The greatest astronomical discoveries of the past 25 years
From finding the long-sought "God particle," gravitational waves and missing neutrinos from the sun to getting the first real clue for elusive dark energy, here's a look back at the greatest discoveries in astronomy in the past 25 years.

- 1999: Planetary system
- 2001: 1st free-floating planet
- 2001: First exo-asteroid belt
- 2001: Sun's missing neutrinos
- 2001: 1st exoplanet with atmosphere
- 2007: Fast radio bursts
- 2012: Higgs boson
- 2016: Gravitational waves
- 2017: 1st interstellar visitor
- 2019: Supermassive black hole photo
- 2020: Milky Way map
- 2024: "Empty" galaxies
- 2024: Dark energy
- 2024: JWST reveals early universe
This summer, Space.com is celebrating its 25th anniversary! To mark the occasion, here's a look back at the past 25 years of discoveries in astronomy. These are findings that have been absolutely revolutionary for exoplanetary research, cosmology and astrophysics.
Astronomy as a field aims to answer big-yet-fundamental questions about our place in the universe, so it is perhaps most apt to start this list with a bombshell discovery 25 years ago, on April 15, 1999, when astronomers found the first planetary system outside our own.
In the past 25 years, astronomers also discovered hundreds of free-floating worlds that challenge the definition of a planet, the long-sought "God particle," "ripples" in the fabric of spacetime, the sun's missing neutrinos, the first real clue about the nature of dark energy, and a lot more. Here are the most amazing astronomical discoveries of the past quarter century
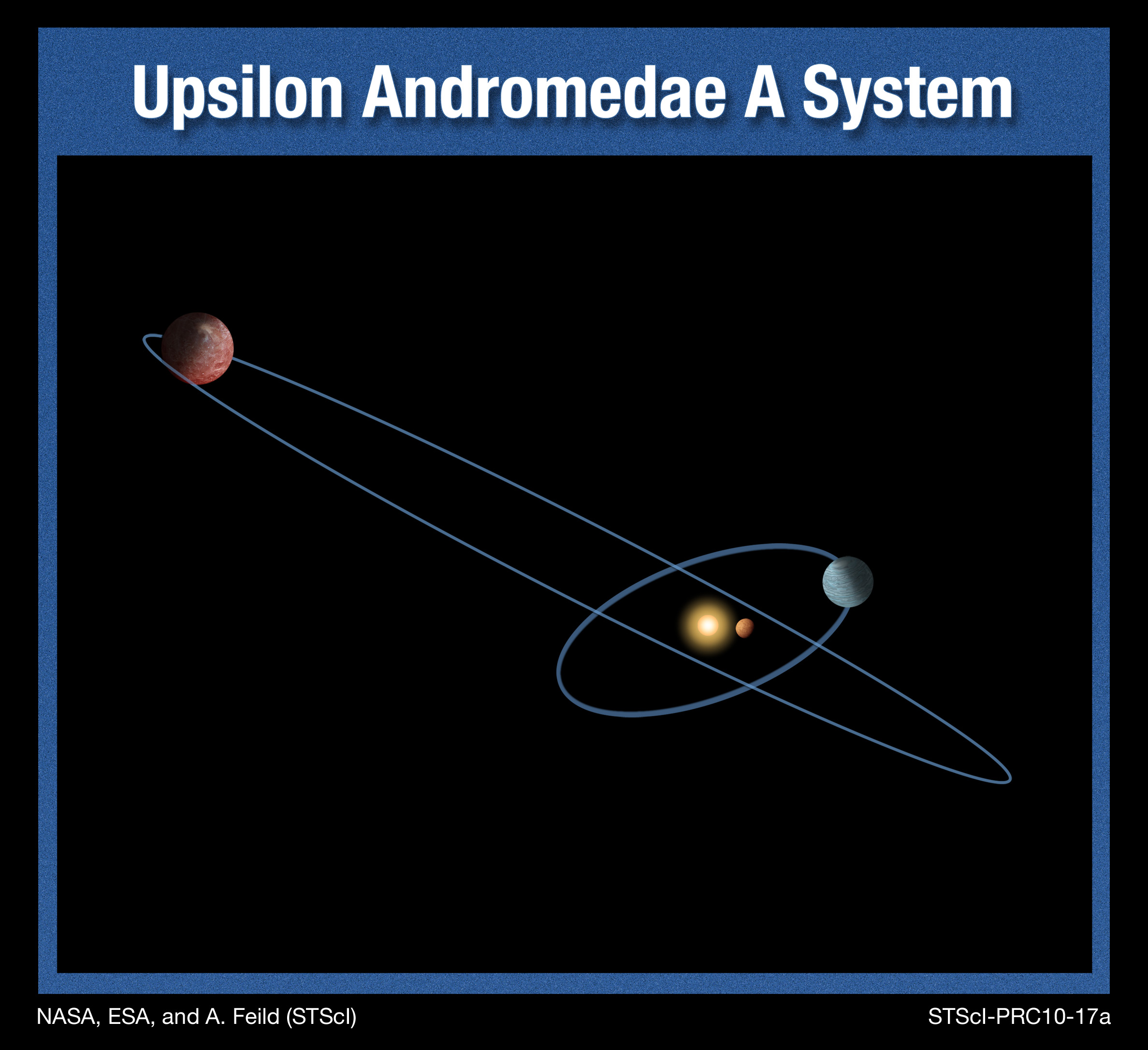
1999: Astronomers discover a planetary system outside our own
Check out a list of Space.com's special 25th anniversary week stories in our hub linked here!
In April 1999, astronomers found a trio of Jupiter-size planets circling the sun-like, yellow-white star Upsilon Andromedae A, located roughly 44 light-years from Earth — the first extraplanetary system ever to be discovered.
The discovery disproved the notion that our solar system was a singular phenomenon in the universe and offered compelling evidence that the discovery of other planetary systems was only a matter of time and technology. In 2010, astronomers also found that unlike the planets in our solar system, the Jupiter-size planets in this extrasolar system do not orbit in the same plane. Rather, two are inclined by 30 degrees with respect to each other — the first such orientation ever spotted — which helps astronomers refine theories of planetary formation and evolution.
As of April 2024, astronomers have found close to 900 stars that host two or more planets.
