The Yuletide evening sky is especially rewarding, with much of the eastern swathe filled with brilliant stars — sort of a celestial Christmas tree.
Distinctive groupings of stars forming part of the recognized constellation outlines, or lying within their boundaries, are known as asterisms. Ranging in size from sprawling naked-eye figures to minute stellar settings, they are found in every quarter of the sky and at all seasons of the year.
The larger asterisms — ones like the Big Dipper in Ursa Major and the Great Square of Pegasus — are often better known than their host constellations. One of the most famous is in the northwest these frosty December evenings.
The Northern Cross
The brightest six stars of the constellation Cygnus (the Swan) — which was known simply as the “Bird” in ancient times — compose an asterism popularly called the Northern Cross. [Night Sky Observing Guide for December 2012 (Gallery)]
Bright Deneb decorates the top of the Cross. Albereo, at the foot of the Cross, is really a pair of stars of beautifully contrasting colors: a third-magnitude orange star and its fifth-magnitude blue companion are clearly visible in even a low-power telescope. (In astronomy, lower magnitudes signify relatively brighter objects. Venus' magnitude is around -5, for example, while the full moon's is about -13.)
While usually regarded as a summertime pattern, the Northern Cross is best oriented for viewing now. It appears to stand majestically upright on the northwest horizon at around 8:30 p.m. local time, forming an appropriate Christmas symbol. (And just before dawn on Easter morning, the cross lies on its side in the eastern sky.)
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The Christmas package
Look over toward the southeast part of the sky at about the same time, 8:30 p.m. or so. Can you see a large package in the sky, tied with a pretty bow across the middle? Four bright stars outline the package, while three others make up the decorative bow. [Stunning Night Sky Photos of December 2012]
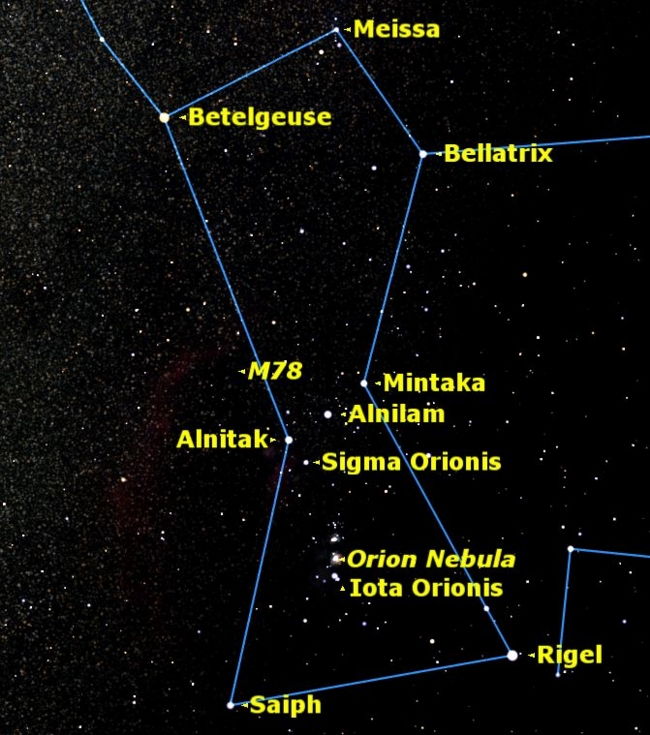
Now you can see how our modern imagination might work, but tradition tells us that those seven stars formed a mighty hunter called Orion, the most brilliant of the constellations and visible from every inhabited part of the Earth. Two stars mark his shoulders, two more his knees and three his belt.
As is also the case with the mighty Hercules, the figure of Orion has been associated in many ancient cultures with great national heroes, warriors or demigods. Yet in contrast to Hercules, who was credited with a detailed series of exploits, Orion seems to us a vague and shadowy figure.
The ancient mythological stories of Orion are so many and so confused that it is almost impossible to choose among them. Even the origin of the name Orion is obscure, though some scholars have suggested a connection with the Greek "Arion," meaning "warrior."
The myths all tend to agree that he was the mightiest hunter in the world, and he is always pictured in the stars with his club upraised in his right hand. Hanging from his upraised left hand is the skin of a great lion he has killed. Orion is brandishing this skin in the face of Taurus, the Bull, who is charging him.
The heavenly manger
The legendary French astronomer Nicolas Camille Flammarion (1842-1925) referred to the three belt stars of Orion as "The Three Kings." If we consider these three stars to represent the Magi, then it's fitting that the star cluster known as Preasepe,(the Manger) lies not far to the east, within the faint zodiacal constellation of Cancer.
A manger is a trough or open box in which feed for horses or cattle is placed. The Book of St. Luke tells us that the baby Jesus was set down in a manger because there was no room at the local inn. In our current Yuletide evening sky, Preasepe thus can represent the manger where Christ was placed...
The constellation Cancer is practically an empty space in the sky, positioned between the Twin Stars (Pollux and Castor) of Gemini and the Sickle of Leo. It’s completely devoid of any bright stars and would probably not be considered a constellation at all, if not for the fact that there had to be a sign of the Zodiac between Gemini and Leo.
