Extreme Astronomy Unlocks Cosmic Secrets From the South Pole
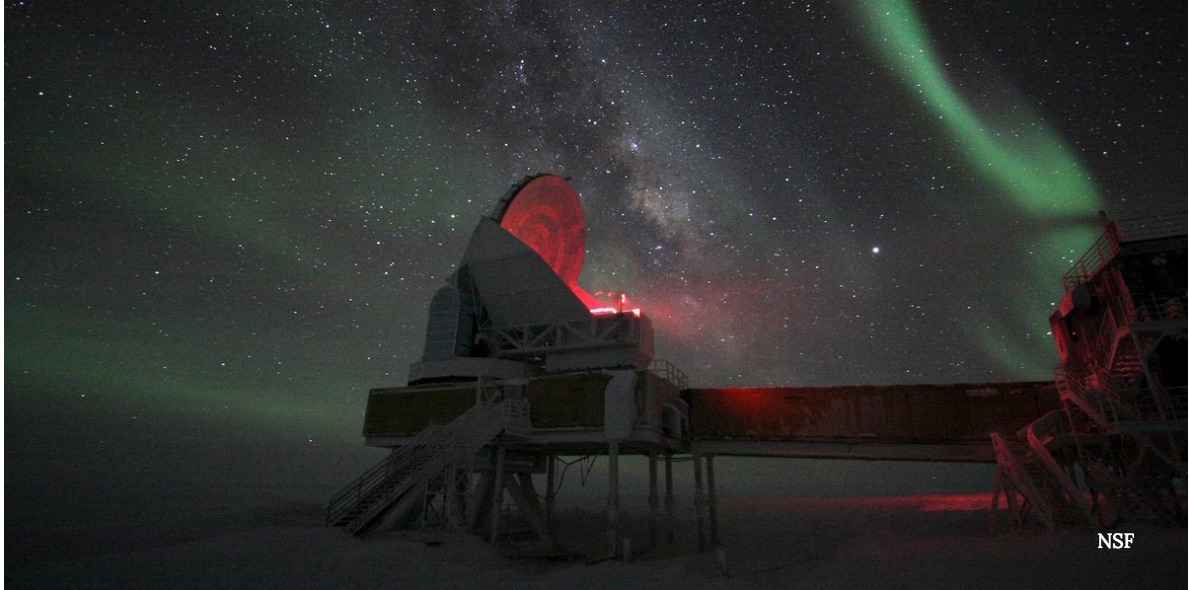

Imagine doing astronomy where grease won't stay greasy, where it's nighttime all day during the winter, and where nighttime temperatures fall to -100 Fahrenheit. Well, there's a hardy group of astronomers that enthusiastically do that, year-in, year-out, at Antarctica's South Pole Telescope.
The South Pole is a harsh environment, but it's excellent for astronomy due to its dry atmosphere (water vapor interferes with observations). Researchers at the Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics are even considering building a telescope at a site called Dome A, about 1,000 miles from the pole and a long trek from habitation.
What is it really like to work down there for up to a year, which is the typical over-winter stay of Antarctic personnel? According to University of Toronto experimental cosmologist Keith Vanderlinde, who spent 11 months there over the winter, it attracts a certain type of person who doesn't necessarily need the company of other people to work well. His group vacillated between being super-social in shared quarters, and choosing to retreat individually to their own quarters. He also saw people "going toasty" (this Antarctic slang for changed behavior comes from bread turning into toast) as they grappled with months of isolation away from families.
"People who didn't work outside at all, they got toasty very quickly. You develop a short fuse," Vanderlinde told Seeker. "People develop a 1,000-mile stare and stare at the wall for an hour and not do anything."
RELATED: How Science Is Keeping Antarctica Ungoverned
Vanderlinde came to the National Science Foundation-funded South Pole Telescope in 2008 after his Ph.D., when the facility was just in its second year of operations. It was a half-hour trek from the living quarters to the telescope, where Vanderlinde and a colleague checked in to make sure the telescope was staying healthy. Overall the work went well, except for occasional mechanical issues. He recalled, for example, one time when the power went out on a Sunday night, which required a long warm-up procedure that Monday to get the telescope up and running again.
