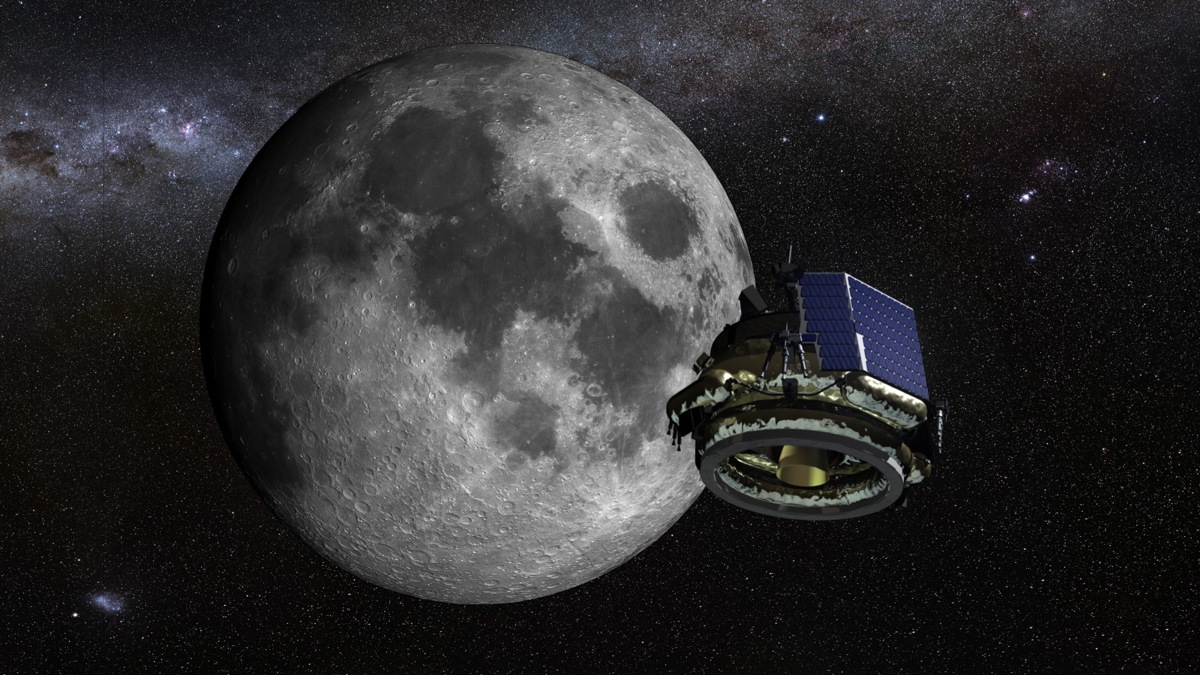
For the first time ever, a private company has permission to land on the moon.
The U.S. government has officially approved the planned 2017 robotic lunar landing of Florida-based Moon Express, which aims to fly commercial missions to Earth's nearest neighbor and help exploit its resources, company representatives announced today (Aug. 3).
"This is not only a milestone, but really a threshold for the entire commercial space industry," Moon Express co-founder and CEO Bob Richards told Space.com. [Images: Moon Express' Private Lunar Lander]
Previously, companies had been able to operate only on or around Earth. The new approval, while exclusive to Moon Express, could therefore serve as an important regulatory guide for deep-space commercial activity in general, Richards said.
"Nobody's had a deep-sea voyage yet. We're still charting those waters," he said. "Somebody had to be first."
Moon Express submitted an application to the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) on April 8. The document then made its way through the U.S. State Department, the U.S. Department of Defense, NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Federal Communications Commission, Richards said.
The interagency approval process "took some time, not because anybody was against or averse to this," he said. "It's just that we asked questions that had never been asked before, and that had to be addressed and worked out."
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Moon Express can now focus exclusively on the financial and technical challenges of the 2017 moon mission, which will begin with the launch of the company's MX-1 lander atop a Rocket Lab Electron booster. (Moon Express signed a multilaunch deal with Rocket Lab last year.)
The main goal of the maiden launch is to test out the MX-1's performance and capability on the lunar surface. Moon Express representatives also hope to win the Google Lunar X-Prize, a $30 million competition to land a privately funded robotic vehicle on the moon by the end of 2017.
The first team to pull off this landing — and get the vehicle to move at least 1,640 feet (500 meters) on the lunar surface, and beam high-definition video and photos back to Earth — will win the $20 million grand prize. (The second team to achieve all of this gets $5 million, and another $5 million is available for meeting other milestones. At the moment, 16 teams remain in the running.)
"We're still shooting for the end of 2017," Richards said of the maiden MX-1 moon mission. "A lot has to go right, but at least we have a shot at our moon shot, given this regulatory approval."
If all goes according to plan, future Moon Express missions will help assess, extract and exploit lunar resources such as water ice, helping to launch a new era in space exploration, company representatives have said.
"Space travel is our only path forward to ensure our survival and create a limitless future for our children," Moon Express co-founder and Chairman Naveen Jain said in a statement today. "In the immediate future, we envision bringing precious resources, metals and moon rocks back to Earth. In 15 years, the moon will be an important part of Earth’s economy, and potentially our second home."
Follow Mike Wall on Twitter @michaeldwall and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook or Google+. Originally published on Space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.