Annular solar eclipse will turn the sun into 'ring of fire' today. Here's what you need to know.
Today's the day for an annular solar eclipse!
Update for 3:45 p.m. ET: The annular solar eclipse of 2023 has completed its pass over the United States and moved into parts of Central America and South America. Read our wrap to see amazing photos and videos.
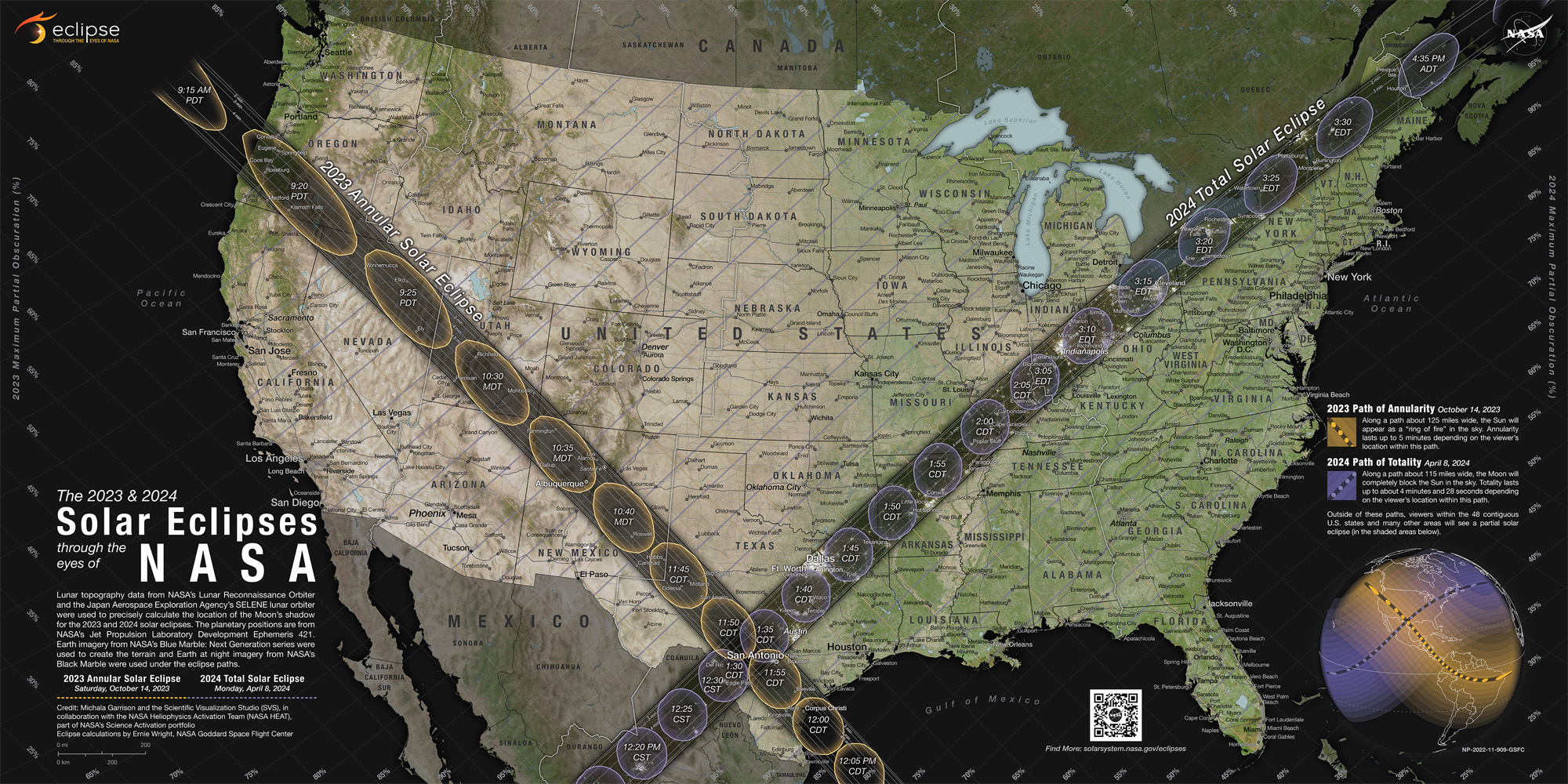
At 9:13 a.m. PDT (12:13 p.m. EDT and 1613 GMT) an annular solar eclipse will begin to sweep across the U.S. from Oregon to Texas before heading across the Gulf of Mexico and over Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia and Brazil.
During the annular solar eclipse, the moon will pass between the sun and Earth, casting a shadow on our planet. A "ring of fire" is created when the moon doesn't entirely cover the sun's disk, leaving a sliver of sunlight around the moon. (Annular eclipses occur when the moon is relatively far from Earth during its elliptical orbit around our planet.)
Our annular eclipse 2023 guide tells you everything you need to know about the upcoming eclipse. You can watch the annular eclipse online here on Space.com courtesy of NASA, beginning at 11:30 a.m. EDT (1630 GMT), and follow along with all the action on our annular eclipse live updates page.
More: Live updates of the Oct. 14 solar eclipse
Related: How long will the annular solar eclipse last on Oct. 14?
