Blue Moon lunar lander: Facts about Jeff Bezos' spacecraft
This lunar lander wasn't selected for the Artemis mission, but is designed for future moon missions.
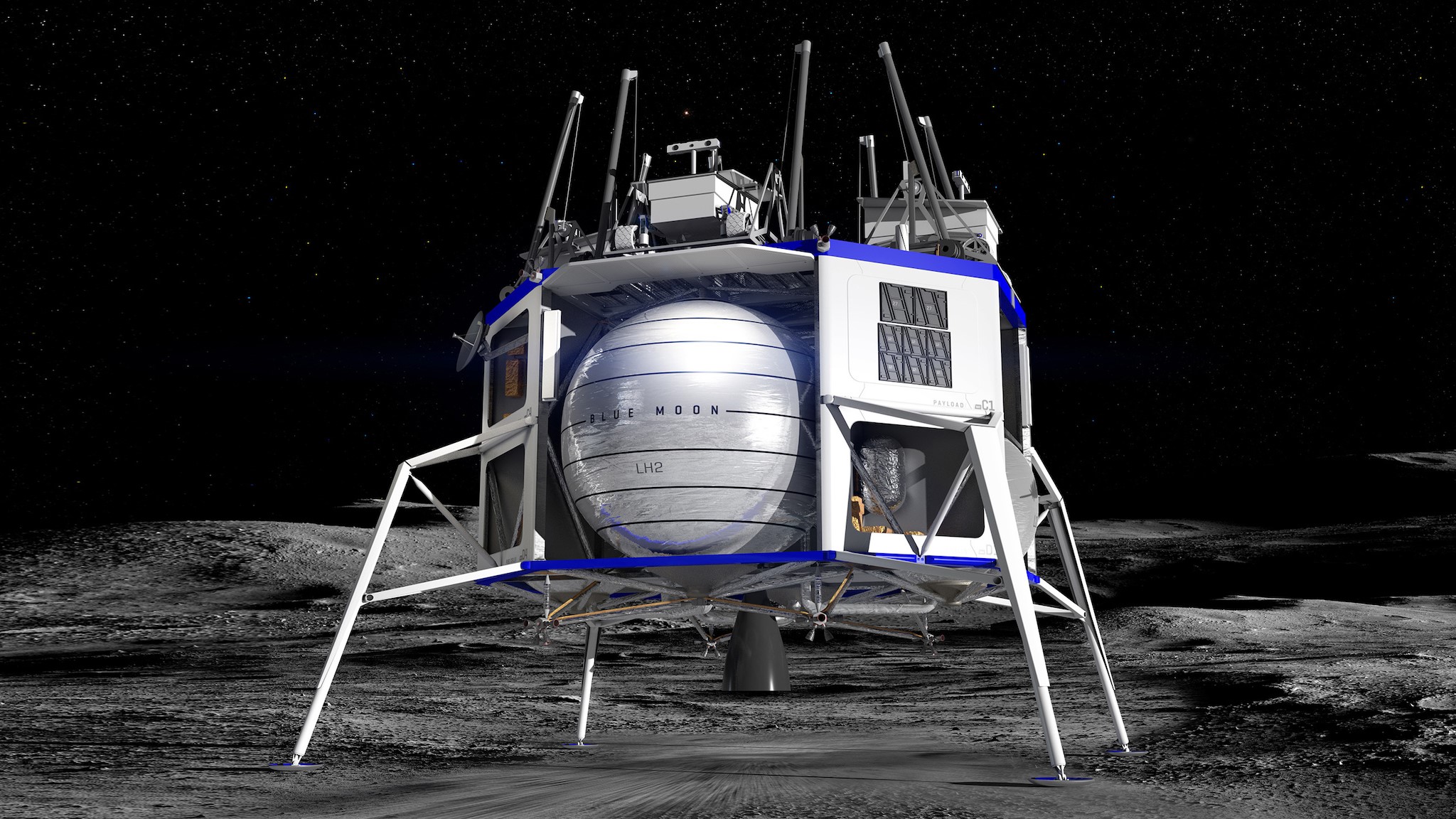

Since the Apollo lunar lander first delivered humans to the moon, just 12 astronauts have walked on the lunar surface. While nobody has set foot on its surface since 1972, plans are in place to return people to the moon. Some people, including American Entrepreneur Jeff Bezos, are envisaging steps much further ahead– creating a human colony on the moon.
In order to increase our knowledge of the moon and carry out experiments on its surface, people and machinery need to be delivered there by lunar landers. One of these currently being developed is the Blue Moon lander, created by the privately funded aerospace manufacturer, Blue Origin. The company, which also focuses on space tourism, is owned by Jeff Bezos. The Blue Moon wasn't selected for NASA's Artemis missions, but Blue Origin hopes to use the moon lander in future missions and achieve sustained human presence in space, according to their website.
Related: Blue Origin loses federal lawsuit over NASA moon lander contract
Lunar lander technology
The Blue Moon lander, which began development work in 2016, uses autonomous technology to land with precision. Equipped with LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors, Blue Origin claims that it is guaranteed to land within 23 metres of the pre-planned landing spot. To scan the moon, laser beams are fired at its surface to create a computerized image of the terrain. This prevents the lander from descending onto hazards and allows the flattest nearby surface to be chosen.
When in lunar orbit, the lander can release micro-satellites into space. Then, once on the moon, the lander will release other apparatus such as rovers from its top deck. The equipment that is attached to the lander can be altered based on specific missions. For those requiring human presence — and to return equipment and lunar samples to Earth — an ascent module can be added. This launches from the lunar lander to travel back to Earth.
Blue Moon anatomy
Refuelling in space
The Blue Moon lander uses liquid hydrogen as fuel. This propellant was chosen with future possibilities in mind. Scientists now know that there is water ice on the moon, from which hydrogen can be extracted. By choosing these elements to power the lander, Bezos hopes that one day the spacecraft can be refuelled in space, using the moon's resources. When separating water into its elements, oxygen is also released which can be used in breathing apparatus.
Additional resources
You can keep up with the latest news from Blue Origin on their website and if you want to learn more about the Blue Moon lunar lander check out this informative video from Blue Origin. Want to know more about why we are going back to the moon? NASA explains with this article on the Artemis mission.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Ailsa is a staff writer for How It Works magazine, where she writes science, technology, space, history and environment features. Based in the U.K., she graduated from the University of Stirling with a BA (Hons) journalism degree. Previously, Ailsa has written for Cardiff Times magazine, Psychology Now and numerous science bookazines.