Watch an asteroid eclipse the puzzling red giant star Betelgeuse tonight live online
Don't miss Orion get the cold shoulder.
A rare astronomical event will be perfectly positioned in the night sky tonight (Dec. 11) for some parts of the world.
At at 8:17 p.m. EST Monday (Dec. 11) (0117 GMT, Dec. 12), an asteroid will pass in front of the curious red star Betelgeuse, eclipsing it from our vantage point here on Earth and blocking it from view for up to 15 seconds in an event known as an occultation. The asteroid is known as 319 Leona, a main belt object that orbits the sun between Mars and Jupiter. Shaped roughly like an egg, 319 Leona measures some 50 by 34 miles (80 x 55 kilometers) in size.
Such an event occurring to a well-known and bright star is an uncommon occurrence. Astronomers are calling the event "an extraordinary and unique opportunity" to study Betelgeuse's photosphere, the star's visible layer from which it emits most of its energy.
The occultation will only be visible along a narrow path, however, that extends from central Mexico eastward across southern Florida. After the path crosses the Atlantic Ocean, the event will be visible from southern Europe and Eurasia. An interactive map of the path of visibility for the occultation can be found at OccultWatcher.net.
This means most of us won't be able to see the occultation happen due to where we are on Earth — luckily, however, the Virtual Telescope Project in Rome, Italy will host a free livestream of the event starting at 8 p.m. EDT on Monday, Dec. 11 (0100 GMT on Dec. 12).
