Robotic Russian Supply Ship Leaves Space Station
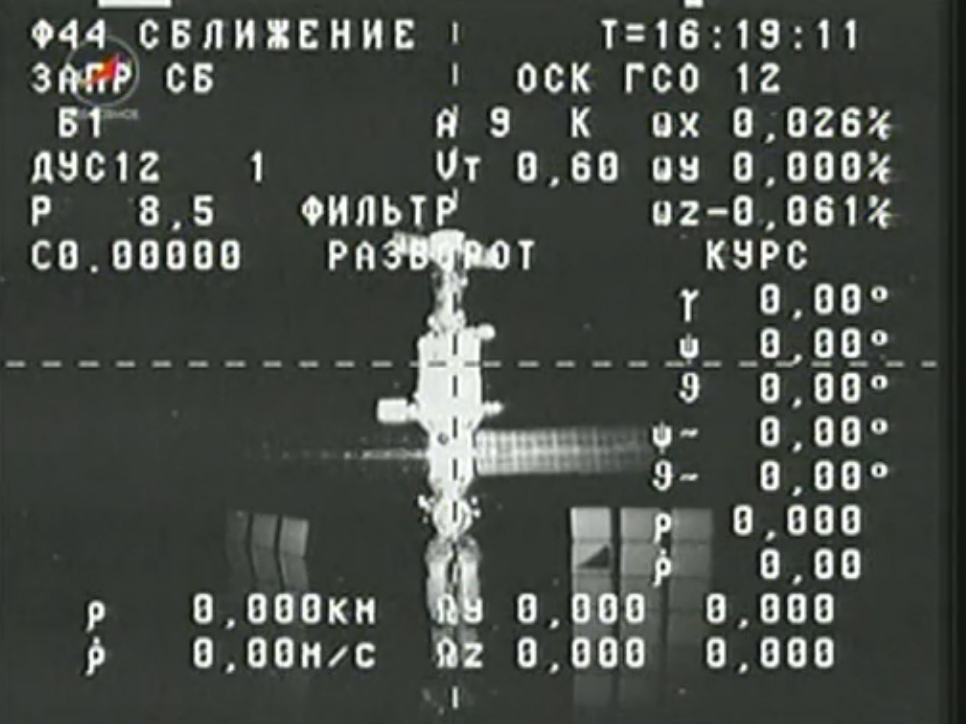
An unmanned Russian cargo ship undocked from the International Space Station Saturday (Feb. 9) to make way for a fresh delivery of supplies for the six astronauts living on the orbiting laboratory next week.
The trash-filled Progress 48 supply ship undocked from the space station's Russian Pirs docking port at 8:15 a.m. EST (1315 GMT) and was expected to intentionally destroy itself by burning up in Earth's atmosphere a few hours later.
"We just undocked a spaceship from our Space Station," Canadian astronaut Chris Hadfield, a flight engineer on the space station, wrote in a Twitter post Saturday. "The Progress robot ship is loaded with trash, to burn up like a meteorite in 3.5 hrs."
The departure of Progress 48 clears a parking spot for the next Russian cargo ship to use when it launches toward the International Space Station on Monday (Feb. 11). That spacecraft, the Progress 50 supply ship, will launch from the Central Asian spaceport of Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan at 9:41 a.m. EST (1441 GMT on Monday, though it will late evening at the launch site. Russia's Progress cargo ships are vital spacecraft that have helped keep astronauts stocked with food, clothing and other vital supplies during their six-month missions.

Progress 50 will deliver nearly 2.9 tons of supplies for the space station's Expedition 34 crew, which includes three Russian cosmonauts, two American astronauts and Hadfield, who represents the Canadian Space Agency. The new cargo ship will deliver about 764 pounds (346 kilograms) of rocket propellant, 110 pounds (50 kg) of oxygen and air, 926 pounds (420 kg) of water and 3,000 pounds (1,360 kg) of spare parts, science equipment and other supplies, NASA officials said.
The Russian Federal Space Agency's three-module Progress spacecraft are similar in appearance to its crew-carrying Soyuz spacecraft. Both vehicles have orbital and propulsion modules, but the Progress spacecraft does not have a crew return capsule in its middle. Instead, it has another cargo module to carry propellant for the space station's maneuvers.
Since Progress cargo ships are not designed to return to Earth, they are regularly filled with tons of trash and unneeded items, and then sent to burn up in the atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean. Robotic resupply ships for the station built by Europe and Japan also meet the same fate.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The American unmanned Dragon cargo ships built by the private spaceflight company SpaceX, which flew to the space station twice in 2012, are designed to re-enter the atmosphere and can return science experiments and other gear to Earth.
NASA will broadcast live views of Monday's Progress 50 spacecraft launch and docking via NASA TV. You can watch the Progress 50 spacecraft live on SPACE.com here, courtesy of NASA's feed.
You can follow SPACE.com Managing Editor Tariq Malik on Twitter @tariqjmalik. Follow SPACE.com on Twitter @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebook & Google+.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Tariq is the Editor-in-Chief of Space.com and joined the team in 2001, first as an intern and staff writer, and later as an editor. He covers human spaceflight, exploration and space science, as well as skywatching and entertainment. He became Space.com's Managing Editor in 2009 and Editor-in-Chief in 2019. Before joining Space.com, Tariq was a staff reporter for The Los Angeles Times covering education and city beats in La Habra, Fullerton and Huntington Beach. In October 2022, Tariq received the Harry Kolcum Award for excellence in space reporting from the National Space Club Florida Committee. He is also an Eagle Scout (yes, he has the Space Exploration merit badge) and went to Space Camp four times as a kid and a fifth time as an adult. He has journalism degrees from the University of Southern California and New York University. You can find Tariq at Space.com and as the co-host to the This Week In Space podcast with space historian Rod Pyle on the TWiT network. To see his latest project, you can follow Tariq on Twitter @tariqjmalik.