Star Explodes Inside Atmosphere of Another
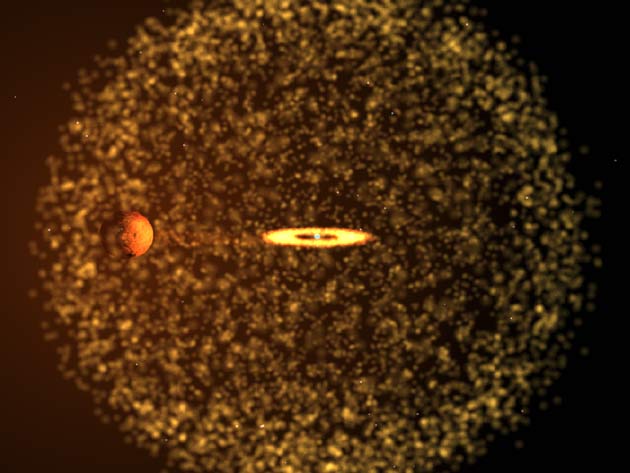
A nova that lights up in the sky every 20 years is the result of a small star exploding repeatedly inside the outer atmosphere of a larger star, astronomers said today.
The eruptions are among the most unusual stellar death cries ever spotted.
The setup is called RS Ophiuchi, or RS Oph. It consists of a burned out corpse of a star known as white dwarf that is very dense and about the size of Earth. It orbits close to a huge, puffed up red giant, which is just one step away from collapsing into a white dwarf itself.
Such setups have been examined before, but this is the first time one star has been shown to be exploding from within the atmosphere of another.
What happens
Hydrogen gas from the outer atmosphere of the red giant is lured by gravity to the smaller white dwarf. Every 20 years, enough gas builds up to create a runaway thermonuclear explosion on the white dwarf's surface. In less than a day, the otherwise dim star brightens to more than 100,000 times the luminosity of the Sun. Much of the gas is shot into space.
"This explosion is similar to that of a terrestrial hydrogen bomb," said study leader Sumner Starrfield of Arizona State University. "RS Oph can be thought of as one of the largest and most powerful hydrogen bombs in the universe."
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The most recent eruption of RS Oph, which sits 5,000 light-years away toward constellation Ophiuchi, made it visible to the unaided eye from Earth on Feb. 12. The event was also recorded by several ground- and space-based telescopes.
Bigger than our solar system
"We were floored to see how bright this star was in X-rays when we first observed it, and then it changed every day," Starrfield said. "We estimate the gas exploded off the white dwarf to be about 100 million degrees, about six times hotter than the gas at the center of our Sun."
An amount of material equal to the mass of Earth was blasted outward at millions of miles per hour.
"The expanding gas from the explosion is now larger in size than our own solar system," he said.
The study revealed that the white dwarf erupts inside the red giant's expanded outer layers, and the exploded material then crashes into those outer layers.
Our own Sun will eventually swell to become a red giant, engulfing the orbit of Earth.
- Recipe for Saving Earth: Move It
- Hubble Captures Rare Image of Star's Dying Burst
- Red Giants and Planets To Live On
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Rob has been producing internet content since the mid-1990s. He was a writer, editor and Director of Site Operations at Space.com starting in 1999. He served as Managing Editor of LiveScience since its launch in 2004. He then oversaw news operations for the Space.com's then-parent company TechMediaNetwork's growing suite of technology, science and business news sites. Prior to joining the company, Rob was an editor at The Star-Ledger in New Jersey. He has a journalism degree from Humboldt State University in California, is an author and also writes for Medium.











