Liftoff! India's First Mars Probe Launches Toward the Red Planet
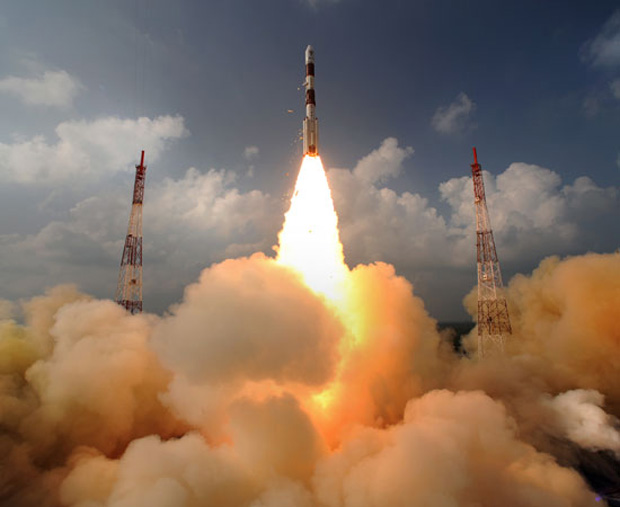

India's first-ever mission to Mars launched into space today (Nov. 5), beginning the country's first interplanetary mission to explore the solar system.
With a thunderous roar, India's Mars Orbiter Mission rocketed into space at 4:08 a.m. EST (0908 GMT) from the Indian Space Research Organisation's Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, where the local time will be 2:38 p.m. in the afternoon. An ISRO Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle launched the probe on its 300-day trek into orbit around the Red Planet.
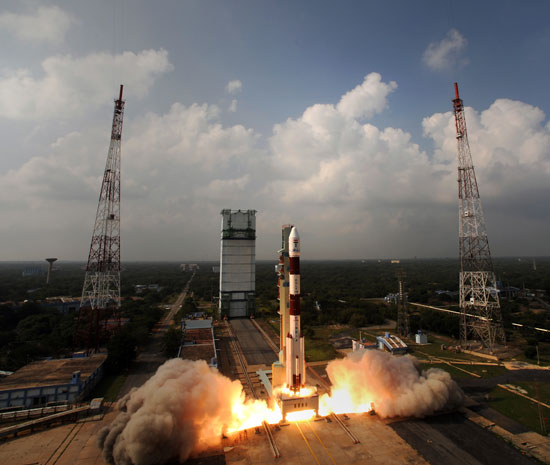

