Explosive Culprit? Russian Fireball's Origins Found
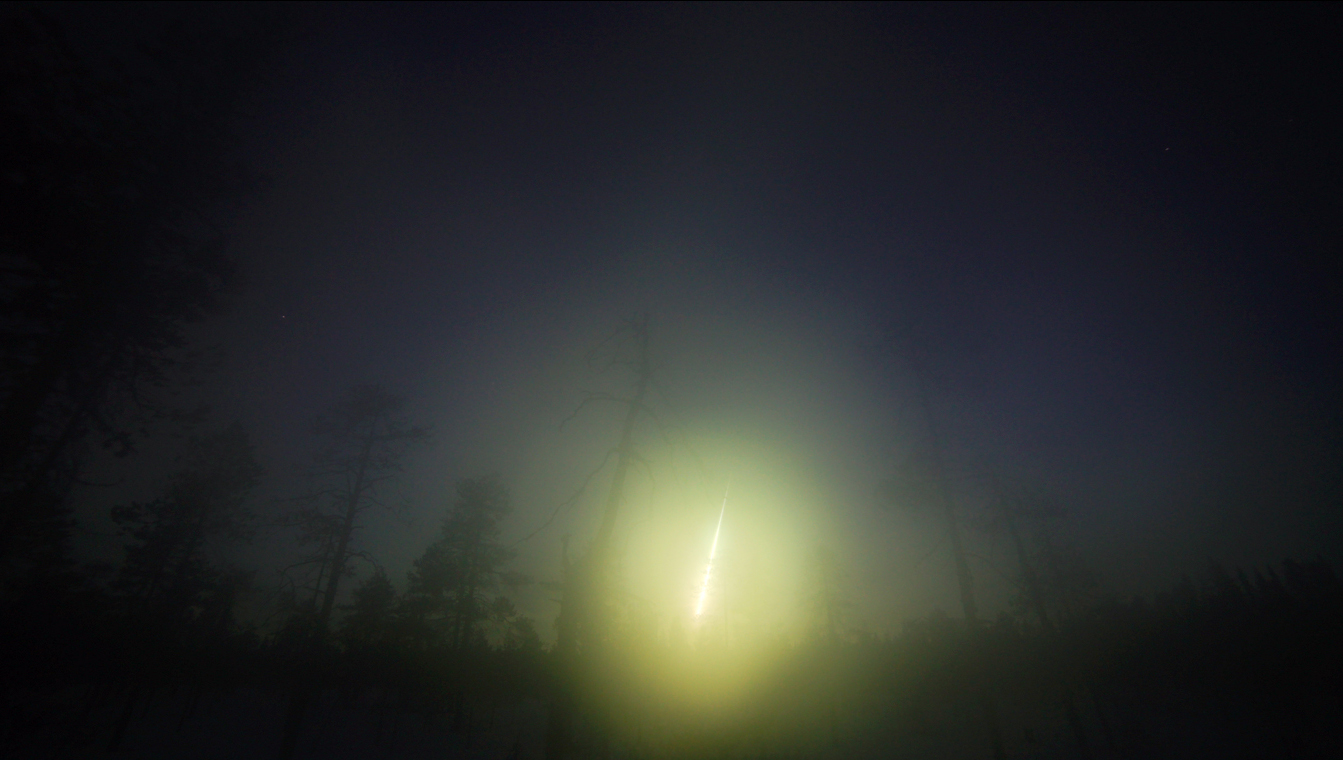

A crackling fireball that exploded over Russia last year appears to share an orbit with a huge asteroid discovered in October 2014, a new study reports.
The Kola fireball was spotted on April 19, 2014, as it lit up the night sky above the Kola Peninsula near the Finnish-Russian border. Its orbit is "disturbingly similar" to the asteroid 2014 UR116, slated to pass by the moon in 2017, the study authors said.
