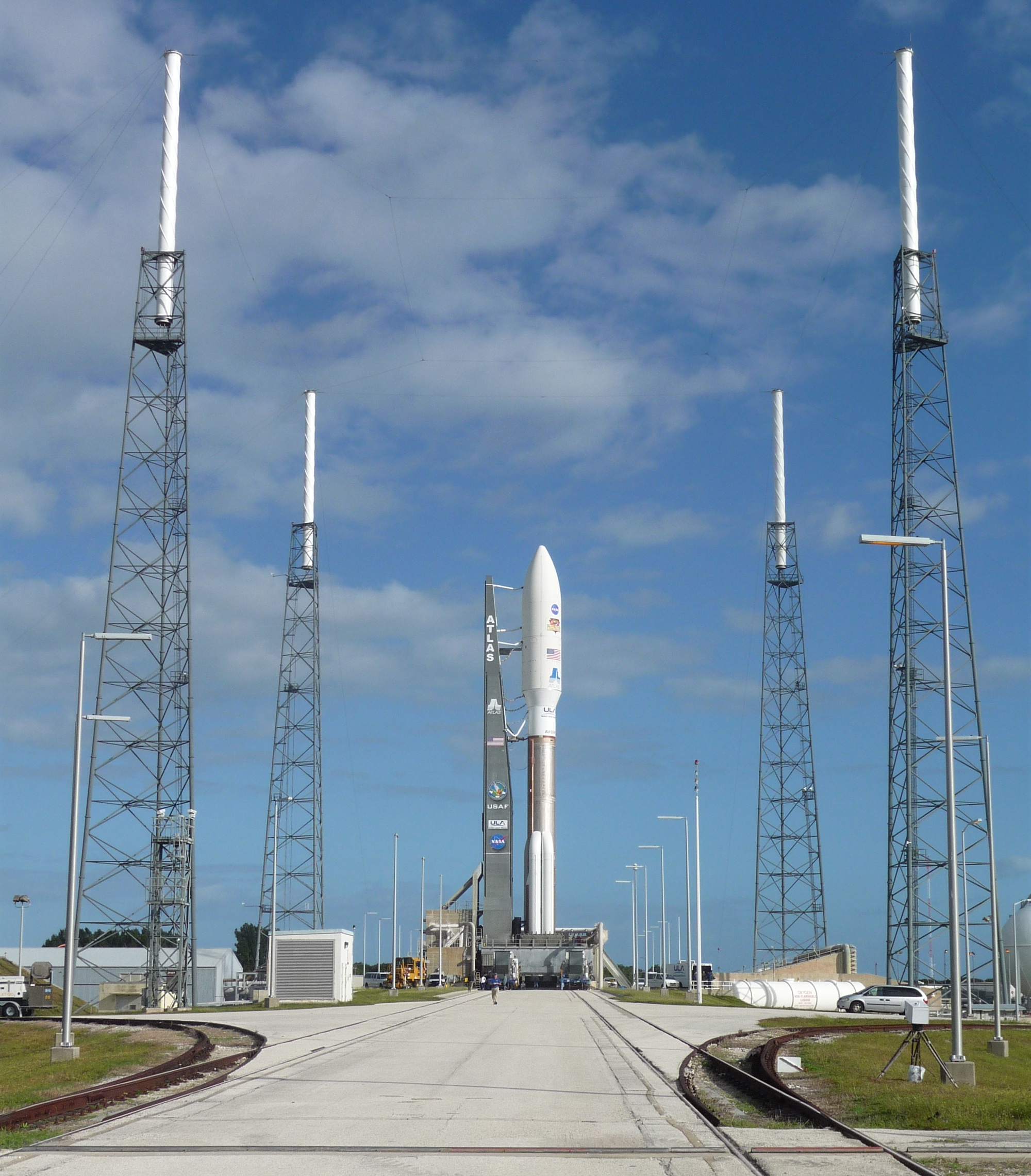
NASA has begun fueling the rocket that will launch its huge Mars rover toward the Red Planet this morning (Nov. 26).
Technicians started loading up the car-size Curiosity rover'sAtlas 5 rocket with super-chilled liquid oxygen propellant just before 8 a.m. EST (1300 GMT) today, about two hours ahead of the planned launch time of 10:02 a.m.
Chances still look good that Curiosity — the centerpiece of NASA's $2.5 billion Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission to assess past and present Martian habitability — will get off the ground on time, officials say. Current forecasts predict just a 30 percent chance that bad weather will postpone the launch, and the mission team is working no issues with the rover or its rocket.
"The Mars Science Lab and the rover Curiosity [are] locked and loaded, ready for final countdown on Saturday's launch to Mars," said Colleen Hartman, assistant associate administrator at NASA's science mission directorate. [Photos: Last Look at Curiosity Rover]
A rover on steroids

At 1 ton, Curiosity weighs about five times more than each of its immediate Mars rover predecessors, the golf-cart-size twins Spirit and Opportunity, which landed on the Red Planet in January 2004 to look for evidence of past water activity.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Both Spirit and Opportunity carried five science instruments. Curiosity boasts 10, including a rock-vaporizing laser and gear designed to identify organic molecules — the carbon-containing building blocks of life as we know it.
Curiosity also sports a drill at the end of its 7-foot (2.1-meter) robotic arm that will allow it to collect samples from the interior of Martian rocks, a first for a Red Planet robot.
"This rover, Curiosity rover, is really a rover on steroids," Hartman said.
Investigating Gale Crater
After liftoff, Curiosity will embark upon an 8 1/2-month cruise to the planet Mars. In August 2012, it will land at a 100-mile-wide (160-kilometer) crater called Gale and begin assessing whether Mars is, or ever was, capable of supporting microbial life.

A 3-mile-high (5-km) mound of layered sediment rises from Gale's center. These layers preserve a record of Martian environmental change spanning about one billion years, and Curiosity is designed to read them like a book.
The rover will pay special attention to layers near the mound's base, where Mars-orbiting spacecraft have identified clays and sulfates — minerals that form in the presence of liquid water.
The rocks shift farther up the mountain, capturing Mars' transition from a relatively warm, wet planet to the frigid, dry and dusty world we see today. Curiosity's observations could help shed light on this dramatic transformation, researchers said.
The MSL team is quick to stress that Curiosity is not hunting for signs of life; if any microbes are squirming about in Mars' red dirt, the rover probably won't be able to spot them. But Curiosity's mission is a necessary precursor to future efforts to hunt down potential Red Planet life, researchers said.
"A habitable environment needs to be described," said MSL project scientist John Grotzinger of Caltech. "You just simply have to know where to look."
You can follow SPACE.com senior writer Mike Wall on Twitter: @michaeldwall. Follow SPACE.com for the latest in space science and exploration news on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.