2001: First free-floating planet detected in the Milky Way challenges the traditional definition of a planet
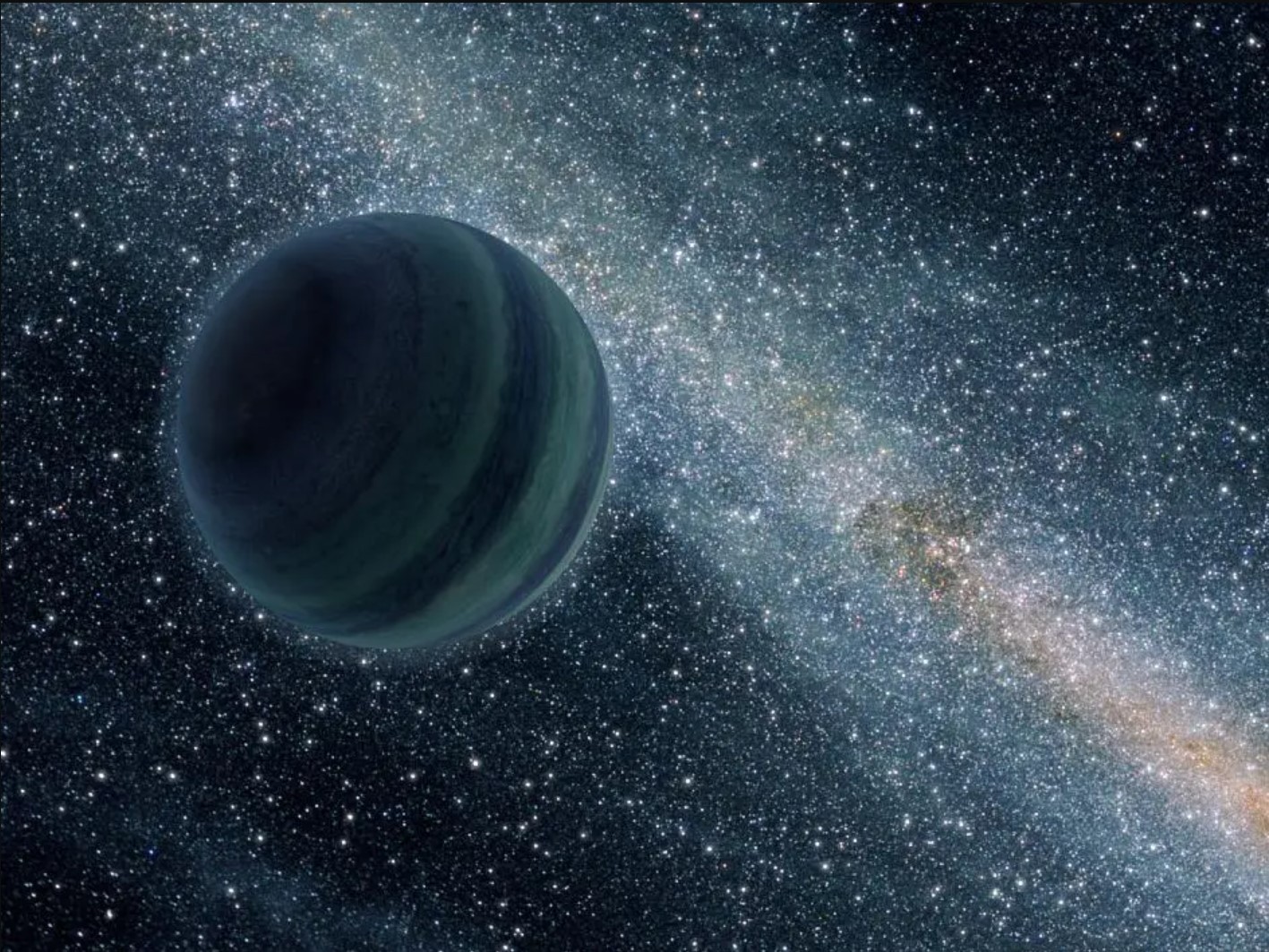

At the turn of the 21st century, astronomers detected the first free-floating planet hovering by itself in the nearby Trapezium Cluster, a stellar nursery near the heart of the Orion Nebula.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
In our galaxy alone, there may be as many as a quadrillion of these "rogue planets," which are kicked out of the star-circling disks of gas and dust in which they are born. Only a handful have been found cruising through our galaxy, however; because they are ultra faint, they are difficult to spot. The orphaned planets are the lightest products of a star's birth and important carriers of information about the environments where they formed.
2001: First exo-asteroid belt found around a nearby, sunlike star
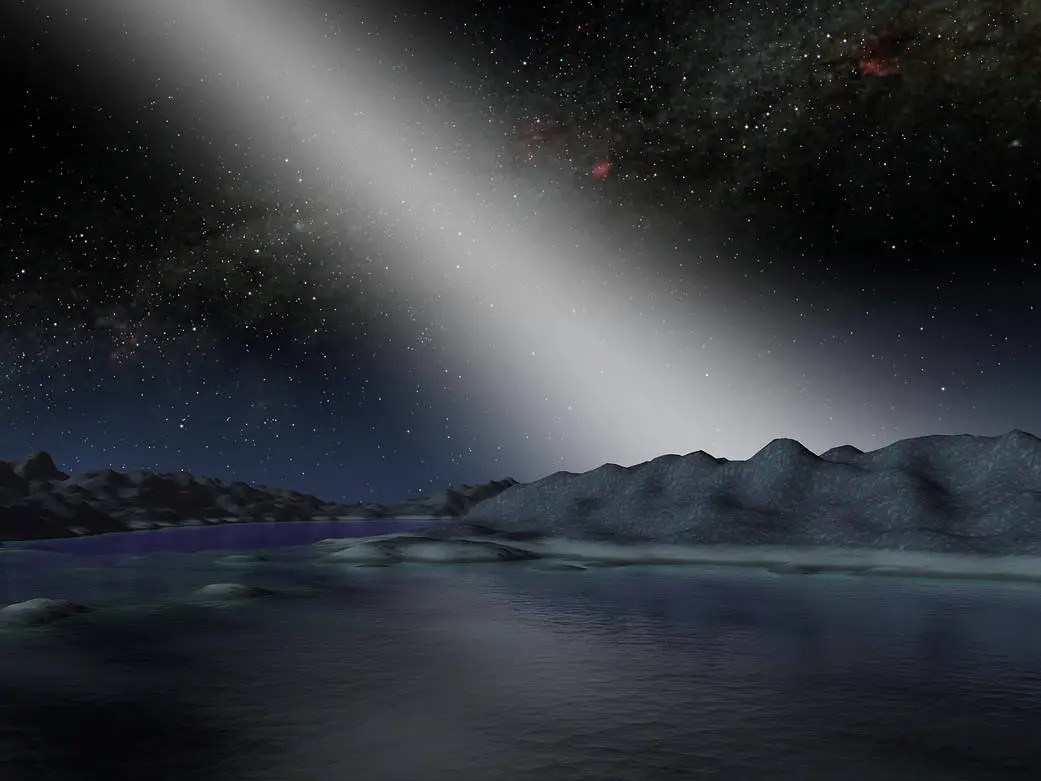

In early 2001, NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope found evidence of the first asteroid belt outside the solar system around the nearby, sunlike star HD 69830, located roughly 40 light-years away, in the constellation Puppis. The belt is estimated to be 25 times more massive than the main asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. In 2005, astronomers discovered three Neptune-like planets orbiting this star, with the outermost planet possibly within the star's habitable zone.
