First-Ever Weather Map of Failed Star Reveals Patchy Alien Clouds
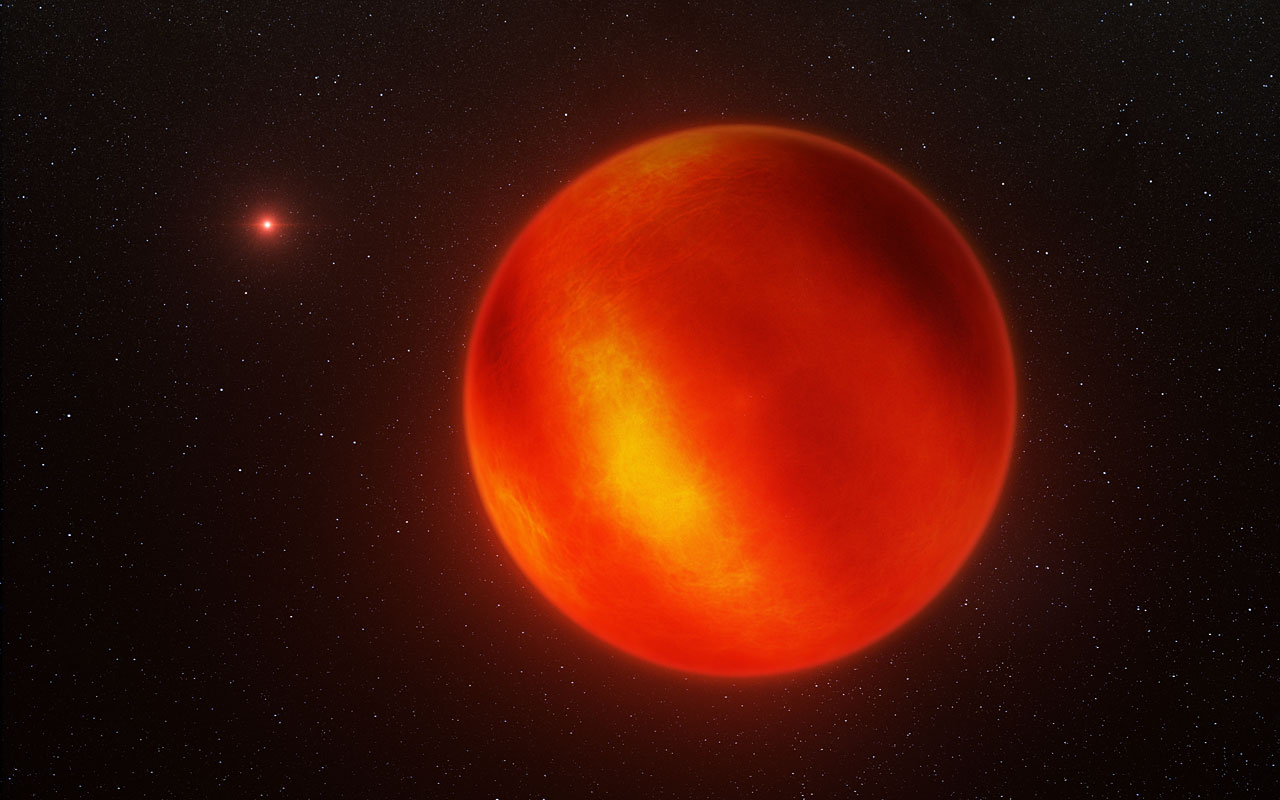
Scientists have created the first weather map of a space oddity known as a brown dwarf, revealing a rare glimpse at alien weather patterns on the failed, wannabe star.
The map shows the weather on the surface of WISE J104915.57-531906.1B (called Luhman 16B for short), the nearest brown dwarf to Earth at 6.5 light-years away. Scientists mapped the light and dark features of the failed star's surface, according to officials with the European Southern Observatory, whose Very Large Telescope in Chile contributed to the new science. You can take video tour of the brown dwarf and its weather map on SPACE.com.
Brown dwarfs are called failed stars because they are larger than gas giant planets like Jupiter, yet still too small to produce nuclear fusion like a true star. Scientists have only found a few hundred of the odd objects, with the first confirmed 20 years ago, ESO officials said. [See more photos of strange brown dwarfs]
"Previous observations have inferred that brown dwarfs have mottled surfaces, but now we can start to directly map them," the new study's lead author, Ian Crossfield of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, said in a statement. "What we see is presumably patchy cloud cover, somewhat like we see on Jupiter."
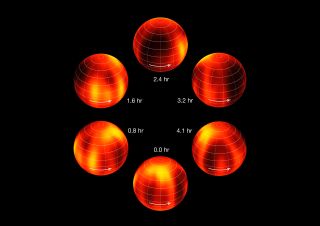
Crossfield and his team found that Luhman 16B probably harbors gaseous clouds made of iron and other minerals in a mostly hydrogen atmosphere. The brown dwarf rotates fully about every four hours. Weather on the brown dwarf would not be favorable for humans, however. Temperatures soar to about 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit (1,100 degrees Celsius), Max Planck officials said.
Luhman 16B is one in a pair of brown dwarfs in the southern constellation of Vela, the sail. Its brighter counterpart is known as Luhman 16A. In another study, scientists were able to dissect what is happening in different atmospheric layers on both Luhman 16B and Luhman 16A.
The two brown dwarfs were first discovered in 2013 using data from NASA's WISE space telescope, which maps the sky in infrared light.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Scientists used Doppler imaging to create the Luhman 16B weather map, which somewhat resembles satellite weather views of Earth, Max Planck officials wrote in a news release.
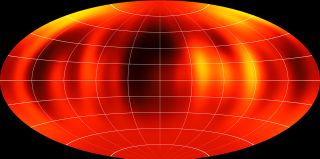
"In the future, we will be able to watch cloud patterns form, evolve and dissipate — eventually, maybe exo-meteorologists will be able to predict whether a visitor to Luhman 16B can expect clear or cloudy skies," Crossfield said in a statement.
By examining weather on brown dwarfs, scientists might be able to better understand how the atmospheres of giant planets outside of the solar system work, researchers have said.
"We've learned that the weather patterns on these brown dwarfs are quite complex," Beth Biller, leader of the second study detailing the atmospheric layers, said in a statement. "The cloud structure of the brown dwarf varies quite strongly as a function of atmospheric depth and cannot be explained with a single layer of clouds."
The brown dwarf surface-mapping results appear in the journal Nature, and the atmospheric layer results are in Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Crossfield and his team have developed a foldable oragami version of the Luhman 16B map. You can download the plans and fold your own brown dwarf here: http://www.mpia.de/Public/menu_q2e.php?Aktuelles/PR/2014/PR_2014_02/PR_2014_02_en.html
Follow Miriam Kramer @mirikramer and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on SPACE.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Miriam Kramer joined Space.com as a Staff Writer in December 2012. Since then, she has floated in weightlessness on a zero-gravity flight, felt the pull of 4-Gs in a trainer aircraft and watched rockets soar into space from Florida and Virginia. She also served as Space.com's lead space entertainment reporter, and enjoys all aspects of space news, astronomy and commercial spaceflight. Miriam has also presented space stories during live interviews with Fox News and other TV and radio outlets. She originally hails from Knoxville, Tennessee where she and her family would take trips to dark spots on the outskirts of town to watch meteor showers every year. She loves to travel and one day hopes to see the northern lights in person. Miriam is currently a space reporter with Axios, writing the Axios Space newsletter. You can follow Miriam on Twitter.