Related: Odd supergiant star Betelgeuse is brightening up. Is it about to go supernova?
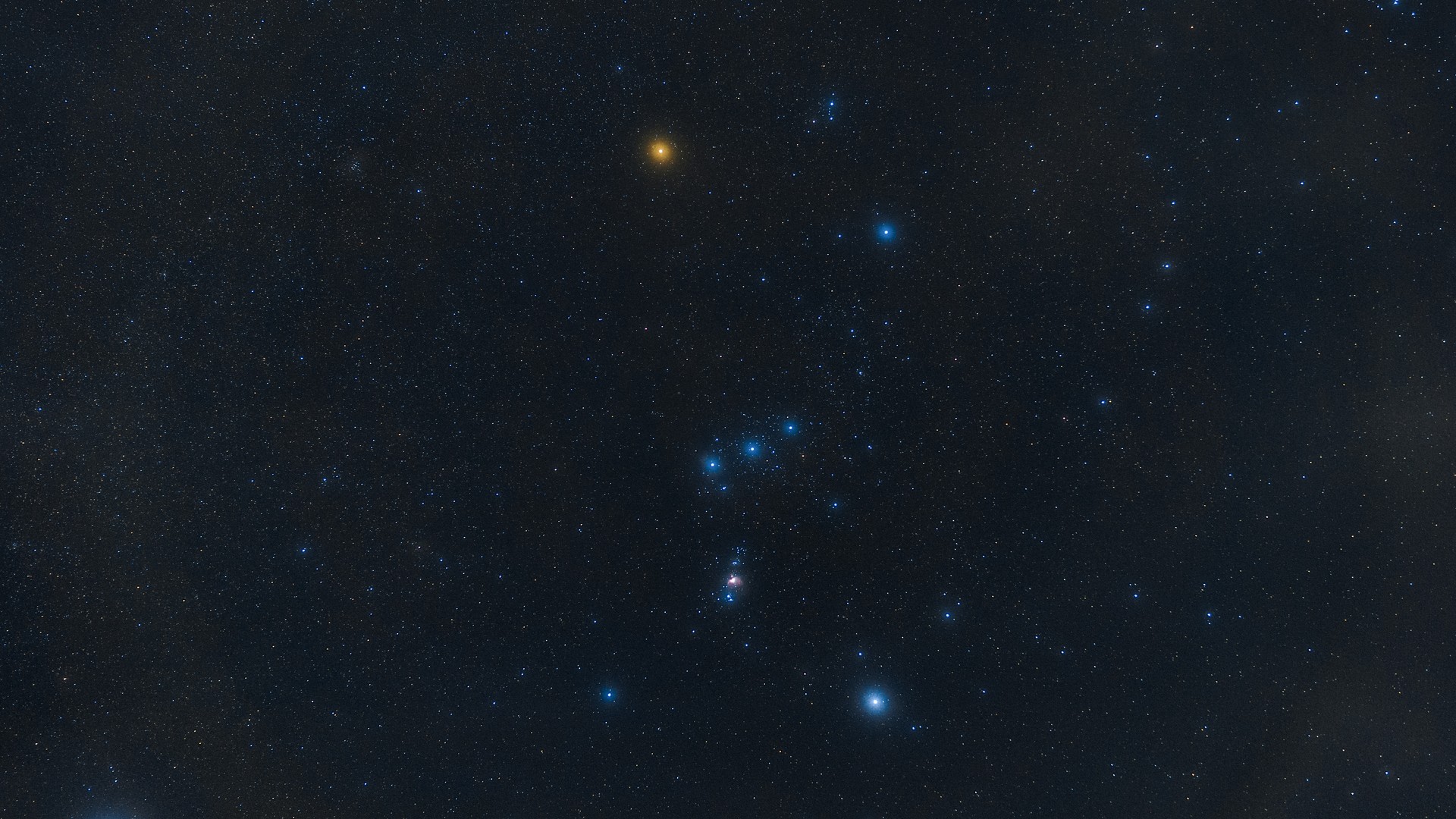

Betelgeuse is one of the largest stars known to astronomers and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. It forms the left shoulder of the Orion constellation and is distinctive for its red color.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
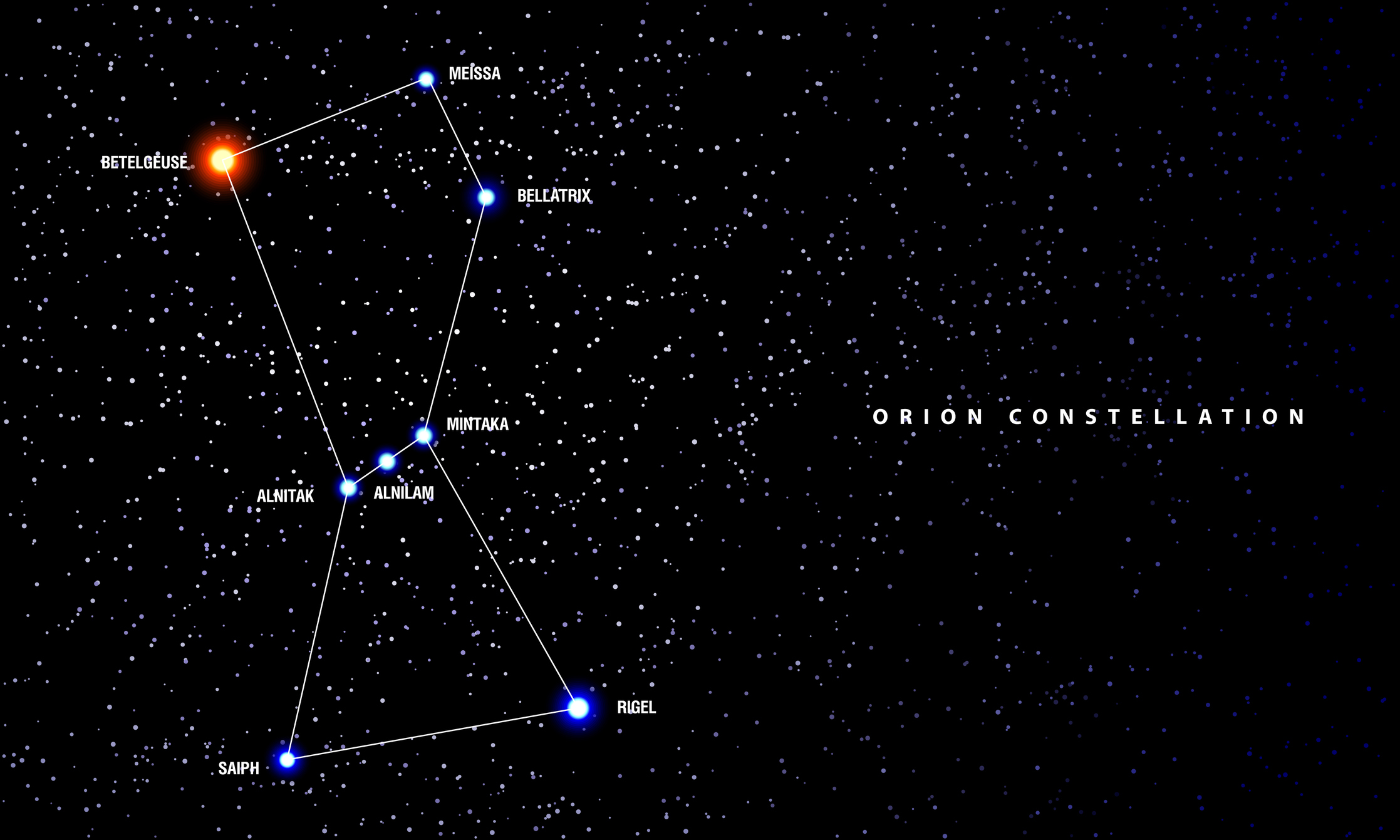
This star has been the subject of astronomers' scrutiny in recent years as it has been observed to both brighten and dim dramatically.
Some astronomers think the star could go supernova and explode in our lifetime, while others think Betelgeuse is still tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of years away from reaching that stage.
Editor's note: If you snap a great photo of the occultation of Betelgeuse by asteroid 319 Leona that you'd like to share with Space.com and our news partners for a story or image gallery, send images and comments to spacephotos@space.com.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Brett is curious about emerging aerospace technologies, alternative launch concepts, military space developments and uncrewed aircraft systems. Brett's work has appeared on Scientific American, The War Zone, Popular Science, the History Channel, Science Discovery and more. Brett has English degrees from Clemson University and the University of North Carolina at Charlotte. In his free time, Brett enjoys skywatching throughout the dark skies of the Appalachian mountains.