Astronomers are interested in the size and location of asteroid belts in multiplanetary systems, as the rocky shards influence the coalescence of planets and even the emergence of life. In our own pocket of the cosmos, a leading theory posits that asteroids delivered water and organic compounds to early Earth, which is supported by recent detections of water molecules in asteroid samples returned to Earth as well as a couple in space.
2001: Mystery of sun's missing neutrinos solved after 30 years
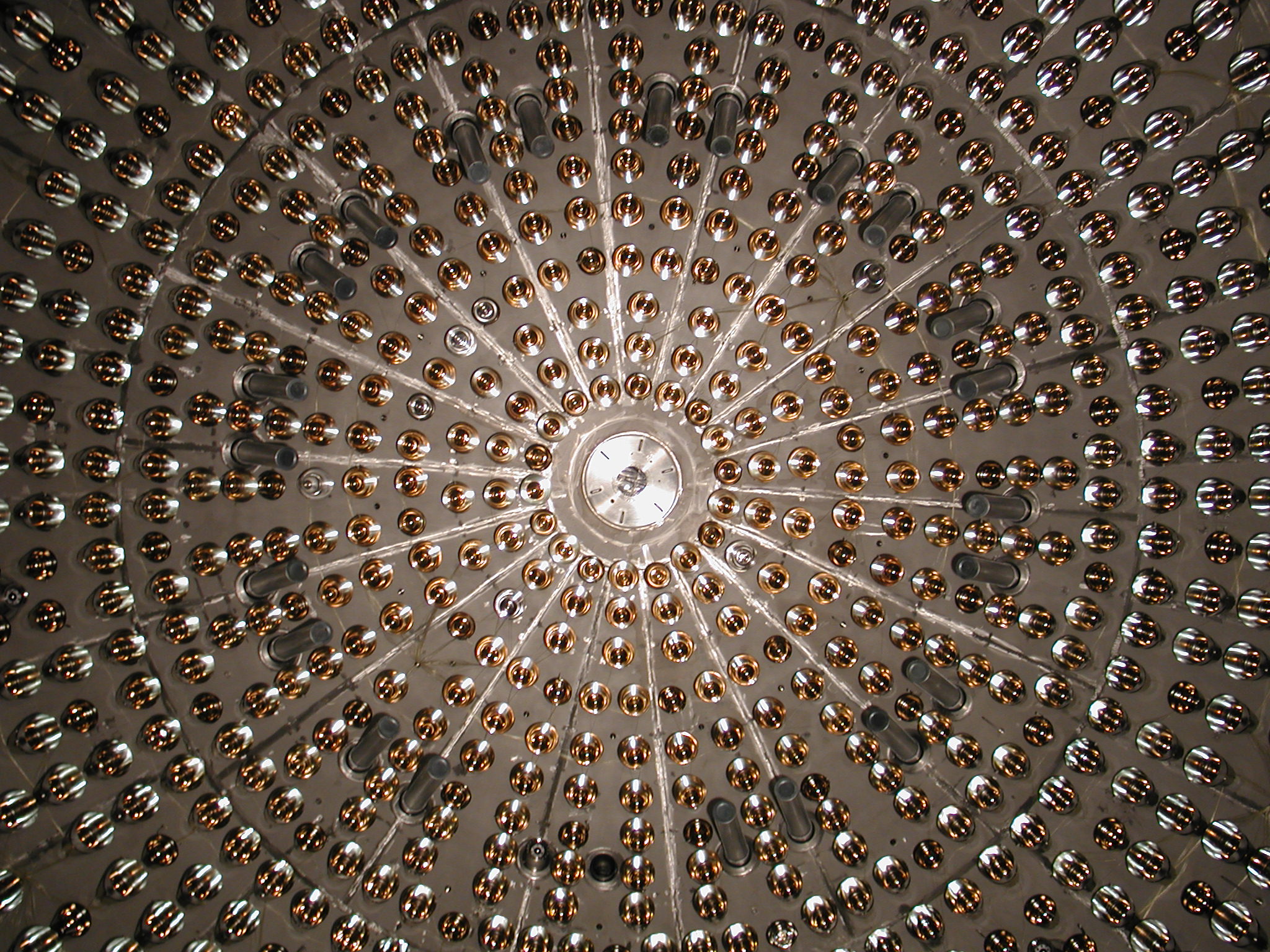
In June 2001, physicists announced that they had found the sun's missing neutrinos — subatomic particles that have no charge and practically no mass. The detection ended a three-decade-long search for the tiny packets of energy but implied they must have a bit of mass.
Nuclear reactions at the sun's heart — the same process by which the sun shines — produce billions of neutrinos, half of which were estimated to make the 93-million-mile (150 million kilometers) journey to Earth. Yet experiments during the late 1960s detected too few of the ghostly particles — a discrepancy that came to be known as the solar neutrino problem.
In 2001, experiments from the Sudbury Neutrino Observatory in Canada revealed that the "missing" neutrinos had, in fact, merely transformed into two other types of neutrinos on their way to Earth and escaped detection. This transformation demands that the ubiquitous neutrinos possess some mass, now estimated to be hundreds of thousands of times less than the mass of the next-lightest particle, the electron.