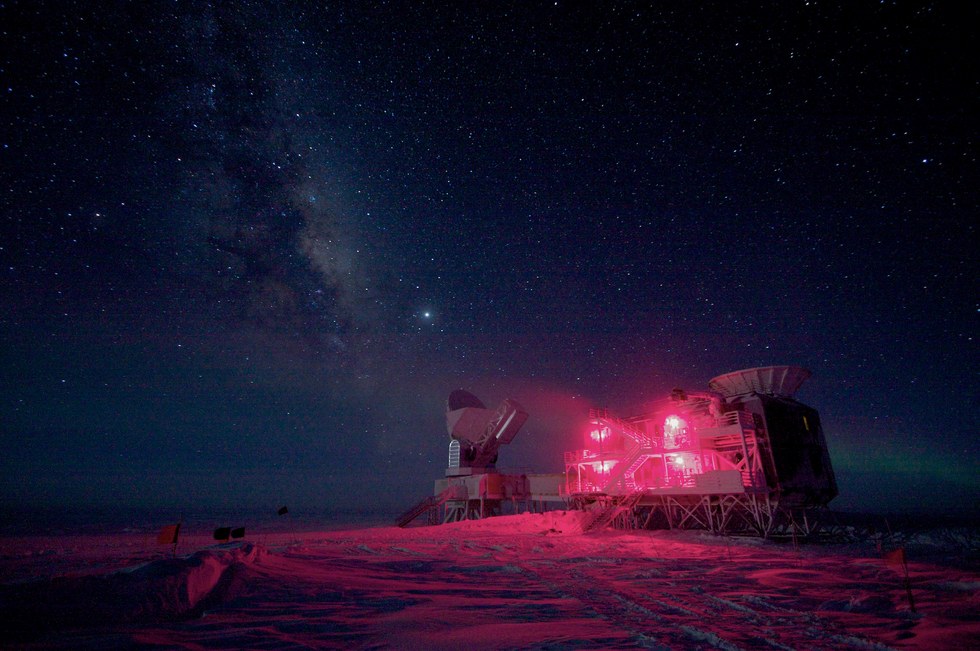

The conditions are harsh, but Vanderlinde says the science is worth it. The telescope is mapping out the cosmic microwave background (CMB), which is the leftover energy from when the universe was first expanding. It can best be seen in microwave wavelengths. As the CMB shines through galaxy clusters, Vanderlinde says, some light scatters off hot electrons and can show up as an excess of energy.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"By looking at these little shadows, you can figure out where all of the largest structures in the universe are," he said. Over time and with observations from the South Pole Telescope's first camera, he said, scientists can also learn how galaxy clusters grew in different eras of the universe, and how dark energy — the ill-understood force that is causing the universe's expansion to accelerate — works.
The second-generation camera on the South Pole Telescope measures the intensity of the light and polarization, or how light is oriented related to the direction where it came from. As the CMB is lensed through galaxies and other structures, scientists can measure how large clumps of matter form over time, which in turn tells them how gravity works. Oddly, he said, tiny particles called neutrinos significantly impact how structure forms in the universe, and how gravity pulls gas and dust together into clusters and galaxies. So by looking at the big scale, scientists can better constrain how massive neutrinos are.
RELATED: BICEP2 Gravitational Wave 'Discovery' Deflates
In 2014, another South Pole telescope called BICEP2 detected polarization modes (known as B modes) that were originally interpreted as gravitational waves, or ripples in space-time that form from gravitational interactions. However, further study revealed a more mundane explanation: the polarization came from dust in our own galaxy.
Would Vanderlinde over-winter again? He's made several summer visits since then, but he said once was enough. "After I left I had recurring nightmares that I went back for another winter," he said. "It was not in any way a bad experience, but at the end you're done ... and the idea of doing it again didn't appeal to me."
Vanderlinde will deliver a public lecture on his experiences later this month in Toronto, Canada. If you can't make the talk, you can watch a TEDx presentation he gave last year on south pole science, or read his blog from his year in Antarctica.
WATCH VIDEO: The Race To See The Black Hole At Our Galaxy's Core
Originally published on Seeker.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., was a staff writer in the spaceflight channel between 2022 and 2024 specializing in Canadian space news. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years from 2012 to 2024. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House, leading world coverage about a lost-and-found space tomato on the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, "Why Am I Taller?" (ECW Press, 2022) is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams.