Greenland ice sheets are weaker to climate change than we thought
'It's really the first bulletproof evidence that much of the Greenland ice sheet vanished when it got warm.'
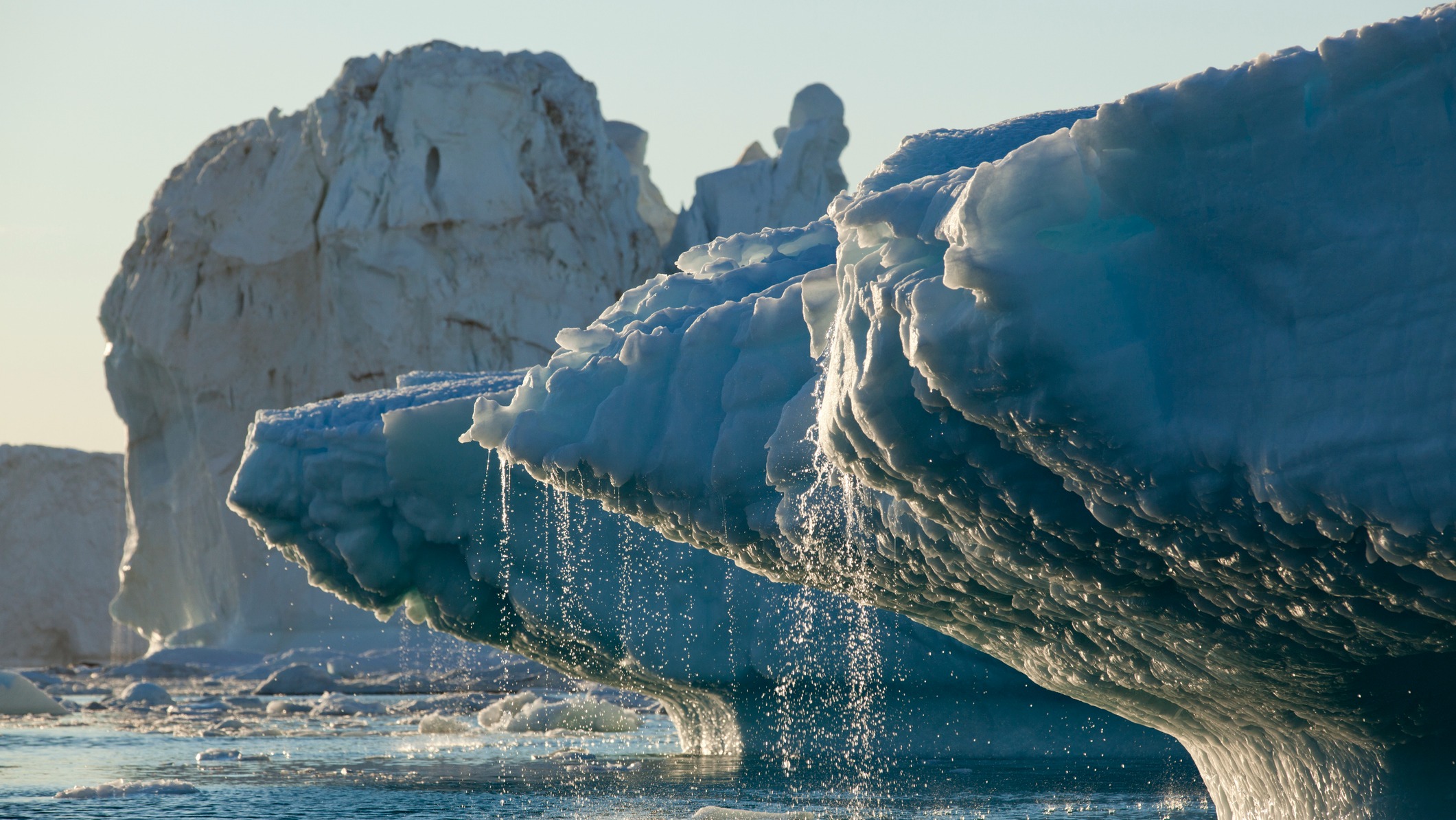

The ice sheets of Greenland are melting, and it could be worse than we thought.
A new study suggests the ice sheets could be much more sensitive to human-driven climate change than previously estimated. Understanding the geological past of Greenland is vital for predicting sea-level rise, as a result of global warming. That's because its ice holds enough water to cause 23 feet (7 meters) of sea-level rise, which is a risk to every coastal region on Earth, the authors state.
Greenland's ice sheet is about 2 miles (3.2 km) thick and spans an area three times the size of Texas. And it's already shrunk in the ancient past. Between 374,000 years and 424,000 years ago, moderate warming caused the ice sheet to melt, leading to a dramatic sea-level rise of around five feet, the study shows.