2001: First exoplanet blanketed by an atmosphere widens exoplanet science
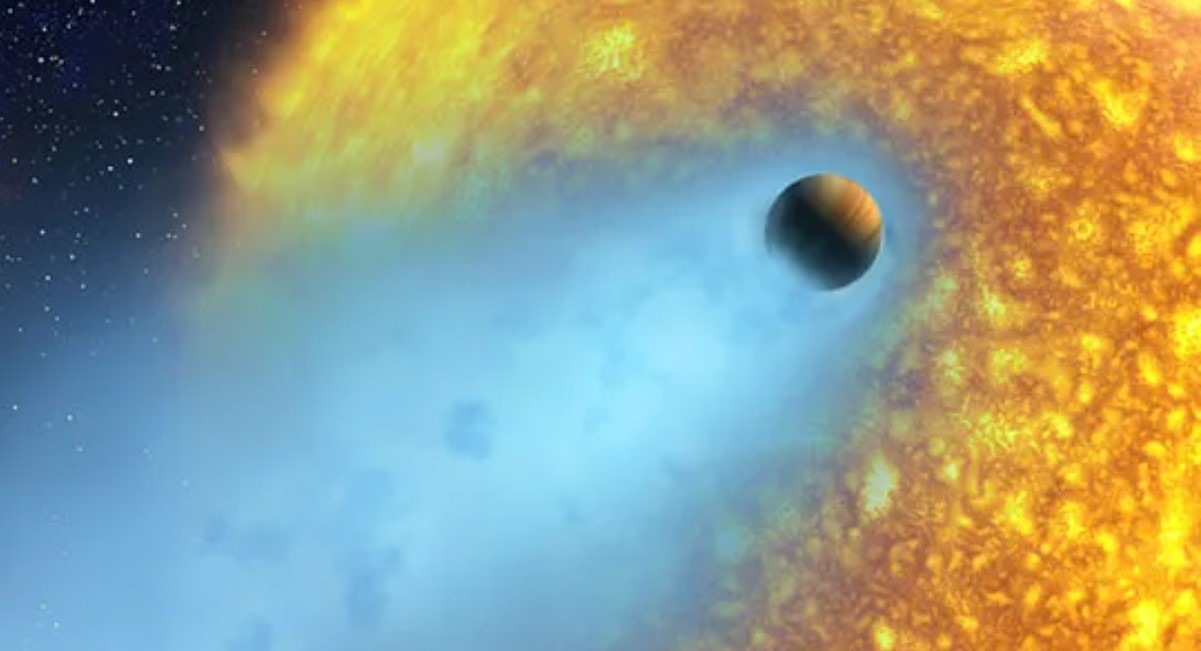

In November 2001, astronomers entered a new phase of exoplanetary science when data from the Hubble Space Telescope revealed for the first time the presence of an atmosphere blanketing an alien world. The exoplanet, HD 209458b, is located 150 light-years away, in the constellation Pegasus. It was the first of many exoplanets now known to host atmospheres ranging from vanishingly thin to very dense, like Jupiter's.
The discovery sparked a new era in exoplanet exploration, as astronomers could begin to compare exoplanets' atmospheres, including the abundances of atmospheric gases known to emerge from life on Earth.
2007: Fast radio bursts reveal the universe's missing mass
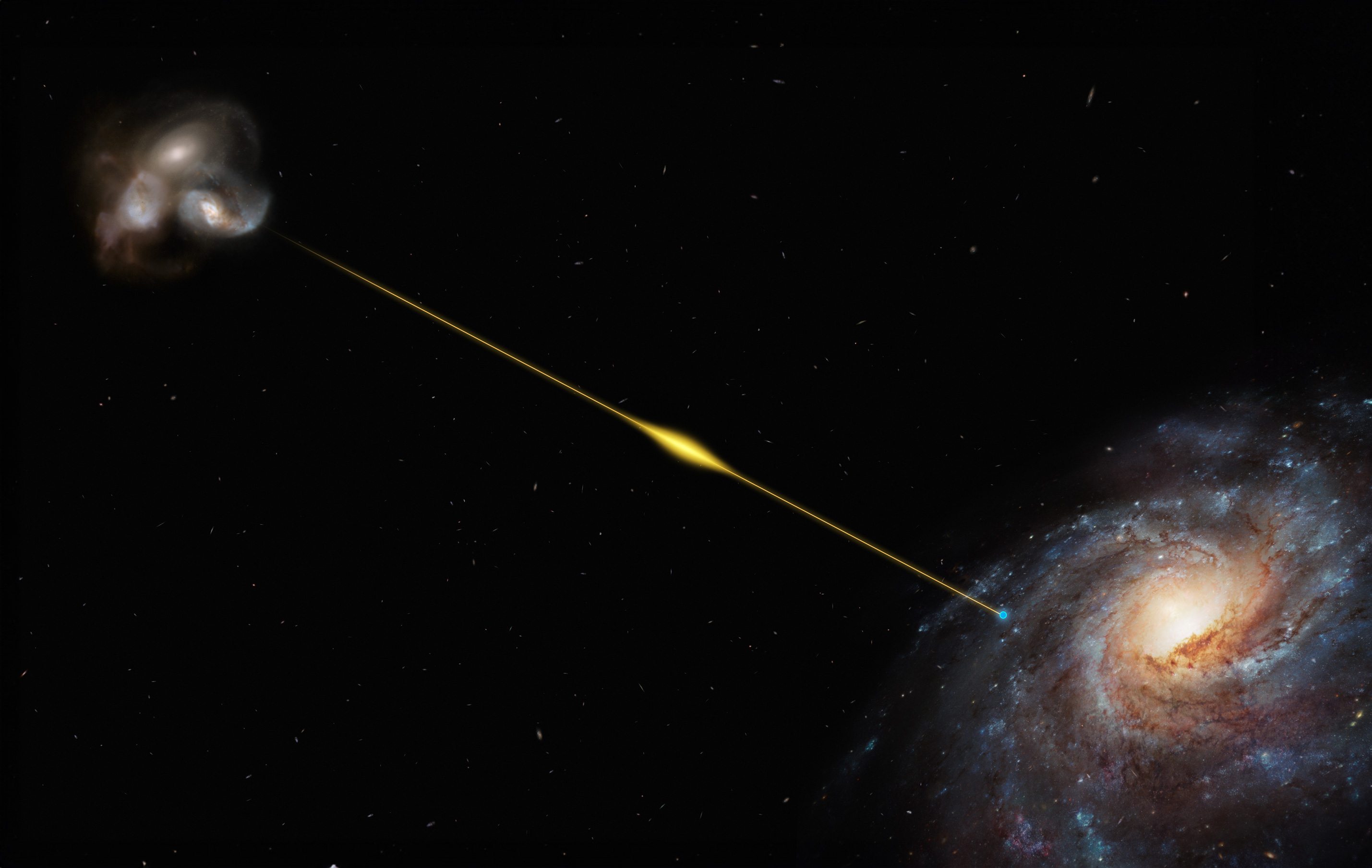

In 2007, astronomers using the Parkes Observatory in Australia discovered a fast radio burst (FRB) — a bright, incredibly short burst of radio waves — from a galaxy billions of light-years from Earth. In just milliseconds, the intensely bright pulse, named Lorimer Burst FRB 010724, blasted into space as much energy as the sun does in 80 years. Since then, hundreds of such intensely bright pulses have been detected from faraway galaxies scattered across the universe, including a few that seem to erupt repeatedly and irregularly.
