An exceptional comet flying ever closer to the sun may offer an amazing naked eye sight to Earth dwellers this fall as it gradually brightens.
As comet C/2012 S1 (ISON) continues to approach the sun, it is slowly responding to the increasing warmth of the sun and getting progressively brighter. The comet is getting considerable scrutiny from both amateur and professional scientists because it's a rare sungrazing comet, destined to approach to within 730,000 miles (1.17 million kilometers) of the surface of the sun on Nov. 28. Because of this extremely close approach, comet ISON holds the "potential" to flare into a dazzling object — possibly becoming bright enough to be briefly glimpsed in broad daylight.
Still, at this early stage in the comet's development, we can't be sure if this will actually happen. [Photos of Comet ISON in Night Sky]
A Swift look
Although still quite far from the sun and very faint, the comet has been imaged by two orbiting observatories. Astronomers from the University of Maryland at College Park and Lowell Observatory used NASA's Swift satellite to check out the comet during January and February. Using images acquired from Swift's Ultraviolet/Optical Telescope, the team was able to make initial estimates of the comet's water and dust production and then used these values to determine the size of ISON's icy nucleus.
These observations revealed that each minute ISON was shedding about 56 tons (51,000 kg) of dust, or about two-thirds the mass of an unfueled space shuttle. Jets powered by sublimating ice also release dust, which reflects sunlight and brightens the comet.

By contrast, however, the comet was producing only about 130 pounds (60 kg) of water every minute, or about four times the amount flowing out of a residential sprinkler system. At the time, however, the comet was nearly half a billion miles from the sun. Typically, a comet's water content remains frozen until it comes within about three times Earth's distance to the sun — about 280 million miles (450 million km) away. ISON won't be this close to the sun until early July at which time the water production rate should markedly increase.
The water and dust production rates from Swift were used to estimate the size of ISON's icy body. Comparing the amount of gas needed for a normal comet to blow off dust at the rate observed for ISON, the scientists estimate that the nucleus is roughly 3 miles (5 km) across, a typical size for a comet. This assumes that only the fraction of the surface most directly exposed to the sun, about 10 percent of the total, is actively producing jets.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Hubble's turn