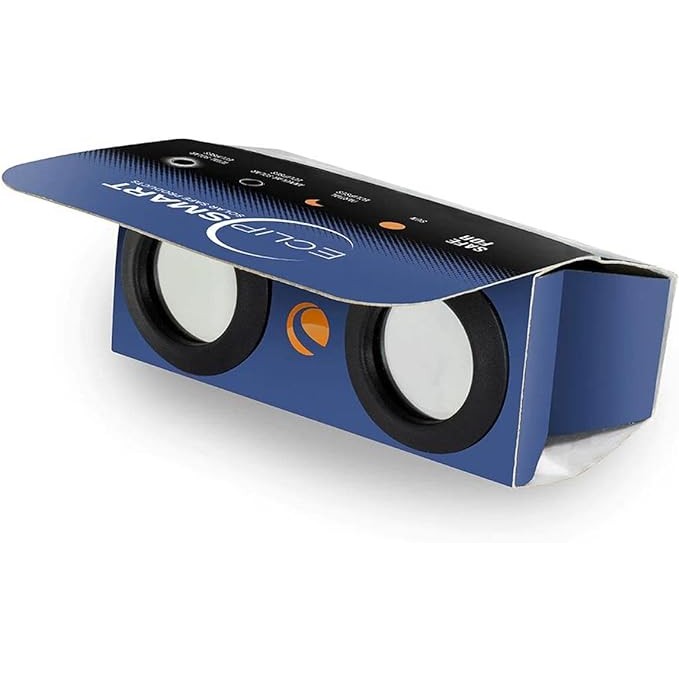

If you're looking for safe optics to view the eclipse, we recommend the Celestron EclipSmart 2x Power Viewers, which have 2x magnification or this travel-friendly solar telescope. You can also consult our guide to photographing the solar eclipse.
Observers situated within the path of annularity — a 125-mile-wide (200 kilometers) track — will experience the "ring of fire," while those just outside the path will see a partial solar eclipse, in which the moon appears to take a "bite" out of the sun — pending clear skies, of course!
If you're lucky enough to be located within the path of annularity, the entire eclipse will last about two and a half hours from start to finish. This is broken down into several eclipse stages, including about 1.5 hours of partial solar eclipse, four to five minutes of annular "ring of fire" solar eclipse and then about another 1.5 hours of partial solar eclipse, according to the eclipse guide site The Great American Eclipse.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
| Location | Local time of 'ring of fire' | Duration of 'ring of fire' |
|---|---|---|
| Oregon Dunes, Oregon | 9:15 a.m. PDT | 4 minutes, 29 seconds |
| Crater Lake National Park, Oregon | 9:17 a.m. PDT | 4 minutes, 19 seconds |
| Great Basin National Park, Nevada | 9:24 a.m. PDT | 3 minutes, 46 seconds |
| Bryce Canyon National Park, Utah | 10:27 a.m. MDT | 2 minutes, 31 seconds |
| Canyonlands National Park, Utah | 10:29 a.m. MDT | 2 minutes, 24 seconds |
| Mesa Verde National Park, Colorado | 10:31 a.m. MDT | 2 minutes, 57 seconds |
| Albuquerque, New Mexico | 10:34 a.m. MDT | 4 minutes, 42 seconds |
| Corpus Christi, Texas | 11:55 a.m. CDT | 4 minutes, 52 seconds |
| Edzná Maya archaeological site, Yucatán Peninsula, Mexico | 11:23 a.m. CST | 4 minutes, 32 seconds |
REMEMBER to NEVER look directly at the sun. You'll need to use solar filters to safely view this eclipse; whether you're going to see the "ring of fire" or a partial solar eclipse, the dangers are the same. Observers will need to wear solar eclipse glasses, and cameras, telescopes and binoculars must have solar filters placed in front of their lenses at all times. Our how to observe the sun safely guide tells you everything you need to know about safe solar observations.
This is the last solar eclipse of 2023, and scientists will be using it as a "warm up" for the upcoming total solar eclipse on April 8, 2024. A solar eclipse offers atmospheric and heliospheric scientists a unique opportunity to study the sun's outer atmosphere — the corona — during the minutes that the sun is almost completely blocked by the moon.
Related: NASA’s plans to point a 34-meter telescope at America’s two upcoming solar eclipses
The two upcoming solar eclipses have scientists particularly excited, as they are happening during a very active time in the current solar cycle — an approximately 11-year cycle of solar activity driven by the sun's magnetic field. During the current solar cycle 25, solar activity is ramping up to the predicted "solar maximum" in 2024.
If you capture a photo of the annular eclipse and would like to share it with Space.com's readers, send your photo(s), comments, and your name and location to spacephotos@space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Daisy Dobrijevic joined Space.com in February 2022 having previously worked for our sister publication All About Space magazine as a staff writer. Before joining us, Daisy completed an editorial internship with the BBC Sky at Night Magazine and worked at the National Space Centre in Leicester, U.K., where she enjoyed communicating space science to the public. In 2021, Daisy completed a PhD in plant physiology and also holds a Master's in Environmental Science, she is currently based in Nottingham, U.K. Daisy is passionate about all things space, with a penchant for solar activity and space weather. She has a strong interest in astrotourism and loves nothing more than a good northern lights chase!