Astronomers have used the intense pulses to find some of the universe's missing matter, which lurks in spaces between galaxies and was detected by studying the dispersion of radio waves from FRBs as they traveled through interstellar gas.
2012: Discovery of the Higgs boson, the "God particle"

In July 2012, the field of particle physics captured the global spotlight with the discovery of the Higgs boson, a long-sought subatomic particle that pervades the universe as a field that gives other elementary particles their masses. The existence of the Higgs boson was first predicted independently by physicists Peter Ware Higgs and François Englert in 1964, close to half a century before it was found by two experiments at the Large Hadron Collider in Switzerland, which detected the "God particle" within just two years of beginning operations.
Higgs and Englert received the 2013 Nobel Prize in physics for their theory of how particles acquire mass.
2016: Detection of gravitational waves confirms Einstein's theory, opens a new way to view the universe

In February 2016, scientists using the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory announced that, in September 2015, they had detected gravitational waves — faint ripples in space-time predicted by Einstein a century ago — for the first time when those that emerged from colliding black holes washed over Earth.
Because these waves traveled unscathed through sizzling matter of the early universe, their detection heralded a new way of studying the universe that was never possible with electromagnetic waves. Three astrophysicists who helped detect the gravitational waves — Rainer Weiss, Barry Barish and Kip Thorne — won the Nobel Prize in physics in 2017 for their work.
Another new era in gravitational wave astronomy began in June 2023, when scientists with the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves (NANOGrav) collaboration revealed compelling evidence for the presence of a faint-but-persistent hum of gravitational waves pervading the universe. They strongly suspect the hum — which, at one-billionth of 1 hertz, was a few hundred times fainter than the gravitational waves detected in 2015 — represents a collective echo of supermassive black hole pairs circling each other in orbits that shrink across millions of years.
2017: First interstellar visitor spotted in our solar system
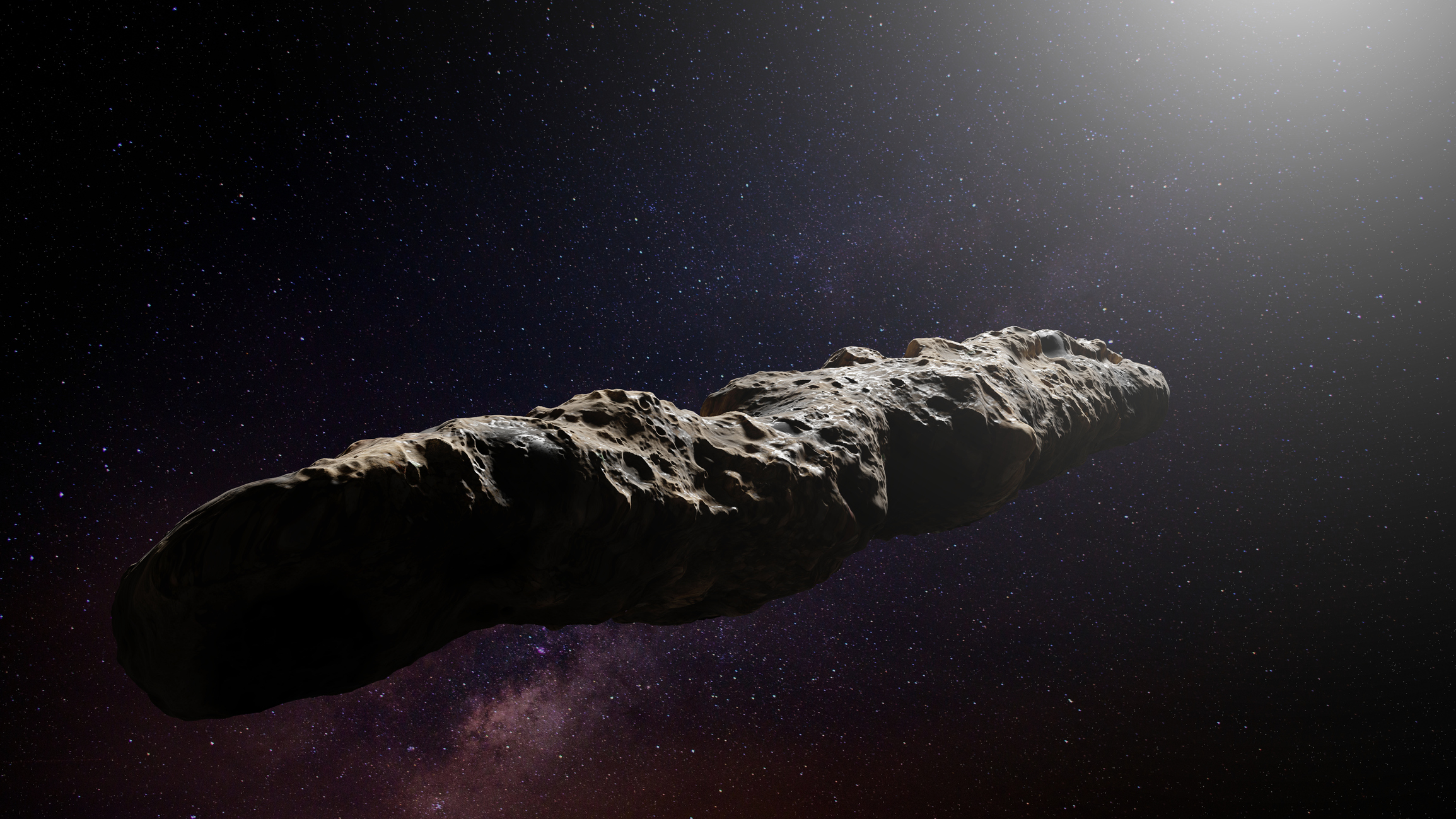

In fall 2017, astronomers spotted a strange object zipping through our solar system — the first known interstellar visitor. The identity of the object, dubbed 'Oumuamua, was shrouded in mystery because its brightness varied more than what would be expected from an asteroid and it didn't act like a comet.
As such, it sparked arguments, with some speculating that it might be an alien artifact. First considered an asteroid, 'Oumuamua was recast as a comet in 2023, with one group of astronomers suggesting it was likely ejected from an extrasolar planetary system and accelerated by tiny amounts of hydrogen gas emerging from the object's icy heart.
In 2019, astronomers found the second interstellar visitor, Borisov, which was soon confirmed to be a comet, thanks to its telltale gaseous coma. The rogue object, which never passed near a star until visiting the sun, is considered the most pristine comet ever studied.
