Hubble Telescope Captures Spectacular New Views of 'Pillars of Creation'
SEATTLE — A famous deep-space object imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope 20 years ago has been reborn in an amazing new photo.
Scientists pointed the telescope at the iconic Eagle Nebula, also known as Messier 16 (M16), capturing the famous "Pillars of Creation" in sharper and wider view. The new and improved image was possible thanks to upgrades made to the Hubble Space Telescope over the past 25 years. You can see the new Pillars of Creation image in detail in a breathtaking new video of the Hubble views as well.
"It allows us to demonstrate how far Hubble has come in 25 years of observation," Paul Scowen, of Arizona State University, said during a news conference here at the 225th meeting of the American Astronomical Society Monday (Jan. 5). Scowen was one of the astronomers who helped take the original iconic image. [See more amazing images from Hubble]
"It really is quite remarkable," he added.
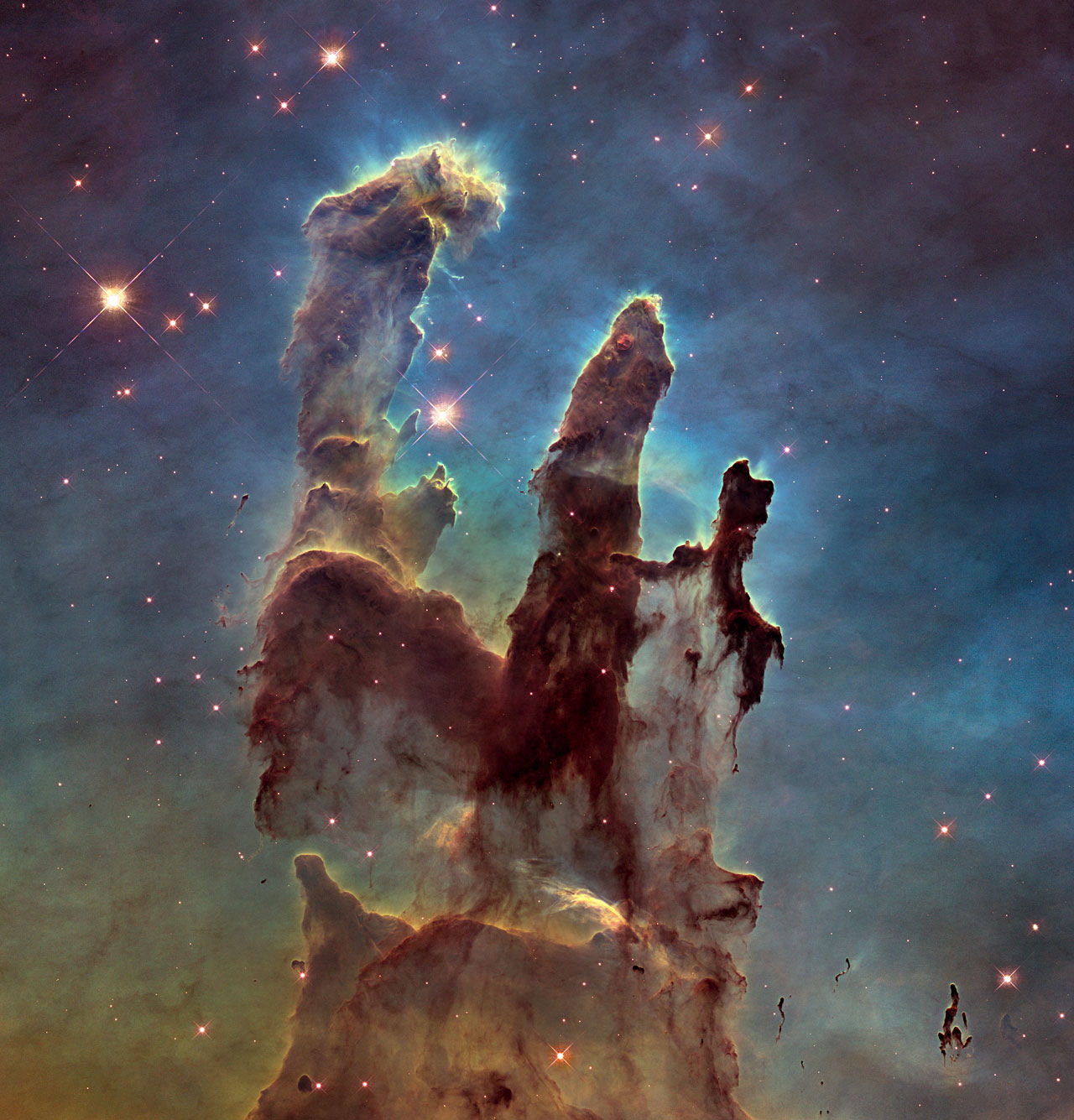

Dubbed the "Pillars of Creation" when it was discovered in 1995, the Eagle Nebula view is arguably the most famous of all of Hubble's images. It has appeared on postage stamps, T-shirts and pillows, and even made the rounds in television shows and movies. Located approximately 7,000 light-years from the sun, M16 is a region of gas and dust where stars form at a rapid clip.
