Neil Armstrong's Death May Spur Apollo 11 Landing Site Preservation
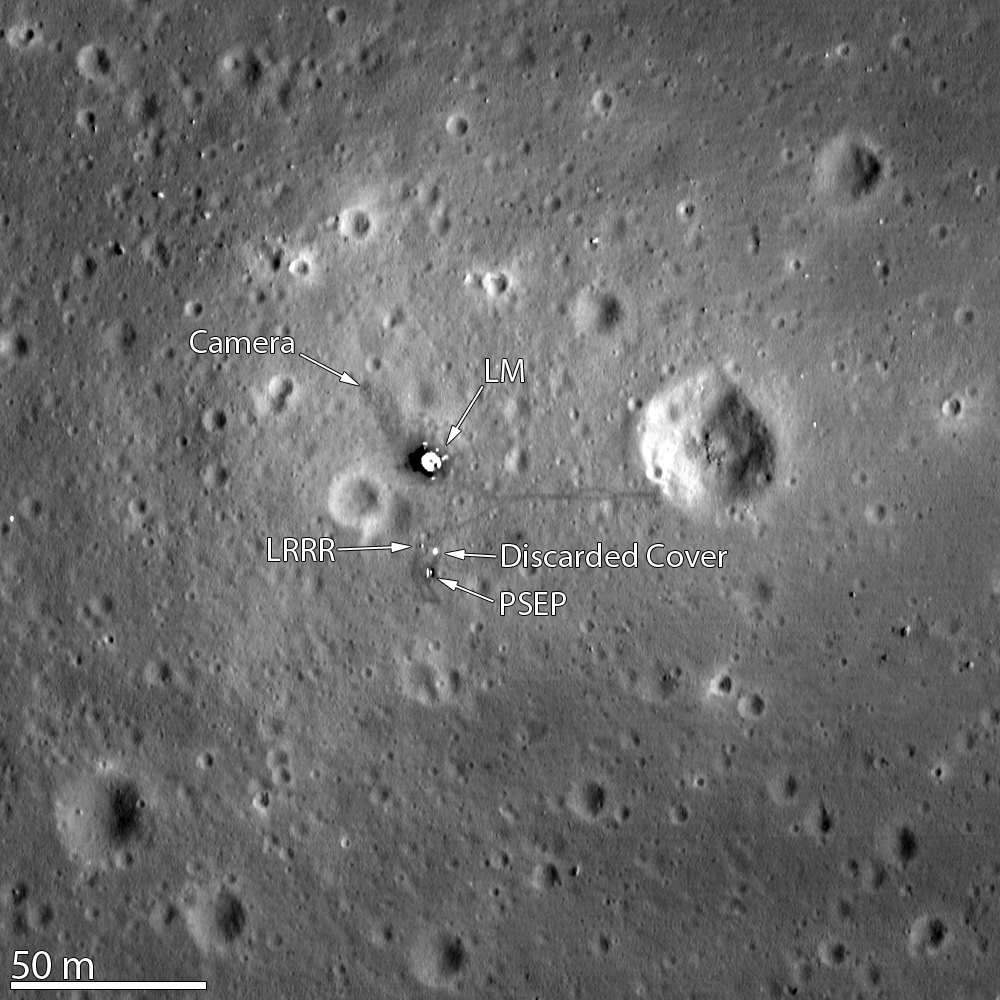

The passing of famed astronaut Neil Armstrong, the first man to walk on the moon and commander of Apollo 11, may strengthen the movement to designate the Tranquility Base lunar landing site as a National Historic Landmark.
The field of space heritage preservation is gaining momentum, and a recently authored bill aims protect the Apollo 11’s Eagle lunar lander touchdown site and all the artifacts that astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin left behind on the lunar surface.
A leading champion of the moon landing site preservation campaign is Beth O’Leary, an associate professor of anthropology in New Mexico State University’s College of Arts and Sciences. “I had one sad thought that with his passing, people may consider the site on the moon more ‘historic,’" she told SPACE.com.
O’Leary and Chico State University archaeology professor Lisa Westwood worked with California Congressman Dan Lungren and his staff to write the bill. [Photos: Neil Armstrong Remembered]
Cultural material
There’s a total of 190 tons of cultural material on the moon, O'Leary said, and there are about 106 artifacts that are specific to the Apollo 11 site. The effort under way is to preserve the significant technological objects that got Armstrong and Aldrin to the moon for that historic flight.
California and New Mexico have already listed Tranquility Base on their state historic registers. The next step would be the National Historic Landmark designation.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Once a property is designated a National Historic Landmark, it can be nominated for inclusion on the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization’s (UNESCO) World Heritage List. [New Photos of Apollo Moon Landing Sittes]
Westwood and O’Leary also have been working with the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS), the World Heritage List’s advisory body, over the last three years to make the case for the Apollo sites to be added to this list.
“Sites on the list now include Chaco Canyon, the Pyramids at Giza, Stonehenge,” O’Leary said in a press statement, “so there are many sites on the Earth that are recognized by this group of people. Putting the first lunar landing on the list means we recognize this is an achievement for humanity.”