2019: Astronomers photograph a supermassive black hole
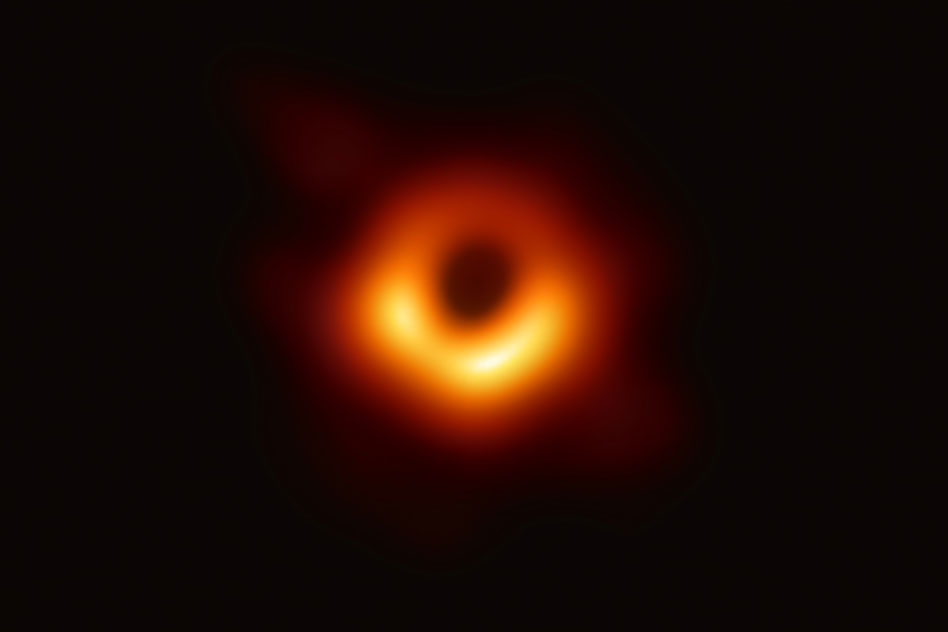

In 2019, astronomers photographed a black hole for the first time. The Event Horizon Telescope project imaged the contours of the monster black hole lurking at the heart of the Messier 87 galaxy, which is located over 50 million light-years from Earth. The image opened up a new way to study black holes and was likened to the first illustrations of what insects and plants look like through a microscope.
In 2021, astronomers unveiled a new image of the object that shed light on how magnetic fields behave close to black holes. In 2023, the black hole image got an AI makeover, which turned the "fuzzy orange doughnut" into a skinny ring. Astronomers also found that the black hole is spinning, although the rate of spin remains unclear.
2020: Milky Way gets the most detailed map ever
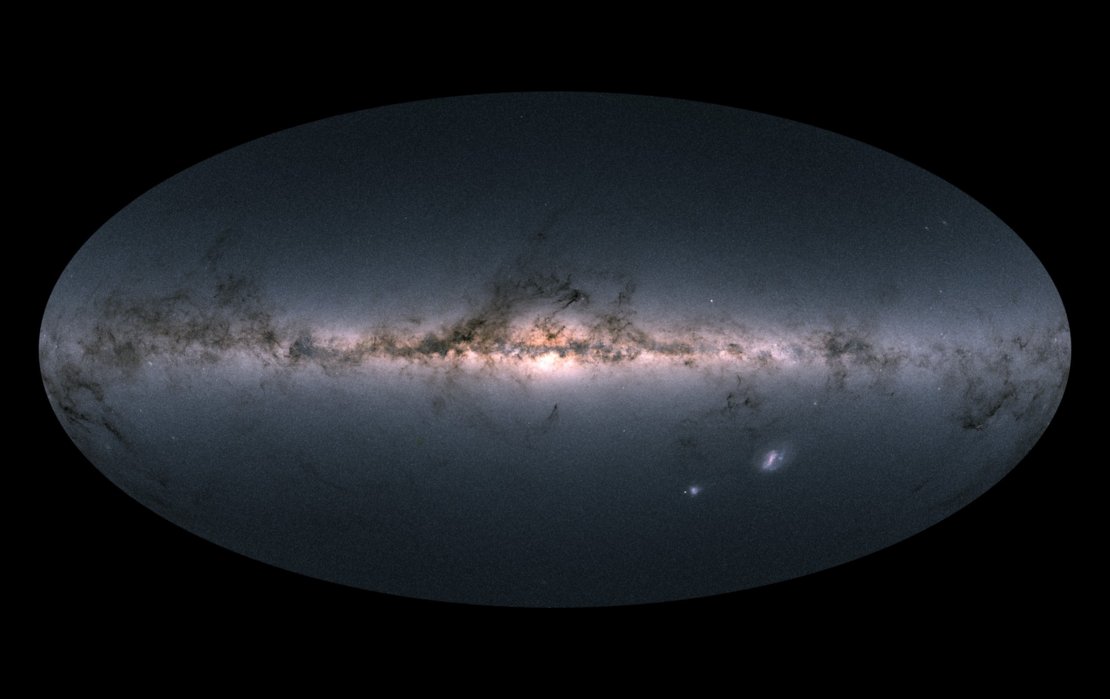

The most detailed map ever of the Milky Way plotted in 3D nearly 1.8 billion stars in unprecedented detail using data from the European Space Agency's Gaia spacecraft. As mind-boggling as the 1.8 billion stars may be, they represent just over 1 percent of our entire galaxy's stars. Astronomers say studying the motions of these plotted stars could reveal long-sought clues about the nature of dark matter.