The new Hubble image utilizes the Wide Field Camera 3, installed in 2009, to reveal the star-forming region at twice the resolution of the original instrument. As with the original image, taken by the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2, elements in the image appear as different colors: Red reveals singly ionized sulfur, blue shows double-ionized oxygen and green highlights hydrogen.
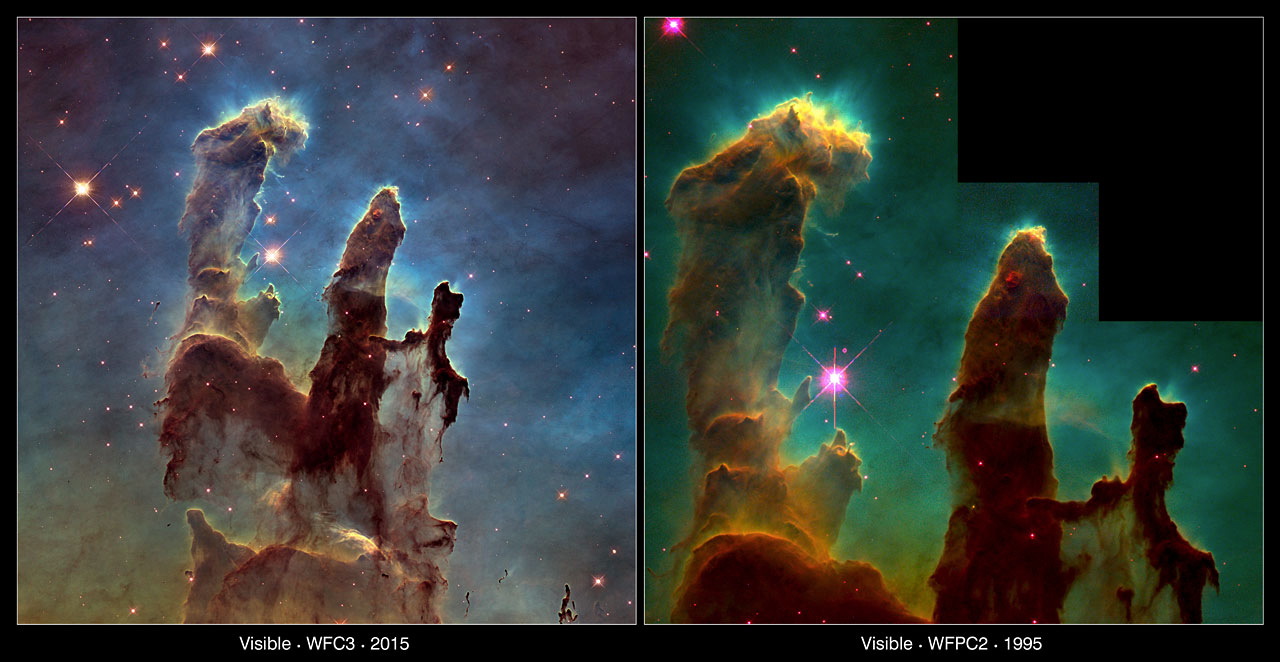

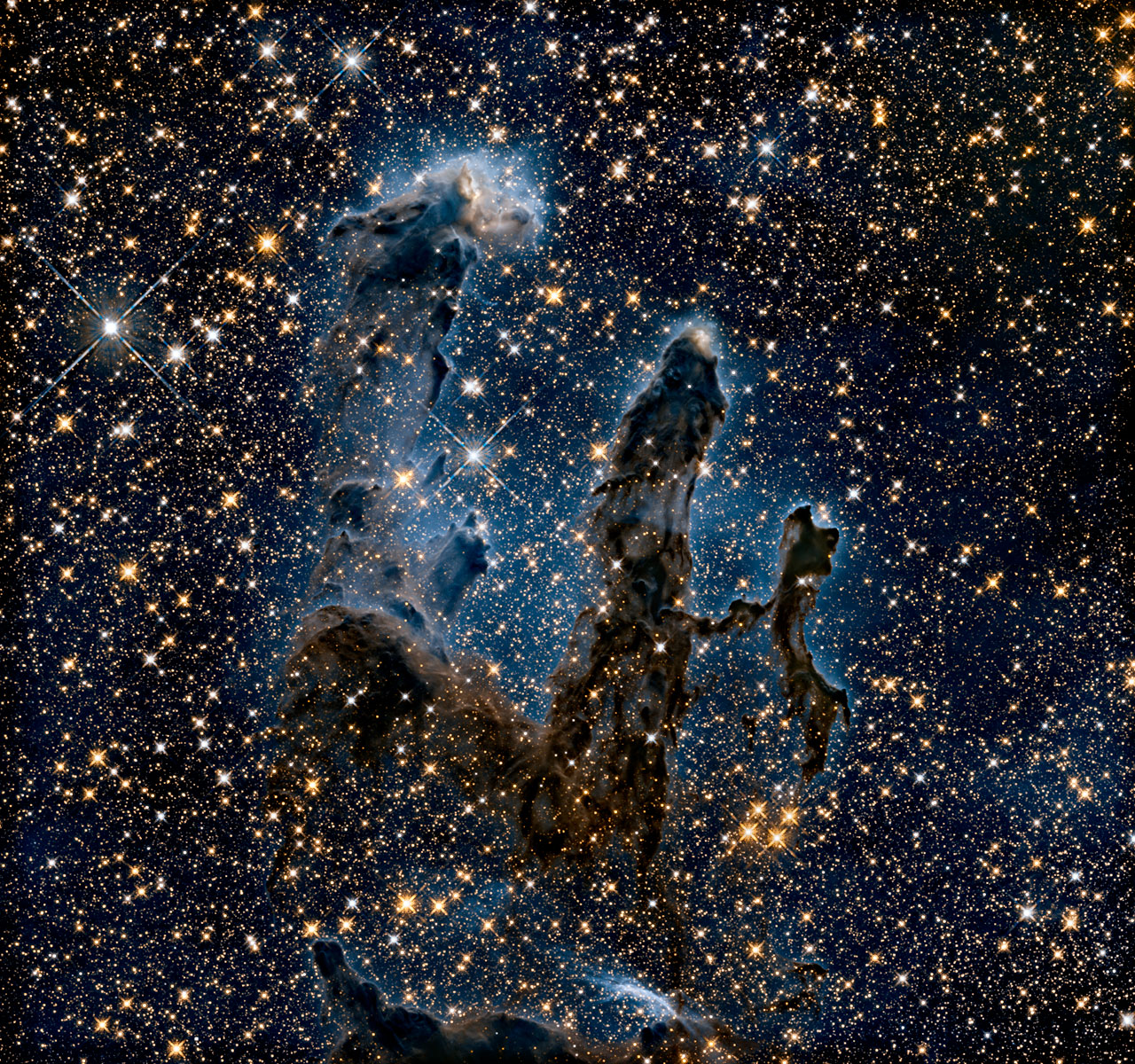
Along with releasing the sharper new photo, the Hubble team revealed an image of the Eagle Nebula in the infrared wavelength, which cuts through the dust and gas to reveal significantly more stars.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"The pillars themselves become quite transparent in the infrared," Scowen said.
The infrared image reveals that the pillars still exist after two decades because their dense heads shadow the gas beneath them. The massive young stars at their hearts are violent places, with rapid stellar winds blowing away the lighter material. Gas between the columns evaporated long ago due to the heat from bright young stars.

The new images also show changes that have taken place in the nebula over the past two decades. Several protostar systems create long jets that Scowen described as "signposts pointing back to 'We just made a star right here.'" Some of these squiggly jets, which cut through the dust and gas, have moved over in the time since the original image was taken.
Scowen called the images "a remarkable example of what Hubble has been able to do in its lifetime."
Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebookand Google+. Original article on Space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Nola Taylor Tillman is a contributing writer for Space.com. She loves all things space and astronomy-related, and enjoys the opportunity to learn more. She has a Bachelor’s degree in English and Astrophysics from Agnes Scott college and served as an intern at Sky & Telescope magazine. In her free time, she homeschools her four children. Follow her on Twitter at @NolaTRedd