"The journey has only just begun," said ISRO Chairman K. Radhakrishnan after the successful launch. [India's First Mars Mission (Photos)]
Less than an hour after liftoff, Radhakrishnan reported that India's Mars probe successfully entered a staging orbit around Earth. Mars Orbiter Mission director Kunhi Krishnan describing the launch as a start to a "grand and glorious" mission.
If all goes well, India's first Mars orbiter — called Mangalyaan (Hindi for "Mars Craft") — will arrive at the Red Planet on Sept. 24, 2014, making India the fourth country to successfully deliver a spacecraft to Mars. The $73.5 million Mangalyaan spacecraft weighs 2,980 pounds (1,350 kilograms). Through the course of several orbits, the spacecraft will perform a series of maneuvers to place it on a path to Mars.
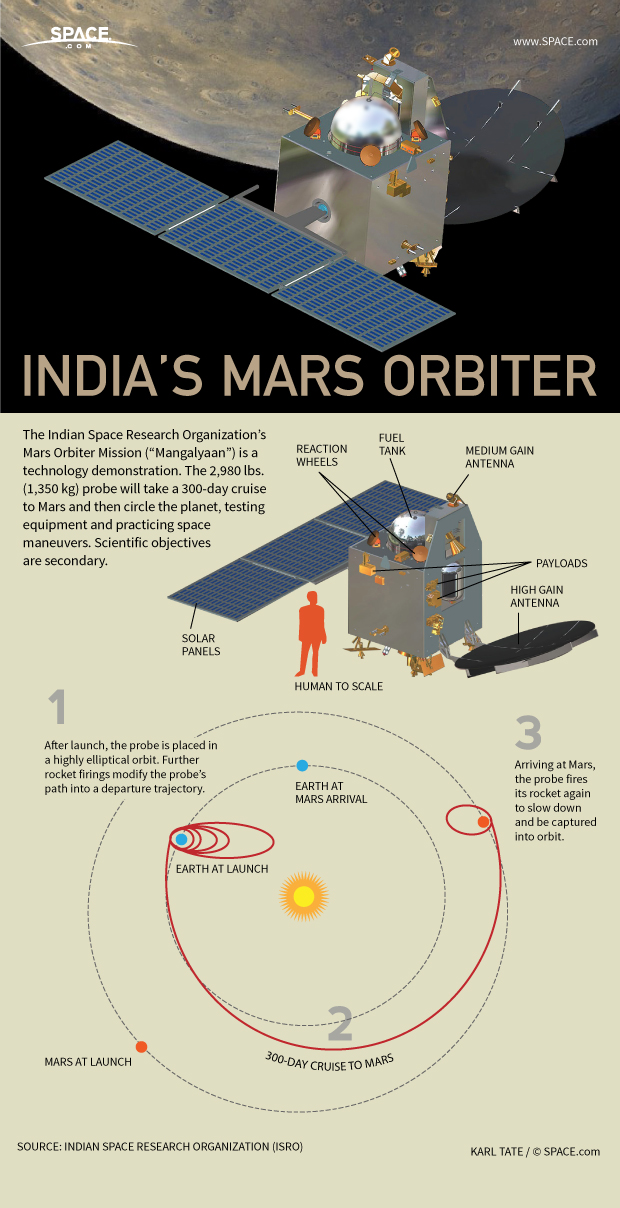
Once at Mars, the probe will explore the surface features of the Red Planet and probe its atmosphere for signs of nonbiological or microbe-emitted methane. The spacecraft is also designed to test technology used for navigation, communication and interplanetary space travel, ISRO officials have said.
"We have a lot to understand about the universe, the solar system where we live in, and it has been humankind's quest from the beginning," Radhakrishnan told the Associated Press before launch.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
If the probe reaches Mars, it will make India the fourth country (or collaboration of countries) to reach the Red Planet after the former Soviet Union, the United States and Europe. Nearly two-thirds of the 51 missions ever launched to Mars have failed.
"To visit another planet is a fantastic thing, the biggest thing," space scientist Yash Pal, a former chairman of India's University Grants Commission who was not involved in developing the Mars mission, told the Associated Press. "If you can afford airplanes and war machines, you can certainly spend something to fulfill the dreams of young people."
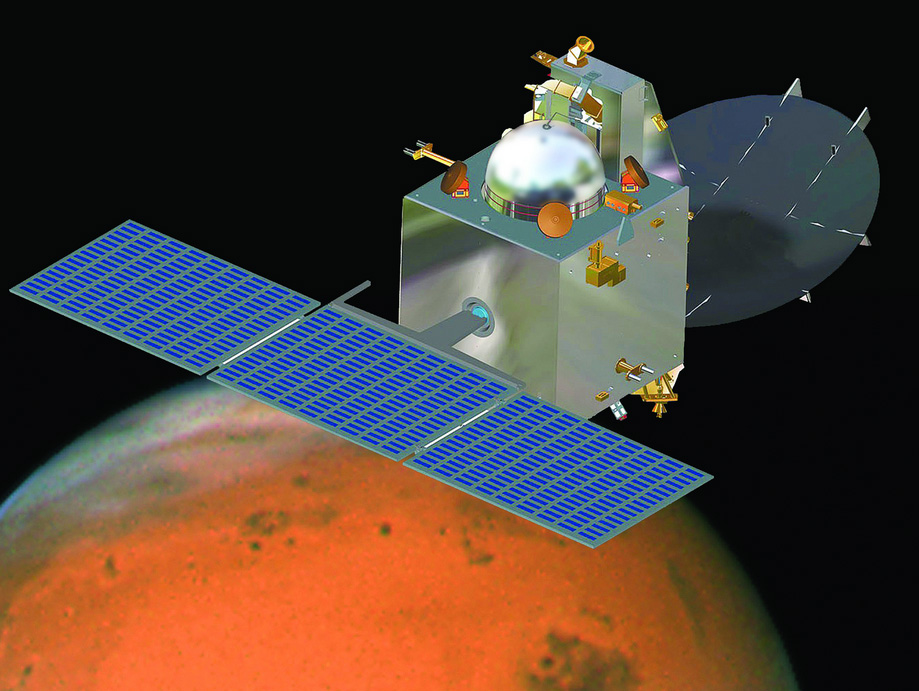
The Mangalyaan orbiter is carrying five instruments to Mars:
- Lyman Alpha Photometer used to measure the loss process of water from the planet.
- Thermal Infrared Imaging Spectrometer to create a map of the Martian surface.
- Mars Exospheric Neutral Composition Analyzer to study Mars' atmosphere.
- Mars Color Camera to take pictures of Mars' surfaces and Martian weather events. The camera will also take photos of moons of Mars, Phobos and Deimos.
- Methane Sensor for Mars will search for methane in the atmosphere of Mars.
India's Mars mission follows the country's Chandrayaan 1 moon orbiter mission, which helped detect evidence of water ice on the lunar surface. The ISRO is also developing Chandrayaan 2, a follow-up mission, to continue its lunar exploration.

India is not the only country launching a mission to Mars this month. In the United States, NASA is planning to launch its own Mars orbiter — called the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (Maven) — on Nov. 18.
NASA's Maven mission to Mars is designed to study the Martian atmosphere in unprecedented detail. The $671 million mission is slated to launch from Cape Canaveral, Fla.
Follow Miriam Kramer @mirikramer and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on SPACE.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Miriam Kramer joined Space.com as a Staff Writer in December 2012. Since then, she has floated in weightlessness on a zero-gravity flight, felt the pull of 4-Gs in a trainer aircraft and watched rockets soar into space from Florida and Virginia. She also served as Space.com's lead space entertainment reporter, and enjoys all aspects of space news, astronomy and commercial spaceflight. Miriam has also presented space stories during live interviews with Fox News and other TV and radio outlets. She originally hails from Knoxville, Tennessee where she and her family would take trips to dark spots on the outskirts of town to watch meteor showers every year. She loves to travel and one day hopes to see the northern lights in person. Miriam is currently a space reporter with Axios, writing the Axios Space newsletter. You can follow Miriam on Twitter.