Related: Earth is getting hotter at a faster rate despite pledges of government action
The new study contradicts previous estimates that the Greenland ice sheet has persisted for most of the last 2.5 million years. The melting of some of Greenland's ice around 416,000 years ago left behind an ice-free tundra landscape that may have been covered by trees and roaming woolly mammoths.
The melting also took place despite carbon dioxide levels in Earth's atmosphere being lower at the time than today: just 280 parts per million (ppm), as opposed to 420 ppm (and rising) in modern times. (Carbon, a greenhouse gas that traps heat easily in Earth's atmosphere, is one of the drivers of global warming.)
The findings were reached by a team of scientists from various institutions, including the University of Vermont and Utah State University, who studied sediment from a long-lost ice core drilled from the Greenland ice sheet.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"It's really the first bulletproof evidence that much of the Greenland ice sheet vanished when it got warm," research co-leader and University of Vermont scientist Paul Bierman said in a statement.
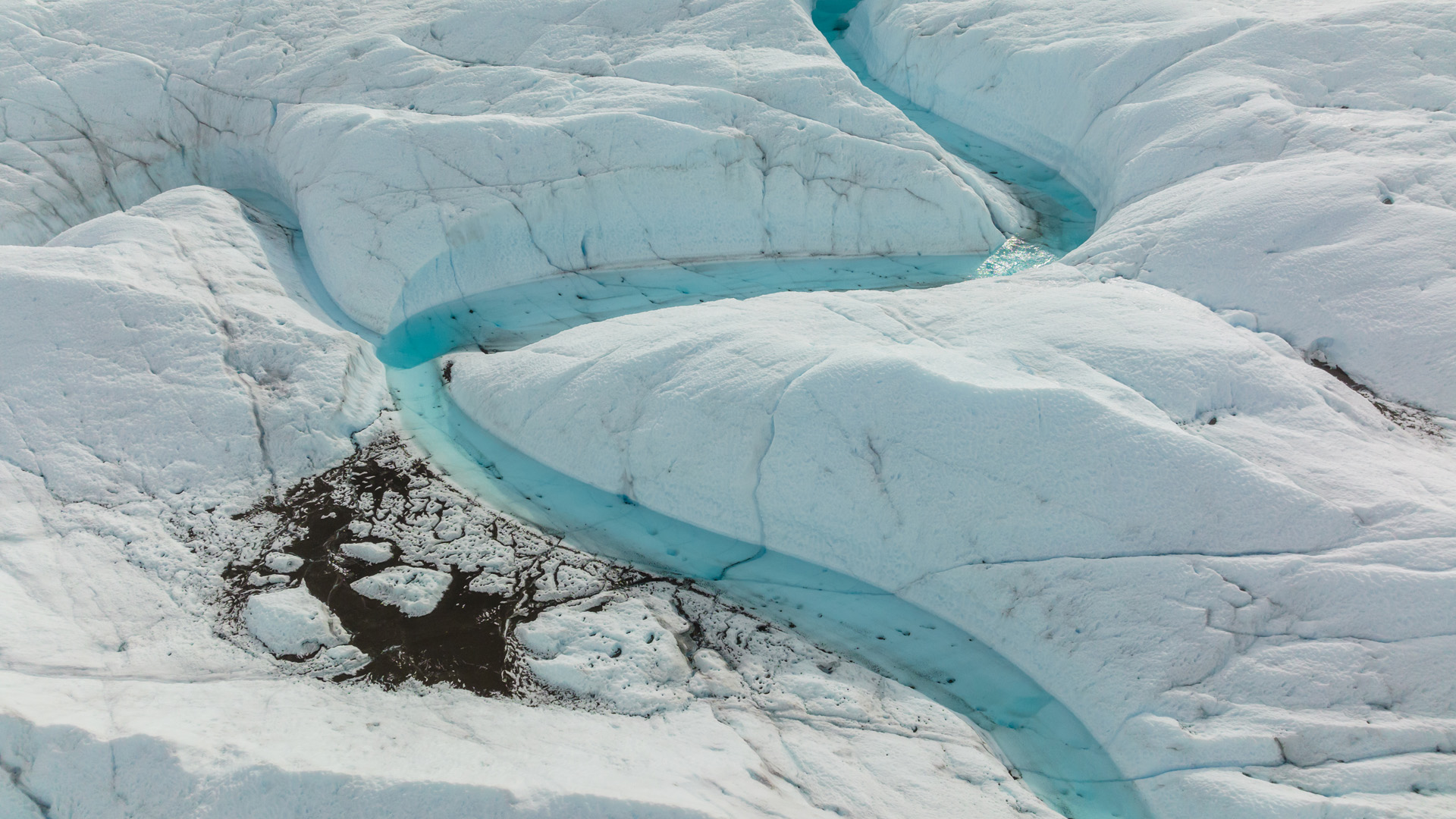

The ice core was collected during a secret mission in the 1960s, when the U.S. Army drilled through more than 4,500 feet of ice at Camp Century in northwestern Greenland. They were working only 800 miles (1,300 km) from the north pole, and about 38 miles (61 km) inland from the coast.
