Giant Crater Found: Tied to Worst Mass Extinction Ever
An apparent crater as big as Ohio has been found in Antarctica. Scientists think it was carved by a space rock that caused the greatest mass extinction on Earth, 250 million years ago.
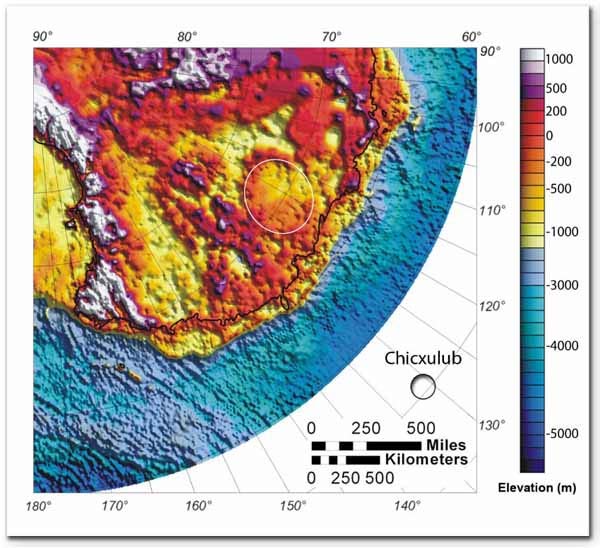
The crater, buried beneath a half-mile of ice and discovered by some serious airborne and satellite sleuthing, is more than twice as big as the one involved in the demise of the dinosaurs.
The crater's location, in the Wilkes Land region of East Antarctica, south of Australia, suggests it might have instigated the breakup of the so-called Gondwana supercontinent, which pushed Australia northward, the researchers said.
"This Wilkes Land impact is much bigger than the impact that killed the dinosaurs, and probably would have caused catastrophic damage at the time," said Ralph von Frese, a professor of geological sciences at Ohio State University.
How they found it
The crater is about 300 miles wide. It was found by looking at differences in density that show up in gravity measurements taken with NASA's GRACE satellites. Researchers spotted a mass concentration, which they call a mascon-dense stuff that welled up from the mantle, likely in an impact.
"If I saw this same mascon signal on the Moon, I'd expect to see a crater around it," Frese said. (The Moon, with no atmosphere, retains a record of ancient impacts in the visible craters there.)
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
So Frese and colleagues overlaid data from airborne radar images that showed a 300-mile wide sub-surface, circular ridge. The mascon fit neatly inside the circle.
"And when we looked at the ice-probing airborne radar, there it was," he said today.
Smoking gun?
The Permian-Triassic extinction, as it is known, wiped out most life on land and in the oceans. Researchers have long suspected a space rock might have been involved. Some scientists have blamed volcanic activity or other culprits.
The die-off set up conditions that eventually allowed dinosaurs to rule the planet.
The newfound crater is more than twice the size of the Chicxulub crater in the Yucatan peninsula, which marks the impact that may have ultimately killed the dinosaurs 65 million years ago. The Chicxulub space rock is thought to have been 6 miles wide, while the Wilkes Land meteor could have been up to 30 miles wide, the researchers said.
Confirmation needed
Postdoctoral researcher Laramie Potts assisted in the discovery.
The work was financed by NASA and the National Science Foundation. The discovery, announced today, was initially presented in a poster paper at the recent American Geophysical Union Joint Assembly meeting in Baltimore.
The researchers say further work is needed to confirm the finding. One way to do that would be to go there and collect rock from the crater to see if its structure matches what would be expected from such a colossal impact.
- Giant Slab of Earth's Crust Found Near Core
- Did Asteroid-Induced Firestorm Destroy the Dinosaurs?
- Scientists Debate Dinosaur Demise
- Huge Crater Found in Egypt
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Rob has been producing internet content since the mid-1990s. He was a writer, editor and Director of Site Operations at Space.com starting in 1999. He served as Managing Editor of LiveScience since its launch in 2004. He then oversaw news operations for the Space.com's then-parent company TechMediaNetwork's growing suite of technology, science and business news sites. Prior to joining the company, Rob was an editor at The Star-Ledger in New Jersey. He has a journalism degree from Humboldt State University in California, is an author and also writes for Medium.