NASA Calls Off Satellite Launch Minutes Before Liftoff Due to Winds

The launch of NASA's newest Earth-gazing satellite will have to wait another day due to high winds that made launch too risky Thursday (Jan. 29).
The space agency's Soil Moisture Active Passive satellite (SMAP) mission was set to launch to space today (Jan. 29) at 9:20 a.m. EST (1420 GMT). High altitude winds, however, prevented the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket carrying SMAP from taking off from Vandenberg Air Force base in California. NASA officials delayed the launch minutes before the 3-minute launch window opened.
Officials will attempt to launch the Earth-monitoring satellite to space again tomorrow (Jan. 30) at 9:20 a.m. EST. You can watch the SMAP launch attempt live on Space.com via NASA TV Friday. [See SMAP mission images]
"We had a beautiful countdown," Tim Dunn, NASA launch manager, said during a webcast after the delay was announced. "Everything on the Delta II rocket was rock solid. The spacecraft had absolutely no issues … The one thing that was kind of dogging us through the countdown was those upper-level winds … Unfortunately today, both from a loading on the rocket and a controllability of the rocket, we were in a condition with upper level winds that we just did not have the capability to fly the Delta II safely through the maximum dynamic pressure region of flight."
Officials expect a 90 percent chance of good weather for launch Friday (Jan. 30).
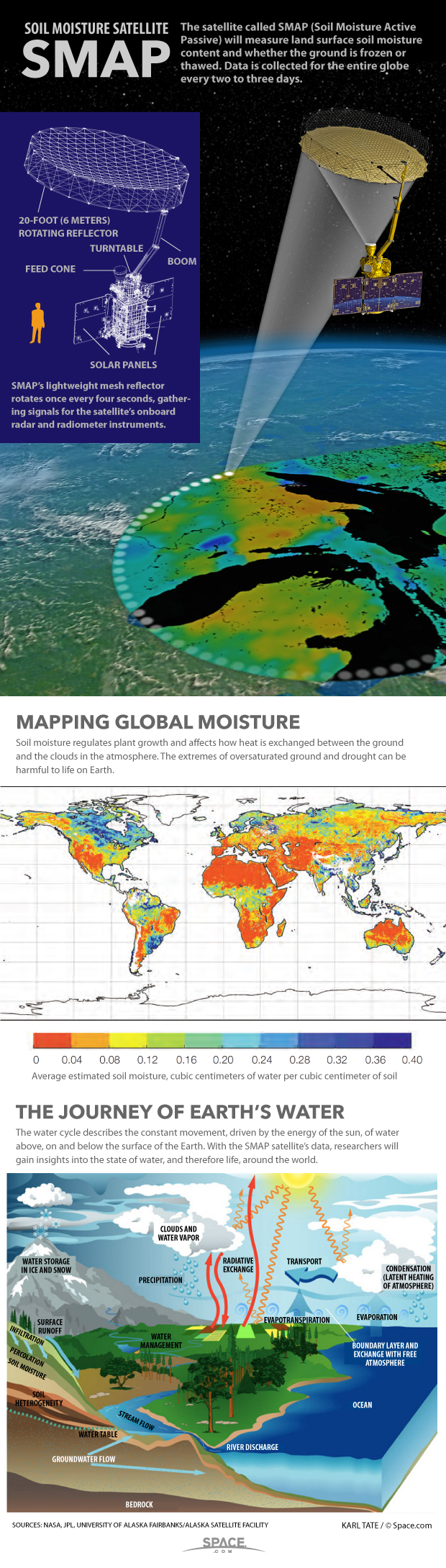
NASA's SMAP mission is designed to monitor the moisture content of soil on Earth. The satellite is expected to create a global map of soil moisture once every two to three days, providing scientists with unprecedented data about droughts and floods.
The soil moisture information can help researchers craft better weather forecasts and understand more about the interconnected nature of Earth's water, energy and carbon cycles, according to NASA.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"SMAP is in a unique position because its measurements impact two distinct domains," Dara Entekhabi, SMAP science team leader, said during a news conference Tuesday (Jan. 27). "One, of course, as a science mission it impacts how we fundamentally understand how the environment works and peer into the metabolism of the environment. And second, it impacts some of the applications that touch our everyday lives."
Once launched, the 3-year, $916 million SMAP mission will join the other Earth-gazing missions currently monitoring the planet from space today. SMAP will be in a polar orbit that takes it about 426 miles (685 kilometers) above Earth's surface.
The satellite comes equipped with a huge, nearly 20-foot (6 meters) rotating mesh antenna that is currently folded up but will be deployed after the spacecraft reaches orbit.
Follow Miriam Kramer @mirikramer. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Miriam Kramer joined Space.com as a Staff Writer in December 2012. Since then, she has floated in weightlessness on a zero-gravity flight, felt the pull of 4-Gs in a trainer aircraft and watched rockets soar into space from Florida and Virginia. She also served as Space.com's lead space entertainment reporter, and enjoys all aspects of space news, astronomy and commercial spaceflight. Miriam has also presented space stories during live interviews with Fox News and other TV and radio outlets. She originally hails from Knoxville, Tennessee where she and her family would take trips to dark spots on the outskirts of town to watch meteor showers every year. She loves to travel and one day hopes to see the northern lights in person. Miriam is currently a space reporter with Axios, writing the Axios Space newsletter. You can follow Miriam on Twitter.









