Chinese Space Station Crash: Why It's So Hard to Predict Where Space Debris Will Land
This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to Space.com's Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights. Read our complete guide to China's Tiangong-1 space station crash here.
The now defunct Chinese space station Tiangong-1 is en route to crash into Earth – completing its “atmospheric reentry phase”. While experts have been aware that this would happen for more than a year, there has been huge uncertainty around the exact timing. As the station’s orbital altitude has decreased, however, this uncertainty has gradually reduced and it is now possible to determine that it will deorbit within a few days.
Most of the 8.5-tonne station will burn up and disintegrate as it passes through the atmosphere, though some debris may hit Earth. And although we have the capability to precisely control a spacecraft such as Rosetta – which orbited a few km away from comet 67P while being 405m km away from Earth and travelling at 55,000km per hour – we cannot actually predict the time and place of Tiangong-1’s potential impact on Earth, despite it being only 200km above us.
But why is it so difficult, and will science one day help us nail such predictions?
Newton’s laws tell us that satellites orbit the Earth in perfectly circular or elliptical orbits, repeating their path again and again (assuming that gravity is the only force acting on them). However, this is not true at low altitudes, say below 1,000km, because the satellite is then moving through the Earth’s atmosphere. This causes “aerodynamic drag” (air resistance) – a force that opposes the satellite’s velocity, which effectively turns the orbit into a downward spiral towards the Earth’s surface.
In theory, we can calculate drag perfectly to predict the path of a satellite. This can be done using an equation that depends on the velocity of the satellite (v²), the density of the atmosphere (ρ), a numerical coefficient that depends on the shape of the satellite and its orientation with respect to the airflow (C), and the object’s area (A). For those who are interested, the equation is: D = ½ × C × ρ × A × v². But you don’t have to understand the equation to grasp why it is so hard to calculate drag.
The spacecraft’s velocity is easy to measure fairly accurately using observations. However, the other parameters are highly uncertain – making it difficult to determine Tiangong-1’s path. For vehicles such as cars and aircraft, C can be estimated theoretically or with computational fluid dynamics and measured experimentally in a wind tunnel. The main problem here is that Tiangong-1’s shape is complex, and the object is uncontrolled and tumbling chaotically, resulting in a constantly changing C.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
The other unknown is the density of the atmosphere, which decreases with altitude. However, particularly at high altitudes, this varies due to a number of unpredictable factors – the most important of which is solar activity.

The solar magnetic activity follows an 11-year cycle, which results in a periodic increase and decrease of the amount of radiation and charged particles emitted. These interact with a part of the Earth’s atmosphere called the ionosphere, changing its density. A good indicator of solar activity is the number of observed sunspots. But while the solar cycle can be monitored, the level of activity also changes unpredictably, leading to unpredictable changes in the density of the atmosphere.
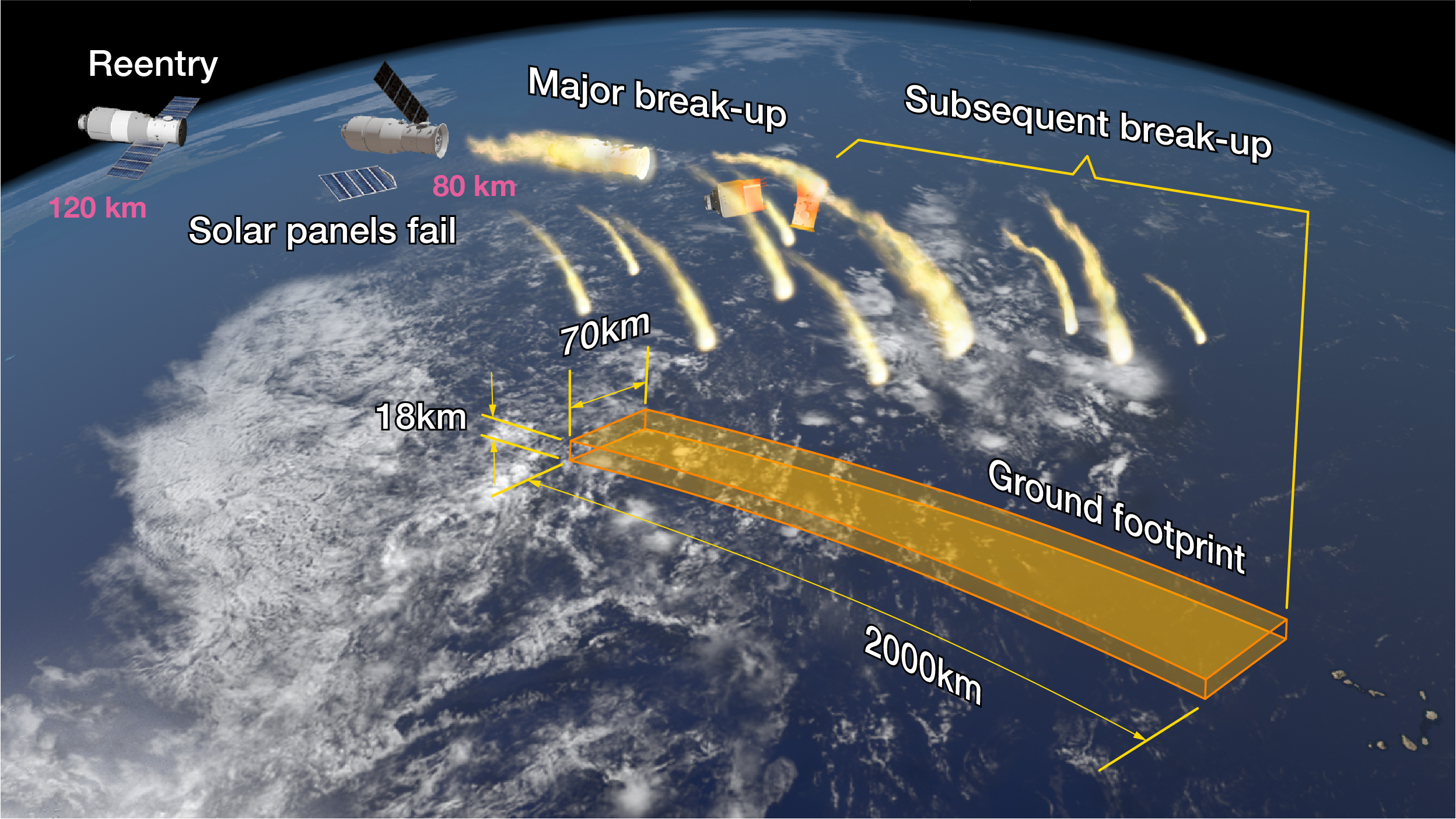
Another important factor is that the satellite will disintegrate and burn during the final phases of reentry, adding further uncertainty to all terms of the drag formula.
