How Close Are We to Kubrick's AI-Controlled Vision of the Future?
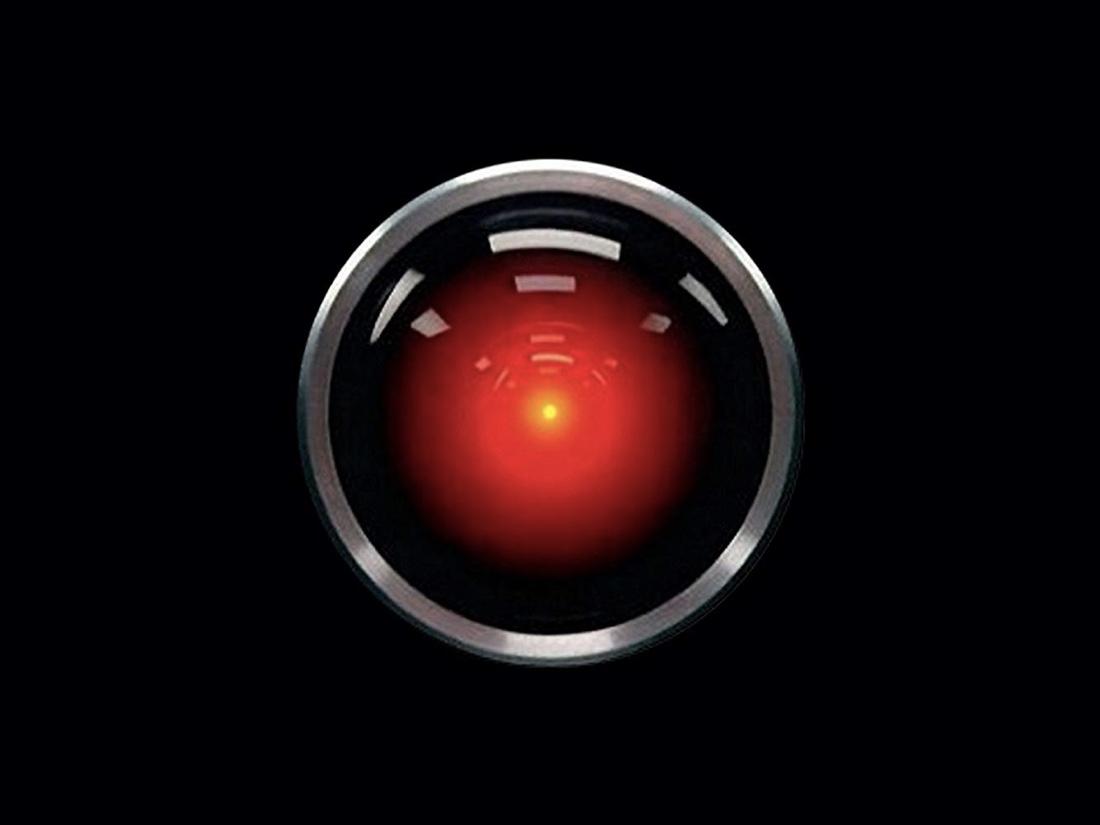

"I'm sorry Dave, I'm afraid I can't do that."
Movie audiences first heard these calmly intoned and ominous words in 1968, spoken by a spaceship's intelligent computer in the science-fiction masterpiece "2001: A Space Odyssey." With that one phrase, the computer named HAL 9000 confirmed that it could think for itself, and that it was prepared to terminate the astronauts who were planning to deactivate it.
Fifty years after director Stanley Kubrick released his visionary masterpiece of space colonization, how close are humans to the future that he imagined, in which we partner with artificial intelligence (A.I.) that we ultimately may not be able to control? [5 Intriguing Uses for Artificial Intelligence (That Aren't Killer Robots)]
We might be a lot closer than we think, with machines as smart — and as potentially threatening — as HAL lurking "in plain sight on Earth," according to an essay published yesterday (Oct. 17) in the journal Science Robotics.
Essay author Robin Murphy, a professor of computer science and engineering at Texas A&M University, knows artificial intelligence well; she was a pioneering leader in the development of disaster-response robots, and she serves as director of Texas A&M's Humanitarian Robotics and AI Laboratory, according to a faculty biography.
Kubrick's portrait of HAL represented a rare glimpse of what were then very young fields: AI and robotics, showcasing three disciplines that were critical for developing artificial intelligence: "natural language understanding, computer vision and reasoning," Murphy wrote in the essay.
HAL learned from observing its environment, watching and analyzing the words, facial expressions and movements of the human astronauts on the spaceship. It was responsible for performing rote functions such as maintaining the spaceship, but as a "thinking" computer, HAL also was capable of responding conversationally to the astronauts, Murphy explained.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
However, when the mission goes awry and the astronauts decide to shut HAL down, the AI discovers their plot by lip-reading. HAL arrives at a new conclusion that wasn't part of its original programming, deciding to save itself by systematically killing off the people onboard.
The prospect of AI doing more harm than good may not be that farfetched. Experts suggest that weaponized AI could play a big part in future global conflicts, and the late physicist Stephen Hawking suggested that humanity might soon find AI to be the biggest threat to our survival.
"The development of full artificial intelligence could spell the end of the human race," Hawking told the BBC in 2014.
During a pivotal scene in "2001," HAL strands astronaut David Bowman (Keir Dullea) outside the spaceship, cutting off his demands for re-entry with an emotionless, "This conversation can serve no purpose anymore." But the conversation about AI today is far from over; humanity's growing dependence on computers for a range of everyday uses demonstrates that AI has already established a firm foothold in our homes and in our lives.
What that could mean for humanity over the next 50 years, however, remains to be seen.
Originally publishedon Live Science.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.