Camera observations by the Finnish Fireball Network, which monitors the sky for meteors and fireballs, and video from eyewitnesses helped scientists recreate the meteoroid's trajectory and hunt down meteorite fragments on the ground.
Josep Maria Trigo-Rodríguez, a researcher at the Institute of Space Sciences in Barcelona, Spain, led the international team of scientists who analyzed the meteorite's orbit. They calculated the fireball's size and path through Earth's atmosphere by examining its flight and the meteorite's final impact site. A computer model based on these figures was used to estimate the space rock's orbital path. [Crash! 10 Biggest Impact Craters on Earth]
The 1,100-pound (500 kilogram) meteorite is an ordinary H5 chondrite, a type of stony meteorite responsible for 31 percent of Earth's impacts. The fragments are called the "Annama meteorite" because the meteorite fell near the Annama River in Russia.
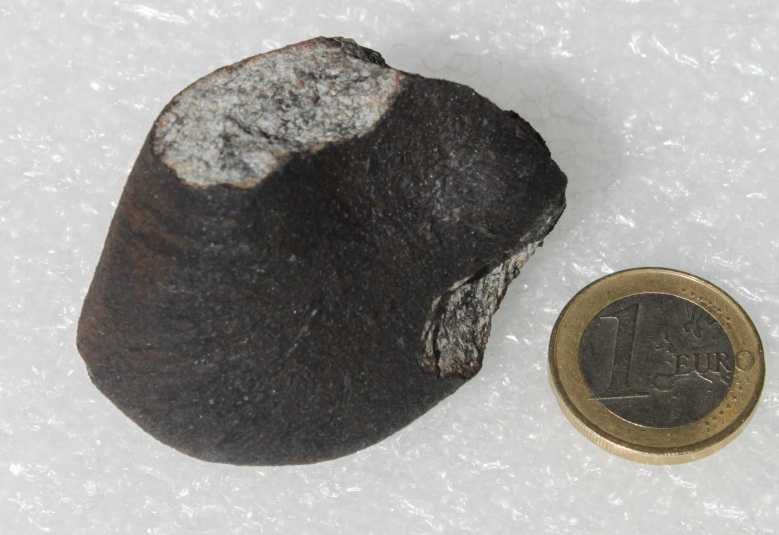

The precise detective works suggests the fireball escaped from the innermost region of the asteroid belt, the study researchers reported. The rock has an elliptical orbit that is typical of the Apollo family of near-Earth orbiting asteroids, and it likely came from the same broad source region as the Lost City, Peekskill and Buzzard Coulee meteorites, the researchers said.
The researchers compared the Annama meteorite's orbit with known near-Earth asteroids (there are more than 1,500). Of 12 potential matches, by far the closest match was with the asteroid 2014 UR116, they said.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The findings were published April 7 in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
The new report does not suggest that asteroid 2014 UR116 flung the Annama meteorite directly at Earth. However, the two bodies could be related. Scientists think that streams of asteroid fragments — such as the remnants of interstellar collisions — can sail on nearly identical orbits. Tidal forces may stretch out these rocky debris patches over time. Asteroids may also fragment from the stress of passing near the planets, the researchers noted.
"The tidal effect on an asteroid, which rapidly rotates under the gravitational field of a planet, can fragment these objects or release large rocks from its surface, which could then become dangerous projectiles at a local scale, such as the one that fell in Chelyabinsk, Russia," Trigo-Rodríguez said in a statement.
Asteroid 2014 UR116, discovered by Russian scientists on Oct. 27, 2014, measures 1,312 feet (400 meters) across, but does not pose an impact danger to Earth, according to NASA.
Follow Becky Oskin @beckyoskin. Follow Live Science @livescience, Facebook & Google+. Originally published on Live Science.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Becky was a science reporter at The Pasadena Star-News. She has freelanced for New Scientist and the American Institute of Physics and interned at Discovery News. She earned a master's degree in geology from Caltech, a bachelor's degree from Washington State University, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what her latest project is, you can follow Becky on Twitter.