Aerojet Rocketdyne Makes $2B Offer for United Launch Alliance

WASHINGTON – Rocket engine maker Aerojet Rocketdyne has offered to buy launch services provider United Launch Alliance from Lockheed Martin and Boeing for at least $2 billion, an industry source told SpaceNews Sept. 8.
The unsolicited bid is the latest twist in what has been a topsy-turvy year for ULA, the primary U.S. government launch services provider.
The proposal is still in discussion, but an announcement could come as early as the week of Sept. 14 at the annual U.S. Air Force Association conference, to be held at National Harbor, Maryland, the source said. [Awesome Atlas V Rocket Launch Photos]
Aerojet Rocketdyne's bid starts at $2 billion, but could go higher after the company does its due diligence, the source said.
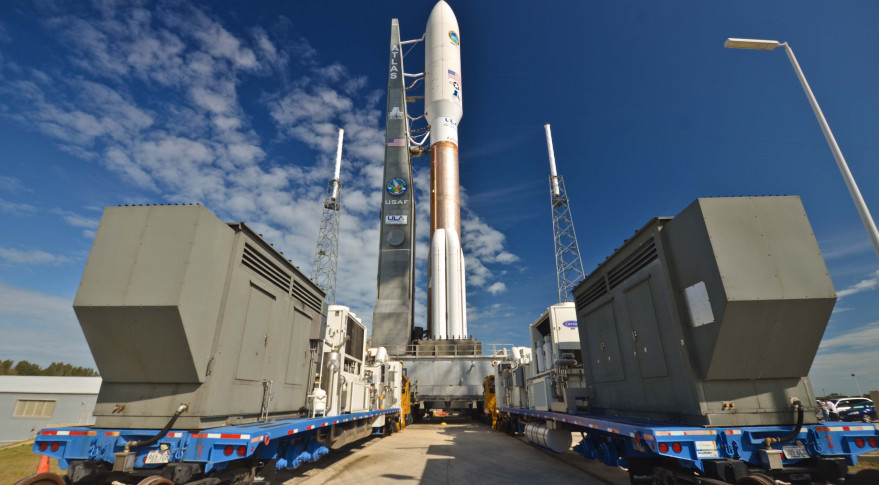
Denver-based ULA operates and owns the production rights for the Atlas V and Delta IV rockets, which together launch the vast majority of U.S. government payloads. The Boeing-Lockheed Martin joint venture, established in 2006, also owns a rocket production plant in Decatur, Alabama, and launch infrastructure at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida and at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
ULA faces an uncertain future owing to a congressional ban on the Russian-built RD-180 engine that powers its workhorse, the Atlas V, and a competitive challenge in its government market from upstart SpaceX. Congress appears willing to fund a U.S.-built RD-180 replacement, and Aerojet Rocketdyne is developing one called the AR-1, but ULA last September announced plans to use an alternative built by the secretive Blue Origin rocket company owned by Amazon.com founder Jeff Bezos.
Kent, Washington-based Blue Origin's planned BE-4 uses a different type of fuel than the RD-180 and as such cannot be retrofitted into the current Atlas V design. ULA, which plans to phase out all but the largest variants of the high-priced Delta IV, in April unveiled a new rocket design called Vulcan that accommodates the BE-4. The new vehicle, to debut around 2020, would essentially be an Atlas 5 outfitted with a new, larger first stage, at least in its initial incarnation.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
But Boeing and Lockheed Martin, who control ULA's purse strings, have yet to agree to invest the roughly $1 billion that ULA says it needs to develop the Vulcan. Blue Origin is funding development of the BE-4, also to the tune of about $1 billion, ULA says.
Spokesmen for Sacramento, California-based Aerojet Rocketdyne, Boeing and Lockheed Martin declined to comment. Jessica Rye, a spokeswoman for ULA, referred questions to Lockheed Martin and Boeing.
In May, a consortium of three companies including Aerojet Rocketdyne asked the U.S. Department of Defense about the possibility of obtaining production rights to the Atlas V. ULA rebuffed that overture.
A purchase of ULA, if approved by the parent companies and the government, would be a dramatic turnaround for Aerojet Rocketdyne, which was stung by ULA's decision to go with the BE-4 over the AR-1. ULA continues to fund work on the AR-1, but views that engine as a backup in case Blue Origin falters in its engine effort.
This story was provided by SpaceNews, dedicated to covering all aspects of the space industry.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Mike Gruss is a veteran defense reporter and Editor-in-Chief of Sightline Media Group, which includes Army Times, Air Force Times, Dense News, Military Times and Navy Times. From 2013 to 2016, Mike served as a Senior Staff Writer for SpaceNews covering national security space programs and military space policy in the U.S. Congress. Mike earned a bachelor's degree in English and American Studies from Miami University and has previously wrote for the Journal Gazette in Fort Wayne, Indiana and the Virginian-Pilot in Virginia before joining SpaceNews. Prior to joining Sightline in 2017, he was a senior editor of FedTech magazine covering technology in federal government. You can see Mike's latest project on Twitter.