2024: Starless, "empty" galaxies begin coming into view
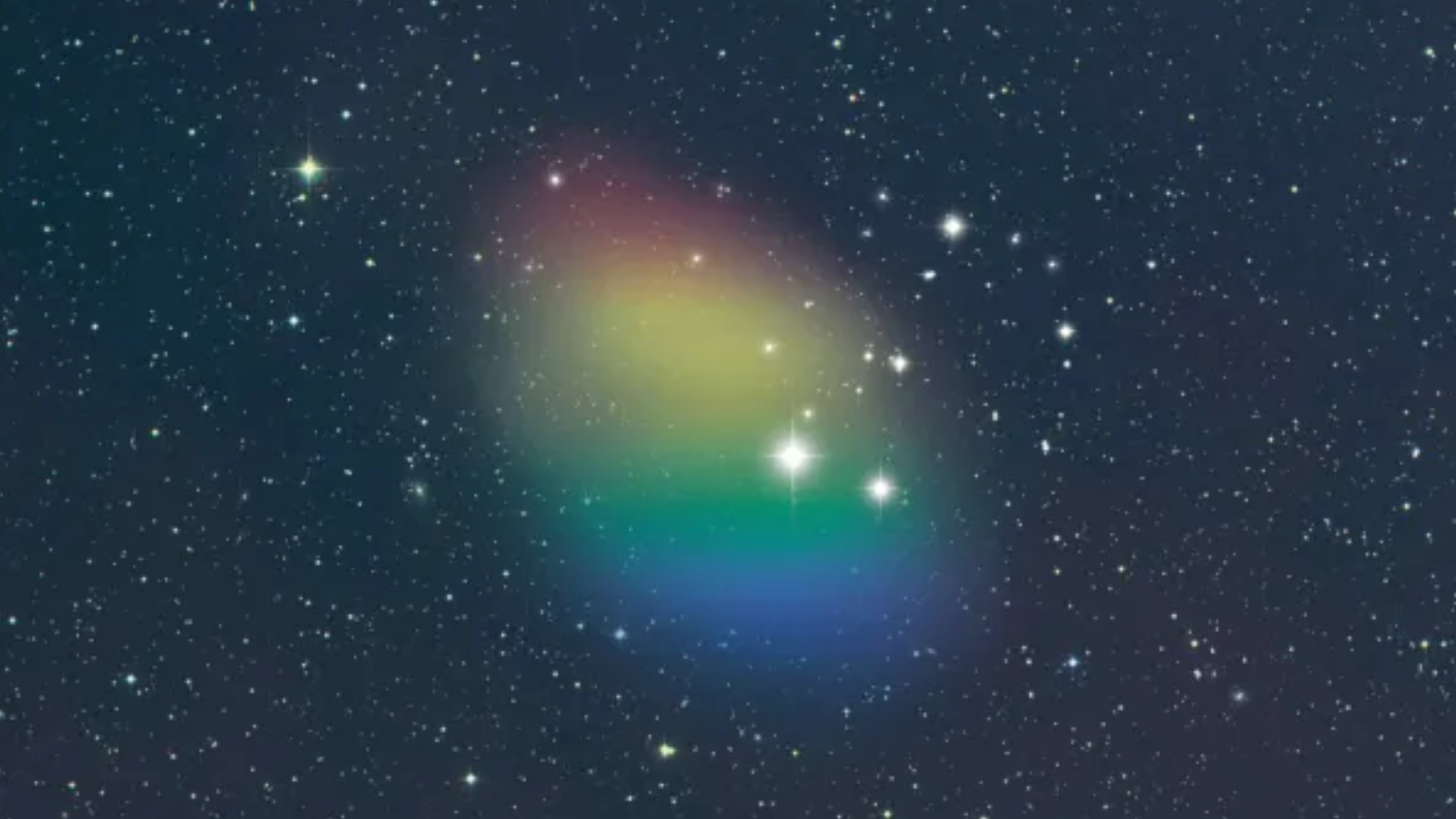

In January 2024, astronomers announced that they had spotted a primordial galaxy that is so diffuse that it hasn't formed stars. The discovery challenges leading theories of how galaxies form and evolve and even the conventional definition of a galaxy. After all, what is a galaxy without stars?
The same week, a different team reported the discovery of another almost-empty galaxy called Nube, which is Spanish for "cloud." Unlike our galaxy's central bulge, Nube is puzzlingly uniform and intriguingly isolated roughly 300 million light-years from Earth; its closest large neighbor is at least 1.4 million light-years away.
Such "dark" galaxies, which were once thought to outnumber all visible galaxies, shine hundreds of times fainter than the Milky Way, whose light is powered by roughly 100 billion stars. Astronomers continue to puzzle over why these "ghost" galaxies lack stars even though they contain pristine star-forming gas.
2024: Dark energy may be evolving
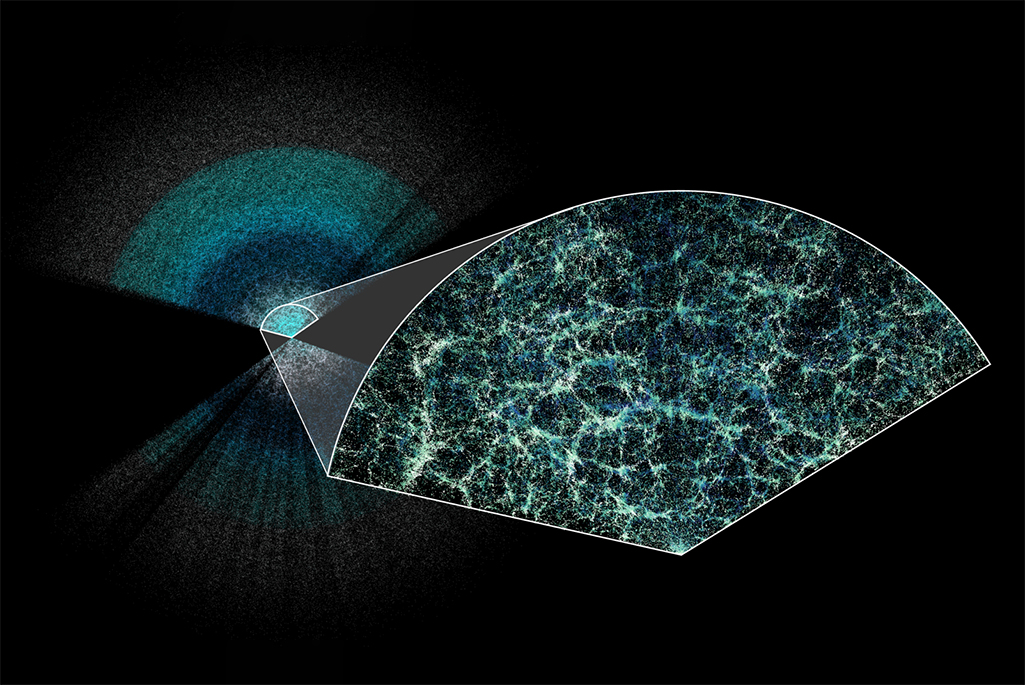
Physicists have long considered dark energy — the mysterious force driving the accelerated expansion of the universe — a "cosmological constant," meaning it remains constant throughout the history of the universe.
In April 2024, however, astronomers who created the largest 3D map of the universe suggested that dark energy may be evolving with time. The discovery might be the first real clue about the elusive phenomenon in the past two decades and one that "would be as revolutionary as the discovery of the accelerated expansion of the universe itself, if confirmed with future data," scientists said at the time.