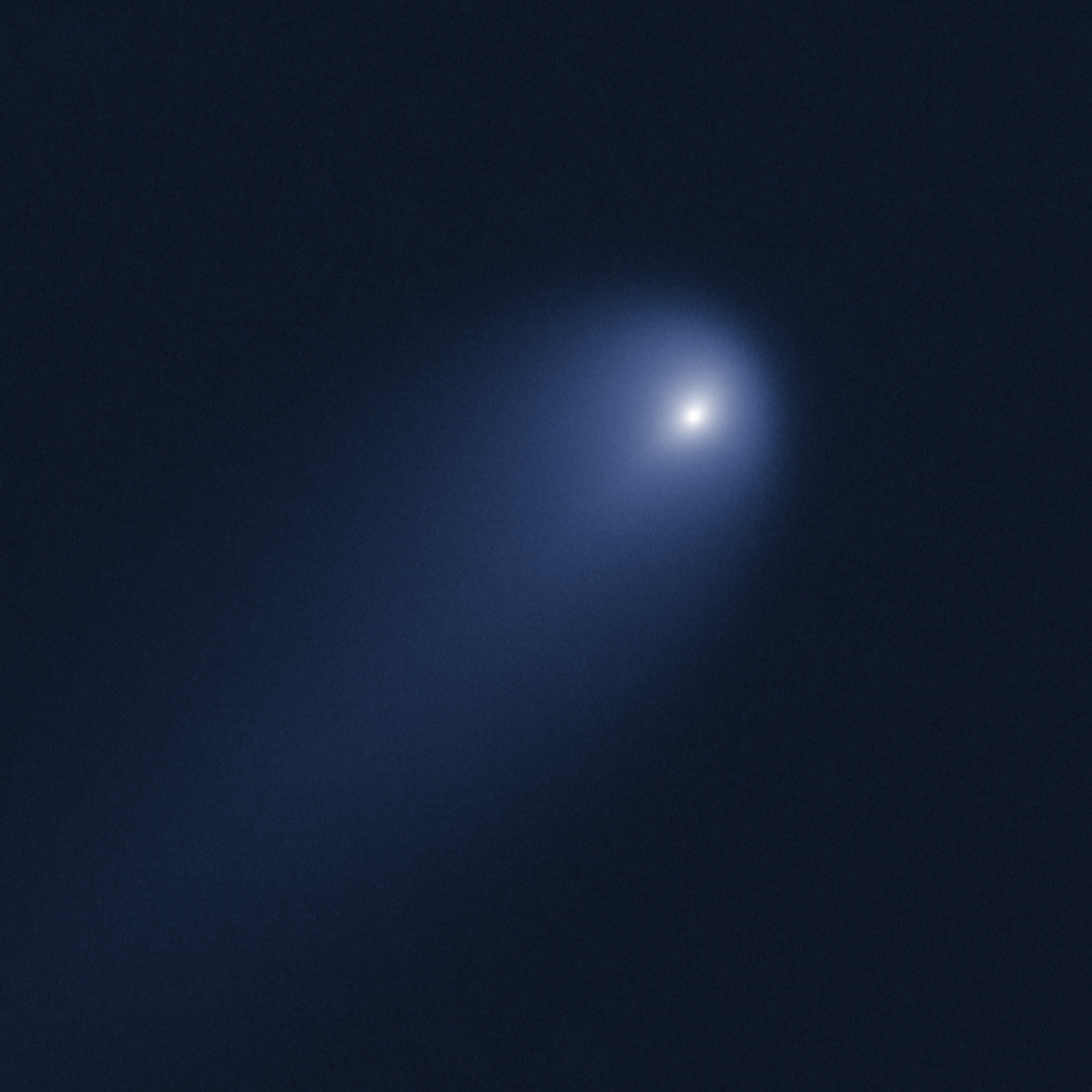
More recently, Planetary Science Institute research scientist Jian-Yang Li led a team that imaged comet ISON with the Hubble Space Telescope on April 10 using the Wide Field Camera 3. At this point, the comet was slightly closer than Jupiter at 386 million miles (621 million kilometers) from the sun and 394 million miles (634 million kilometers) from Earth.
The comet's dusty coma, or head of the comet, is currently about 3,100 miles (5,000 kilometers) across, or 1.2 times the width of Australia. A dust tail extends more than 57,000 miles (92,000 kilometers), far beyond Hubble's field of view.
A detailed analysis of the dust coma surrounding the nucleus reveals a strong jet blasting dust particles off the sun-facing side of the comet's nucleus. This jet, as projected on the sky, extends at least 2,300 miles (3,700 kilometers).
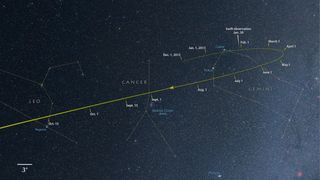
A "promising" future
What does all of this mean regarding the comet's performance later this year?
"It looks promising, but that's all we can say for sure now," said Matthew Knight, an astronomer at Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Ariz., and a member of the Swift and Comet ISON Observing Campaign teams. "Past comets have failed to live up to expectations once they reached the inner solar system, and only observations over the next few months will improve our knowledge of how ISON will perform."
We'll just have to wait and see how ISON evolves in the coming weeks and months. Stay tuned to SPACE.com for future updates.
Editor's note: If you capture an amazing photo of Comet ISON or any other night sky sight that you'd like to share for a possible story or image gallery, please contact managing editor Tariq Malik at spacephotos@space.com.
Joe Rao serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York's Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for The New York Times and other publications, and he is also an on-camera meteorologist for News 12 Westchester, New York. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on SPACE.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Joe Rao is Space.com's skywatching columnist, as well as a veteran meteorologist and eclipse chaser who also serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York's Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for Natural History magazine, Sky & Telescope and other publications. Joe is an 8-time Emmy-nominated meteorologist who served the Putnam Valley region of New York for over 21 years. You can find him on Twitter and YouTube tracking lunar and solar eclipses, meteor showers and more. To find out Joe's latest project, visit him on Twitter.