A Solar Eclipse Can Blind You (Read This Before Looking at the Sun!)
During the Great American Total Solar Eclipse on Aug. 21, millions of people will gaze at the sun to see the moon slowly pass in front of it, blocking out the light. But those who aren't careful risk doing some nasty damage to their eyes.
You've probably been told that it isn't safe to stare at the sun and that watching a solar eclipse without proper eye protection can make you go blind. That's because the light from the sun is so intense that it can literally burn your eyeballs — even during a solar eclipse, when part of the sun's disk is still visible.
Even the tiniest sliver of a crescent sun peeking out from behind the moon emits enough light to scorch your eyes, Ralph Chou, professor emeritus at the School of Optometry & Vision Science at the University of Waterloo in Canada, told Space.com. "I have seen instances where the patient has eventually shown up with crescents burned into the back of the eye, and you can almost tell exactly when they looked." [How to View a Solar Eclipse Without Damaging Your Eyes ]

How eyeballs get "sunburned"
Sunlight damages the eyes by triggering a series of chemical reactions in the retina, the light-sensitive part at the back of the eye. Retinas contain two types of photoreceptors: rods that help you see in the dark and cones that produce color vision.
When intense solar radiation hits the retinas, it can damage and even destroy those cells, in what doctors call a retinal photochemical injury, or solar retinopathy. Whether looking at the sun will cause this type of injury depends on both how long you look without protection and the sun's position in the sky. Overhead, the sun is brighter and more dangerous to look at than when it is close to the horizon during sunrise or sunset.
"You can think of it in the same way as this: Let's suppose you decide to really pig out for dinner, and afterwards you're not feeling very well," Chou said. "Well, [it's the] same thing with all the light hitting the light-sensitive receptors at the back of the eye. They get so much of this light energy coming in that they really can't handle [it]."
In severe cases, this type of photochemical damage may also come with thermal injuries, or literal burns, that destroy the rods and cones in the retina. This can happen to people who repeatedly look at the sun without any protection, those who stare at the sun for an extended time, or even those who glance through a telescope or binoculars without solar filters.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Instinct vs. willpower
Not many people look at the sun long enough to be blinded by the light, Chou said, but the risk is certainly exacerbated during a solar eclipse.
Under normal circumstances, it's more difficult to look at the sun long enough to incur damage because of something called an aversion reflex. "We learn early on in life we just shouldn't be looking at something that bright, because it is uncomfortable and we can't see anything," Chou said.
"The problem when it comes to looking at a partially eclipsed sun is that you are trying to see something that you know is going on that's different, and willpower is an amazing thing to override an aversion reflex."
To make matters worse, it's possible to look directly at the sun "with a certain degree of comfort" when the sun is partially covered by the moon, Chou said. Even when the sun is almost completely covered, though, the tiny crescent that remains is still bright enough to burn your retinas.
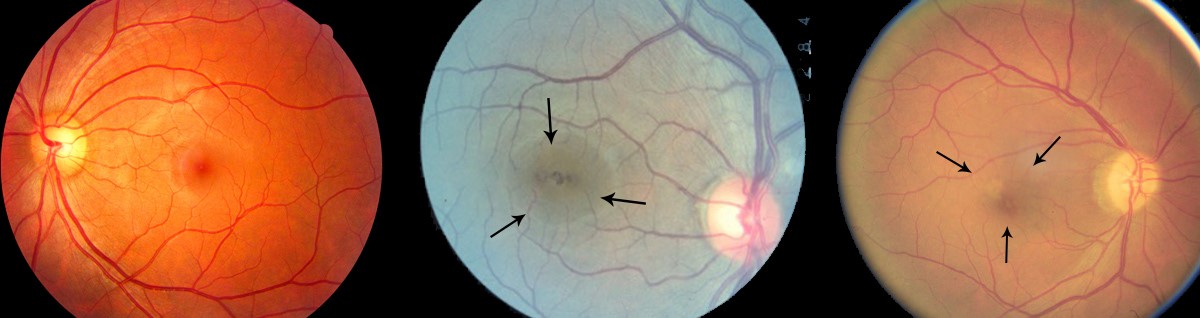
Seeing with eclipse blindness
One thing that makes eclipse blindness particularly dangerous is that a person who looks at the sun long enough to incur damage probably won't notice any of the effects until the next morning, Chou said.
"Let's say you take a look at the sun in the afternoon. The cells get overloaded, and they're actually still able to function for a little while, but overnight while you're asleep … the cells start lose their function, and then they even start to die depending on exactly how badly they've been affected," he explained.
People who wake up to discover their vision has become impaired may look in the mirror to find their face is a featureless blur, Chou said, or they may try to read the newspaper only to find that there are no words on the page. While peripheral vision is usually spared, the center of vision is affected the worst. That's the part of the retina responsible for seeing in high resolution and in color.
"Most people, they don't see a black spot," Chou said. "For the most part they have damaged photoreceptors that just aren't capable of doing more than just registering maybe the presence of light but can't really build up enough information for them to be able to see clearly."
An unclear path to recovery
Most patients with eclipse blindness are legally blind when they go to see an eye doctor, Chou said. Unfortunately, the prognosis for these patients is nearly impossible to determine.
"You just sort of end up having to wait it out, and that's the really unfortunate part about it," Chou said. "The typical person who's been injured is going to wait six to 12 months before they know what their ultimate status is going to be."
Statistically, about half of those who are diagnosed with eclipse blindness will recover full vision in six months, he said. The other half either partially recover or are stuck with the problem for the rest of their lives.
