How NASA's Mars 2020 Rover Will Work (Infographic)
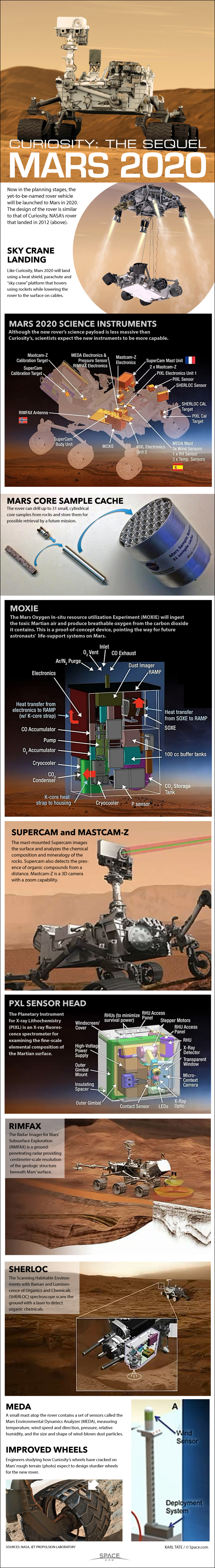
Now in the planning stages, the yet-to-be-named rover vehicle will be launched to Mars in 2020. The design of the rover is similar to that of Curiosity, NASA’s rover that landed in 2012.
Like NASA's Curiosity rover, Mars 2020 will land using a heat shield, parachute and "sky crane" lander that hovers using rockets while lowering the rover to the surface on cables.
NASA's Next Mars Rover to Collect Martian Samples, Carry Lasers
Although the new rover’s science payload is less massive than Curiosity’s, scientists expect the new instruments to be more capable.
The rover can drill up to 31 small, cylindrical core samples from rocks and store them for possible retrieval by a future mission.
NASA's Mars Rover 2020 Mission in Pictures (Gallery)
The Mars Oxygen In-situ resource utilization Experiment (MOXIE) will ingest the toxic Martian air and produce breathable oxygen from the carbon dioxide it contains. This is a proof-of-concept device, pointing the way for future astronauts’ life-support systems on Mars.
The mast-mounted Supercam images the surface and analyzes the chemical composition and mineralogy of the rocks. Supercam also detects the presence of organic compounds from a distance. Mastcam-Z is a 3D camera with a zoom capability.
The Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry (PIXL) is an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer for examining the fine-scale elemental composition of the Martian surface.
The Radar Imager for Mars' Subsurface Exploration (RIMFAX) is a ground-penetrating radar providing centimeter-scale resolution of the geologic structure beneath Mars’ surface..
The Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman and Luminescence of Organics and Chemicals (SHERLOC) spectroscope scans the ground with a laser to detect organic chemicals.
A small mast atop the rover contains a set of sensors called the Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA), measuring temperature, wind speed and direction, pressure, relative humidity, and the size and shape of wind-blown dust particles.
The Boldest Mars Missions in History
Mars Explored: Landers and Rovers Since 1971 (Infographic)
Amazing Mars Rover Curiosity's Martian Views (Latest Photos)
Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook or Google+.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Karl's association with Space.com goes back to 2000, when he was hired to produce interactive Flash graphics. From 2010 to 2016, Karl worked as an infographics specialist across all editorial properties of Purch (formerly known as TechMediaNetwork). Before joining Space.com, Karl spent 11 years at the New York headquarters of The Associated Press, creating news graphics for use around the world in newspapers and on the web. He has a degree in graphic design from Louisiana State University and now works as a freelance graphic designer in New York City.