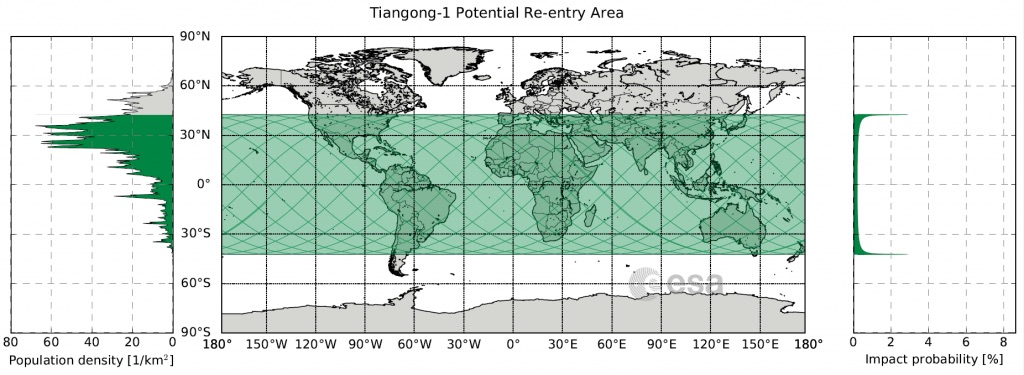
This explains why it is near impossible to predict an impact point (or region) along the satellite path. That said, you can get a rough idea of the area of probable impact, based on the inclination of the spacecraft’s orbit. We know that Tiangong-1’s orbit only enables it to reenter between the latitudes of -43 (north) and +43 (south) degrees around the equator. As you can see in the map above, this leads to an extended band of probable impact, mainly south of the equator.
Technological improvements
To prevent accumulation of debris in orbit around the Earth, which can pose a threat to spacecraft and satellites, it is now recommended that satellites in low Earth orbit are commanded to reenter Earth’s atmosphere within 25 years of mission completion.

It is therefore of growing importance to be able to avoid threats to population and objects on Earth as these spacecraft crash. Models and experimental data for atmospheric drag are continuously being improved, but it is unlikely that they will ever reach the required accuracy to allow us to predict exact impact points.
Instead, future satellites need to be designed with reentry as a crucial part of the mission. Active and controlled reentry – for example, by using drag sails or thrusters – could reduce uncertainties and ensure that the satellite burns completely in the atmosphere while following a trajectory carefully calculated in advance.
Satellites should also be designed and tested such that, during reentry, they fragment in a desired way and not cause a threat to Earth. This concept, analogous to controlled deformations in cars to protect the passengers in an accident, is known as “design for demise”. This is not something that is enforced today.
There can always be improvements in safety. But even though the spacecraft’s reentry isn’t controlled or predictable, we needn’t worry about being struck by it. The odds of you being hit are next to zero, while the chances of it striking anyone at all are about one in 3,200.
Matteo Ceriotti, Lecturer in space systems engineering, University of Glasgow
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article. Follow all of the Expert Voices issues and debates — and become part of the discussion — on Facebook, Twitter and Google +. The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the publisher. This version of the article was originally published on Space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Dr Matteo Ceriotti is a Senior Lecturer in Space Systems Engineering at the University of Glasgow. He holds an MSc and a PhD in space engineering. Matteo’s main research interests are space mission analysis and trajectory design, orbital dynamics and control, trajectory optimisation and spacecraft formation flying, with most applications being novel, visionary, high-risk high-gain space missions. He has deeply investigated the dynamics and control of advanced spacecraft propulsion systems such as solar sailing and hybrid propulsion. He is author of several scientific publications in international journals and two edited book chapters. He teaches courses in control and space flight dynamics in Engineering courses at honours year and postgraduate levels. During the free time, he enjoys hill walking, rock climbing or snowboarding, depending on the place and the weather.