And when it comes to treatment, there really aren't any options. "Over the years, certainly ophthalmologists have tried various ways, pharmacological and otherwise, to try and reduce the amount of damage and swelling that is thought to be the main cause for the loss of vision," Chou said. "For the most part, those types of treatments don't seem to be effective."
The only thing doctors can do to help these patients is to treat the case as any other case of visual impairment, Chou said, by teaching the individuals how to get around in the world and function without central vision.
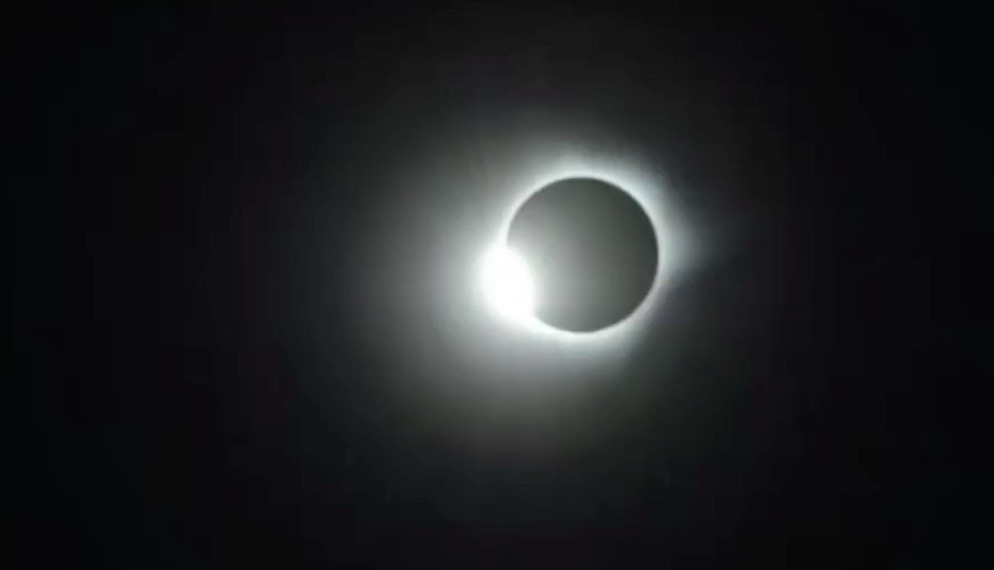

When it's safe to look
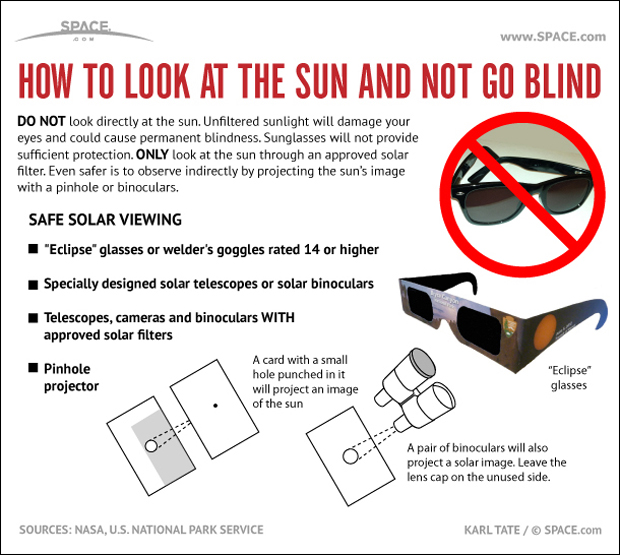
The only time it's safe to look at the sun without eclipse glasses or other solar filters is during totality, when the moon is completely blocking out the sun's rays and only the corona is visible. If you're planning on watching any kind solar eclipse, whether it's of the total, annular or partial variety, you absolutely must use proper eye protection if you want to spare your eyes. Otherwise, you'll risk long-term or even permanent blindness.
But definitely don't forget to take off your solar eclipse glasses during totality, when the sun is 100 percent covered by the moon. In fact, if you don't remove your solar filters during totality, you won't be able to see anything at all.
While official recommendations by NASA and the American Astronomical society say you shouldn't look directly at the sun when any part of it is showing, experienced eclipse watchers like Chou say it's safe to remove your eclipse glasses during the 2-3 seconds before and after totality to see the so-called diamond ring effect, or "Baily's beads." During this phase of the eclipse, the light of the crescent sun forms points of light on the edge of the disk for just a few seconds.
Other safety tips
Anyone who plans to observe the eclipse with a telescope, binoculars or cameras should practice using the equipment before the eclipse, Chou said. Don't wait until the eclipse starts to figure out how to insert and remove the filters from your lenses. For those using eclipse glasses or handheld viewers, make sure to put the filters in front of your eyes before looking up at the sun, not the other way around, Chou said. And children observing a solar eclipse should always be supervised to ensure they're practicing proper eye safety, he said.
Email Hanneke Weitering at hweitering@space.com or follow her @hannekescience. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Hanneke Weitering is a multimedia journalist in the Pacific Northwest reporting on the future of aviation at FutureFlight.aero and Aviation International News and was previously the Editor for Spaceflight and Astronomy news here at Space.com. As an editor with over 10 years of experience in science journalism she has previously written for Scholastic Classroom Magazines, MedPage Today and The Joint Institute for Computational Sciences at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. After studying physics at the University of Tennessee in her hometown of Knoxville, she earned her graduate degree in Science, Health and Environmental Reporting (SHERP) from New York University. Hanneke joined the Space.com team in 2016 as a staff writer and producer, covering topics including spaceflight and astronomy. She currently lives in Seattle, home of the Space Needle, with her cat and two snakes. In her spare time, Hanneke enjoys exploring the Rocky Mountains, basking in nature and looking for dark skies to gaze at the cosmos.