Tangible memory
“The passing of an American hero, Neil Armstrong, saddened the world," Westwood said. "It also brings to light the importance of preserving Apollo sites on the moon, because the human experience on the lunar surface was realized by only 12 humans — a staggeringly slim percentage of humankind.” Westwood said that these brave astronauts are only with us for a brief period of time, and a generation from now, they will have passed on, no longer able to speak to their experiences and the historical significance of their achievement.
“By preserving the sites they left behind on the moon, we are, in a sense, preserving not only the historical event of the first lunar landing, but the tangible memory of the Apollo astronauts,” Westwood said.

Legal gray area
“Our ideas on lunar preservation were presented by our ICOMOS ‘caseworker’ — for lack of a better word — in Helsinki a month ago,” O’Leary said. She and Westwood are working on getting the Tranquility Base Act in front of Congress to secure National Historic Landmark status; co-sponsors for Lundgren’s bill are still needed.
Objects at Tranquility Base are in a legal gray area. O’Leary said. By treaty, however, countries own the property they have placed on the moon, but no one can own the lunar surface.
In 2010, Robert Kelso, former director of NASA’s lunar commercial services, invited O’Leary to join a group of NASA scientists and engineers to help create guidelines to protect U.S. objects on the moon from future visitors. The recommendations were developed in response to a request from the Google Lunar X Prize.
Important first step
Although it is not legally binding, the paper, "NASA’s Recommendations to Space Faring Entities: How to Protect and Preserve the Historic and Scientific Value of U.S. Government Lunar Artifacts," took an important first step toward protecting these sites on the moon, O’Leary said.
“Some of those guidelines include where these spacecraft can land and the distance at which they have to be,” said O’Leary. “They can image the objects, but we would hate for a rover that is mobile to go over the tracks that Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin made or to crash into some of the artifacts that are standing…some of them are scientific experiments."

Robots to the moon
In May of this year, NASA and the X Prize Foundation of Playa Vista, Calif., announced that the Google Lunar X Prize is recognizing guidelines established by the space agency to protect lunar historic sites and preserve ongoing and future science on the moon.
The Google Lunar X Prize offers $30 million to the first privately funded team to send a robot to the moon. Twenty-six teams will compete for the prize.
Meanwhile, O’Leary said she plans to keep pressing forward on space heritage preservation.
“I’m one of those believers that if it’s not in two years or five years or 20 years, we will go back to the moon, I think first with robotics and second with humans,” O’Leary said. “If we don’t have a preservation framework in place, if we don’t have rules and ideas about what is important to preserve and how to preserve it, we really run the risk of destroying sites and artifacts."
Preserved for posterity
“In terms of the preservation of artifacts on the moon, I hope Neil’s passing will raise the priority in everyone’s mind the need to preserve this critically significant history,” said Roger Launius, senior curator, Division of Space History and the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C.
“I think there have been great strides made in the last couple years in that regard, but it still is at the realm of informal ‘rules of the road,’ rather than specific protections carrying the force of law,” Launius told SPACE.com.
“Perhaps that will change in the next few years. Regardless of the form these efforts to preserve the record of the Apollo moon landings may take, the loss of the heroic figure prompts us to reflect on this historic occurrence and to redouble efforts to ensure that it is preserved for posterity,” Launius said.
Leonard David has been reporting on the space industry for more than five decades. He is a winner of last year's National Space Club Press Award and a past editor-in-chief of the National Space Society's Ad Astra and Space World magazines. He has written for SPACE.com since 1999.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Leonard David is an award-winning space journalist who has been reporting on space activities for more than 50 years. Currently writing as Space.com's Space Insider Columnist among his other projects, Leonard has authored numerous books on space exploration, Mars missions and more, with his latest being "Moon Rush: The New Space Race" published in 2019 by National Geographic. He also wrote "Mars: Our Future on the Red Planet" released in 2016 by National Geographic. Leonard has served as a correspondent for SpaceNews, Scientific American and Aerospace America for the AIAA. He has received many awards, including the first Ordway Award for Sustained Excellence in Spaceflight History in 2015 at the AAS Wernher von Braun Memorial Symposium. You can find out Leonard's latest project at his website and on Twitter.