2024: Dwarf galaxies flooded the early universe with its first light, JWST reveals
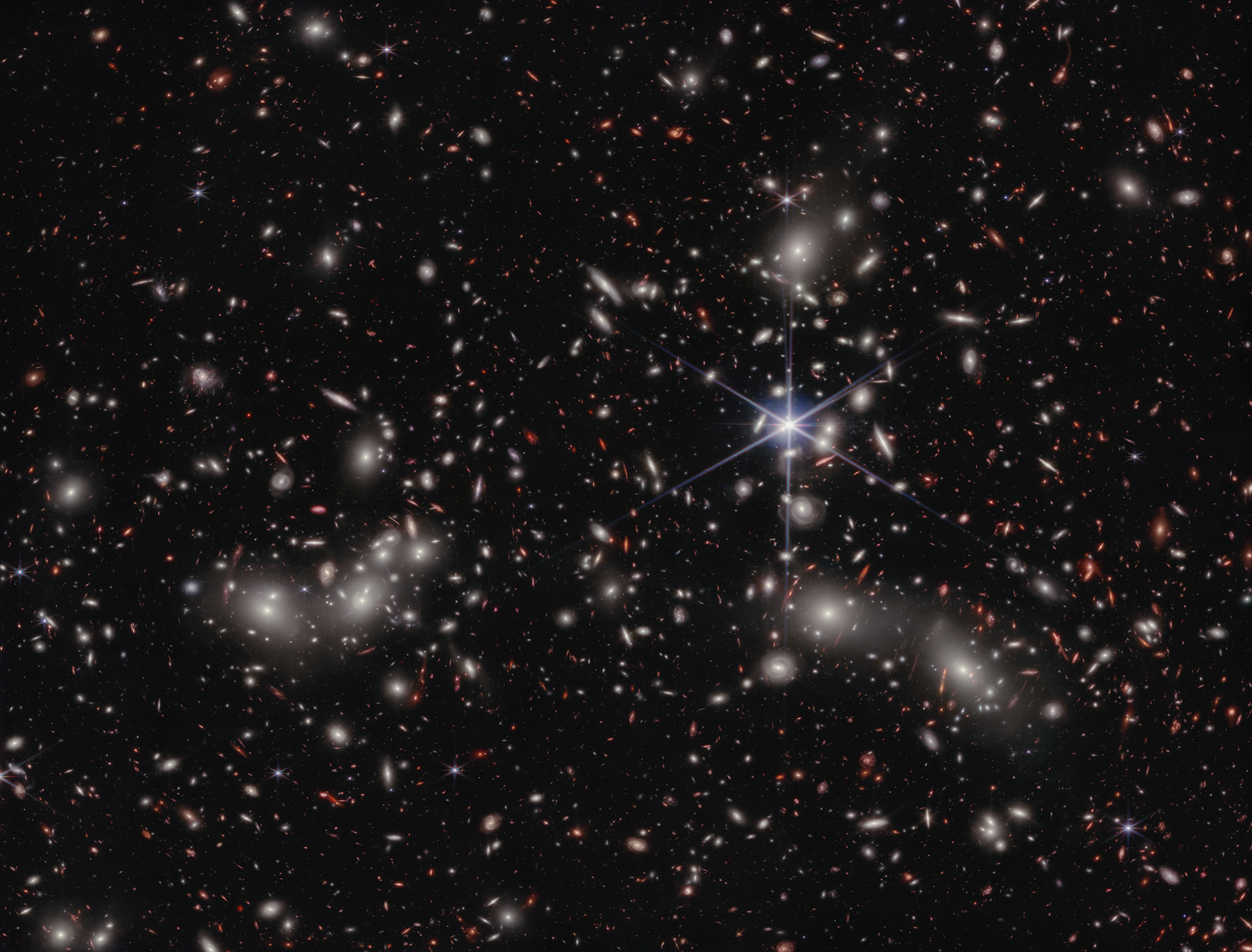

Astronomers have long wondered just how the universe resurfaced from the cosmic dark ages, when the cosmos was cloaked in dense fog of neutral hydrogen gas, to make way for the first starlight. In early 2024, astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) revealed dwarf galaxies that existed in the first few hundred million years packed enough punch to flood the early universe with its first light. The discovery is a remarkable testament to the telescope's unprecedented infrared capabilities that allow it to collect light from the faintest objects.
JWST's amazing discoveries and breathtaking views have stunned the world since the observatory began operations in 2022. For instance, the telescope captured the "Pillars of Creation," revealing in stunning detail both the colorful tapestry of the dusty cloud formation and the cosmic processes occurring in the region. As astronomer Derek Ward-Thompson put it, the image can be likened to "taking the X-ray of a human."
JWST continues to awe astronomers and the public alike with its detailed images of the most distant galaxies in the universe, faraway supermassive black holes, exoplanets and more.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Sharmila Kuthunur is a Seattle-based science journalist focusing on astronomy and space exploration. Her work has also appeared in Scientific American, Astronomy and Live Science, among other publications. She has earned a master's degree in journalism from Northeastern University in Boston. Follow her on BlueSky @skuthunur.bsky.social
-
Torbjorn Larsson The "dark energy evolves over time suggestion" is statistically indistinguishable from a constant dark energy.Reply
An interesting development is that astrophysicists may have found how supermassive black holes form and grow quickly to dominate early galaxies, a trend which has recently been discovered. It is a robust formation from star massed black hole seeds in sufficiently dense early gas clouds. The holes sink to the middle and gather weak magnetic fields to a torus dominated "flux frozen" in accretion mechanism. The magnetic fields dominates thermal effects and the accretion can grow stably super-Eddington - something which traditionally have been "forbidden".
The papers even suggest that the result looks like the mysterious "little red dots" that Webb recently found.
https://aasnova.org/2024/07/19/a-new-way-to-grow-a-supermassive-black-hole/https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ad5a95 -
Classical Motion It was I, Classical Motion that made the most important of all discoveries for the last century.Reply
And that discovery is that light is not a wave, but an intermittence with a duty cycle. I found this by feeding a precision full wave rectified carrier into the feedpoint of an antenna. Which allowed me to emit one photon at a time. With an 180 degree input.
This disproved current light theory and presented a new type of shift for starlight. This will also increase our light measurements 100 fold.
And as a side note, the shifts of our shifts has not changed in a hundred years. So if this universe is expanding, it’s expanding at a constant rate. Not an accelerating rate.
This is new and the only reference is me. But if you are familiar with radio my claim is easy to verify.
Patent pending. I’m going to license light.
Pay now at a reduce subscription rate or pay later by the photon.









