World's Smallest Space Telescopes Launching Monday
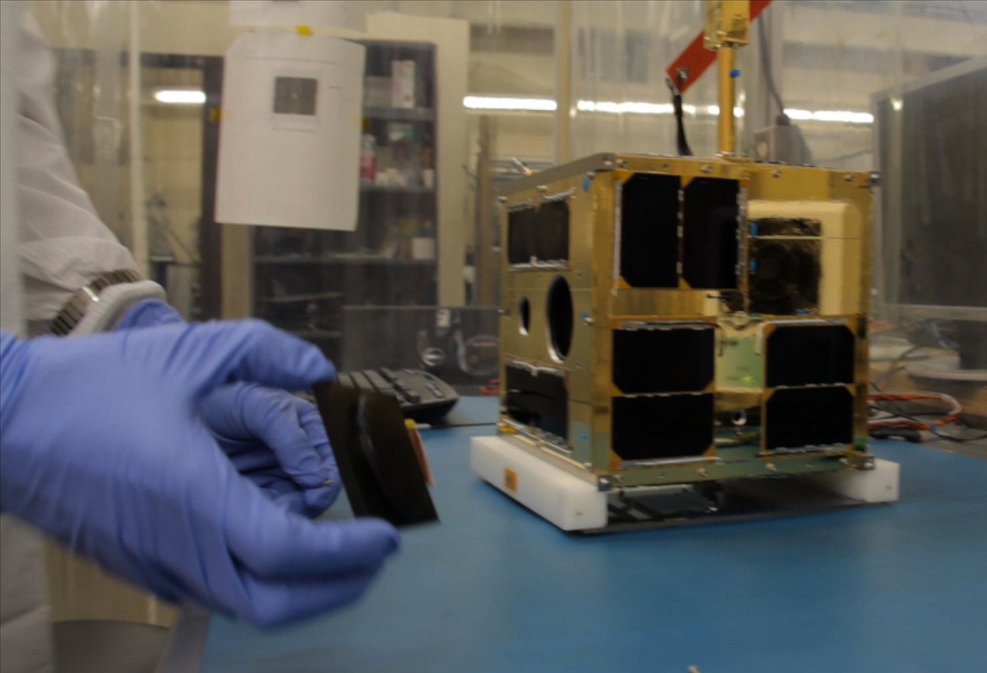
Two tiny satellites billed as the world's smallest space telescopes will launch into orbit Monday (Feb. 25) on a mission to study the brightest stars in the night sky.
The Bright Target Explorer (BRITE) nanosatellites look like little cubes and will blast off atop an Indian Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) at 7:20 a.m. EST (1220 GMT) on Monday from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, India.
While tiny nanosatellites have launched into space before, they have been mainly used to study Earth or test new spaceflight technologies, but the BRITE satellites will be the first to peer into the cosmos, their builders say. The diminutive spacecraft are less than 8 inches (20 centimeters) wide and weigh less than 15.5 pounds (7 kilograms). Once in orbit, they are expeted to observe the brightest stars (from Earth's perspective), including those that make up well-known constellations like Orion, the Hunter.
"BRITE is expected to demonstrate that nanosatellites are now capable of performance that was once thought impossible for such small spacecraft," said Cordell Grant, manager of satellite systems for the Space Flight Laboratory at the University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies (UTIAS), where the satellites were designed.

One of the BRITE satellites launching Monday was designed and built at the Space Flight Laboratory. The other was designed by the center, but assembled in Austria, university officials said in a statement. They are two of seven satellites set to blast off with India's rocket launch on Monday.
The nanosatellites can only fit small telescopes, so they won't be capturing amazing high-resolution images of the cosmos, Grant explained in the statement. But they will be able to observe and record changes in a star's brightness over time. Such observations could help scientists find spots on the star, an orbiting planet or secondary star, or "starquakes" caused by oscillations within the star itself.
The nanosatellites can monitor their target stars from whatever orbit they are placed on. They just need to be above the atmosphere to avoid the twinkling, or scintillating effect, that overwhelms stars' relatively small changes in brightness, researchers said.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

By keeping the satellites small, they can be built faster and at a lower cost than their larger counterparts, and be launched as a piggyback payload on rockets carrying larger spacecraft, UTIAS officials said.
"A nanosatellite can take anywhere from six months to a few years to develop and test, but we typically aim for two years or less," Grant said.
You can watch the launch of NEOSSat live via India's official Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle webcast.
Follow SPACE.com on Twitter @Spacedotcom. We're also on Facebook and Google+.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Space.com is the premier source of space exploration, innovation and astronomy news, chronicling (and celebrating) humanity's ongoing expansion across the final frontier. Originally founded in 1999, Space.com is, and always has been, the passion of writers and editors who are space fans and also trained journalists. Our current news team consists of Editor-in-Chief Tariq Malik; Editor Hanneke Weitering, Senior Space Writer Mike Wall; Senior Writer Meghan Bartels; Senior Writer Chelsea Gohd, Senior Writer Tereza Pultarova and Staff Writer Alexander Cox, focusing on e-commerce. Senior Producer Steve Spaleta oversees our space videos, with Diana Whitcroft as our Social Media Editor.