More Jupiter Weirdness: Giant Planet May Have Huge, 'Fuzzy' Core
Jupiter's deep interior appears to be as strange and otherworldly as the gas giant's storm-studded exterior, new observations by NASA's Juno spacecraft suggest.
Scientists have generally thought that Jupiter either harbors a relatively compact core 1 to 10 times as massive as Earth or no core at all, said Juno principal investigator Scott Bolton, who's based at the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio.
But neither of these hypotheses fits with the gravity data collected so far by Juno, which has been orbiting Jupiter since July 2016.
"There seems to be a fuzzy core, and it may be much larger than anybody had anticipated," Bolton said Thursday (May 25) during a NASA press conference announcing the first detailed science results from Juno's mission.
This core may even be partially dissolved, Bolton said, adding that Juno's initial observations are also consistent with "some deep motions or zonal winds" occurring far beneath the enormous planet's cloud tops.
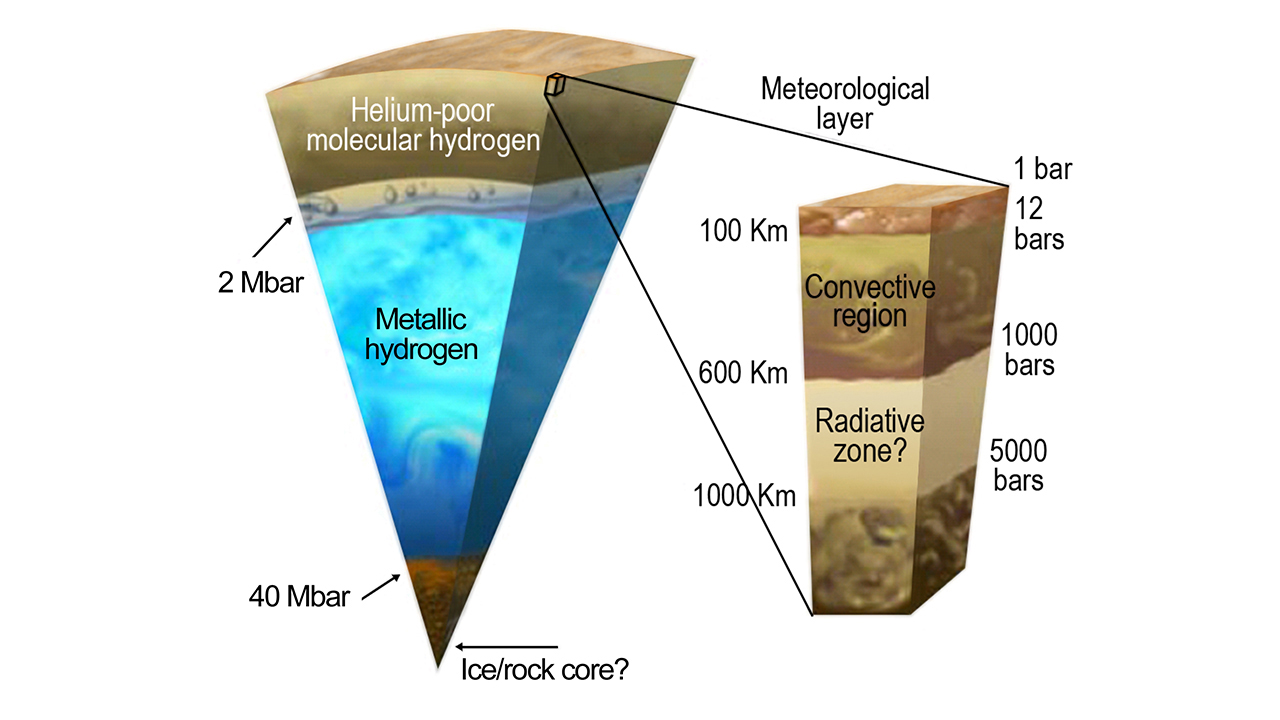
Identifying and characterizing Jupiter's core is a key goal of Juno's $1.1 billion mission, which seeks to better understand how the gas giant formed and evolved. Learning about Jupiter's history should yield insights about planet formation and solar-system evolution in general, mission team members have said.
Juno uses its eight science instruments to study Jupiter's structure, composition and gravitational and magnetic fields. The probe collects most of its information during close flybys over the gas giant's poles, which occur once every 53.5 days. (Juno orbits Jupiter on a highly elliptical path.)
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

Juno has completed just five of these data-gathering "perijove" passes to date, so mission scientists still have a lot to learn about Jupiter's core and other characteristics. But they've already been able to determine quite a bit — that Jupiter's weird, bluish poles are very different from the gas giant's belted midsection, for example, and that the mechanisms powering auroras on Earth and on Jupiter are not identical.
"The general theme of our discoveries is really how different Jupiter looks from what we expected," Bolton said.
Follow Mike Wall on Twitter @michaeldwall and Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook or Google+. Originally published on Space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.