In the middle of Cancer are two stars called the Aselli ("donkeys") that are feeding from the manger; Asselus Borealis and Asselus Australis bracket Preasepe to the north and south, respectively.
To the unaided eye, the manger appears as a soft, fuzzy patch or dim glow. But in good binoculars and low-power telescopes, it is a beautiful object to behold, appearing to contain a smattering of several dozen stars. Using his crude telescope, Galileo wrote in 1610 of seeing Preasepe not as one fuzzy star, but as " . . . a mass of more than 40 small stars."
The shepherd’s star
If you are up about an hour or so before sunrise, look toward the east-southeast to get a glimpse of what Flammarion described as "The Shepherd’s Star," the planet Venus. He wrote:
"She shines in the east in the morning, with a splendid brightness which eclipses that of all the stars. She is, without comparison, the most magnificent star of our sky; the star of sweet confidences."
Indeed, Venus is always bright. This year, it will remind those who rise early on Christmas morning of the Biblical "Star in the East."
Telescope targets
Venus may be rather disappointing to those who receive a telescope as a holiday gift, appearing as nothing more than a dazzling disk of light. But there are two other splendid planetary targets to gaze at.
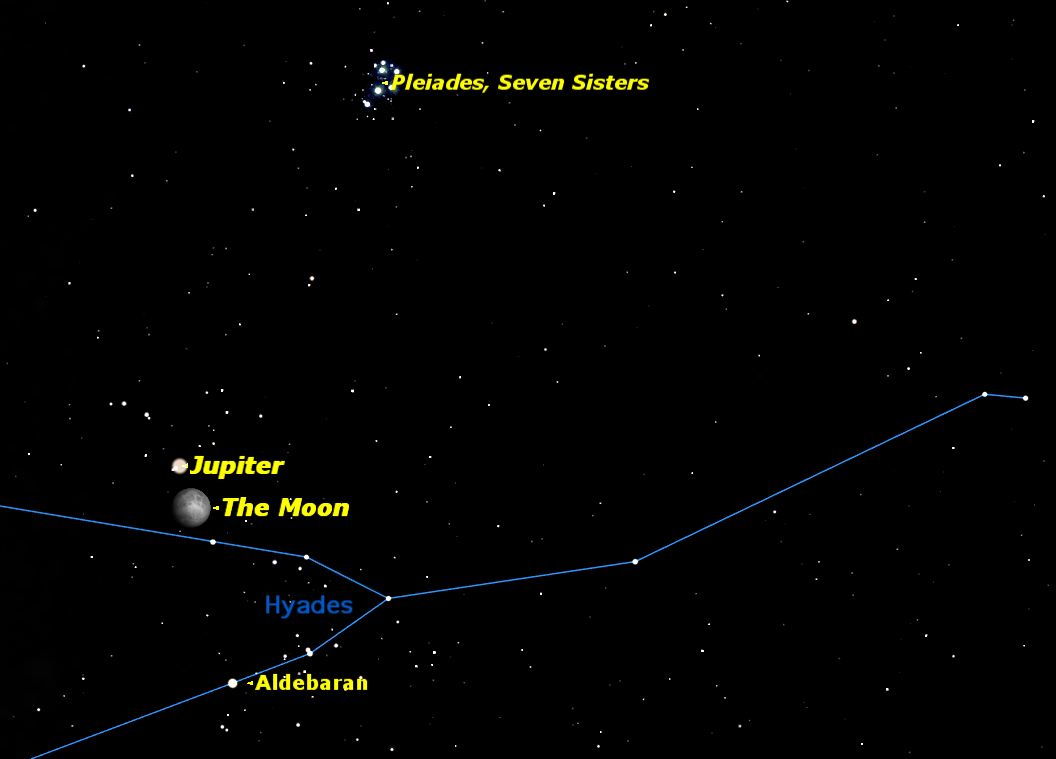
That very bright 'star" that you notice at day’s end in December, glowing about one-quarter of the way up from the east-northeast horizon right after sundown, is actually Jupiter. The gas giant is a superb telescopic showpiece, with cloud bands crossing its disk and a retinue of four large moons. On Christmas night, Jupiter will be visible just above the waxing gibbous moon, making for an eye-catching sight.
And lastly, in the predawn morning sky is "the lord of the rings," Saturn, which this week rises above the east-southeast horizon around 3 a.m. local time and just before sunrise can be found about 30 degrees above and to the right of Venus.
Your clenched fist held at arm's length measures about 10 degrees, so Saturn will appear about "three fists" up and to Venus’s right. .A telescope magnifying 30-power or more will reveal Saturn’s famous rings, now tilted almost 19 degrees to our line of sight.
Joe Rao serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York's Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for The New York Times and other publications, and he is also an on-camera meteorologist for News 12 Westchester, New York. Follow SPACE.com on Twitter @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebook & Google+.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Joe Rao is Space.com's skywatching columnist, as well as a veteran meteorologist and eclipse chaser who also serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York's Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for Natural History magazine, Sky & Telescope and other publications. Joe is an 8-time Emmy-nominated meteorologist who served the Putnam Valley region of New York for over 21 years. You can find him on Twitter and YouTube tracking lunar and solar eclipses, meteor showers and more. To find out Joe's latest project, visit him on Twitter.