The mission recovered a 12-foot (4-meter) tube of soil and rock from below the ice, which was then lost in a freezer. Happily, the sample was found again in 2017. Upon reinspection, scientists found the cored material not only had rock and soil, but it also harbored leaves and moss.
This plant material suggested the existence of an ice-free landscape in Greenland’s recent geological past, and perhaps even the presence of a boreal forest. Ancient greenery suggests that the ice sheet had melted at some point in the past million years of Earth's history, but scientists weren't sure when.

Using advanced luminescence technology and the analysis of rare forms of chemical elements, with differing atomic compositions called isotopes, Bierman and the team developed a stark picture that suggests large parts of Greenland melted much more recently than a million years ago.
"We had always assumed that the Greenland ice sheet formed about two and a half million years ago—and has just been there this whole time and that it’s very stable," research co-author and Utah State University scientist Tammy Rittenour said in the same statement.
"Maybe the edges melted, or with more snowfall, it got a bit fatter—but it doesn't go away, and it doesn't dramatically melt back. But this paper shows that it did."

The research shows that sediment below the ice sheet was deposited by flowing water during an ice-free period that coincided with a moderate warming period in Earth's history.
The period, called Marine Isotope Stage 11, took place roughly 424,000 to 374,000 years ago. It was a long interglacial period, with temperatures similar to or slightly warmer than those today.
This finding suggests that Greenland ice is much more sensitive to warming than previously predicted. It also suggests the risk of an irreversible melting of ice.
"Greenland's past, preserved in twelve feet of frozen soil, suggests a warm, wet, and largely ice-free future for planet Earth unless we can dramatically lower the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere," Bierman said.
The team investigated something within the sample called a luminescence signal, which arises as the result of trapped electrons (charged particles) when materials are buried.
As pieces of rock and sand are transported as a result of water or the wind, they are exposed to sunlight, which "resets" that luminescence signal. This process means that the number of trapped electrons can serve as a rudimentary "clock" that shows when the sediments were last exposed to the sun.
The only way these sediments in this core could have seen sunlight would be if there was less than a mile (1.6 km) of ice over the top of them. That light would also have been essential for the plant matter in the sample.
Also serving to reveal when these sediments were exposed to the sky were isotopes of beryllium and aluminum, in quartz. These isotopes are only created when sediment is at the surface and exposed to cosmic rays, which are charged particles that stream into the atmosphere from beyond the solar system.
Ratios of beryllium and other isotopes gave the scientists an idea of how long rocks in the sample were exposed, and how long they were buried under layers of ice. The ratios revealed that sediments in this sample were exposed to the sky less than 14,000 years before being deposited under the ice. Finding this timeline narrowed down the window when this area of Greenland must have been ice-free.
The sea-level rise triggered is estimated by the team to have been between 5 feet and 20 feet (1.5 meters to 6 meters), a relative melt of a two-floor office building. Of course, the significant difference between then and today is that there was no climate change made by humans.
"If we melt just portions of the Greenland ice sheet, the sea level rises dramatically," Rittenour said, estimating that modern-day sea rise will probably go by tens of feet or meters.
Looking at the coast, Rittenour added, such a melt would put many urban centers and seaside populations at risk. "Look at the elevation of New York City, Boston, Miami, and Amsterdam. Look at India and Africa—most global population centers are near sea level."
The team's results were published July 20 in the journal Science.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.’s Open University. Follow him on Twitter @sciencef1rst.
-
Macadoodle There is no way that this ice sheet could have ever melted leaving Greenland covered in trees and wools mammoths as we all know any warming brings death to the whole planet.Reply -
Unclear Engineer More evidence that we are not going to "stop sea level rise" by stabilizing the CO2 level in our atmosphere at the levels we have reached, now. This previous melt supposedly happened when CO2 levels were only 280 ppm, and now we are at 420 ppm. The interglacial period 400,00 years ago was "unusually long", and the current one is headed that way too, so far as we can tell.Reply
So, as I keep saying, we need to plan to cope with sea levels at least 25 feet higher than what we see now. The modeling we really need for planning purposes is to determine how fast sea level will rise in the near future.
But, this realization does not mean that we should just stop worrying about CO2 levels or any of the other human population caused impact issues like deforestation, species extinction, etc. We can still make things worse than what the Earth has already gone through 400,000 years ago, worse for ourselves as well as other species. If everything melts, sea level comes up about 350 feet above today's level. -
El Hado Helado All feedback loops to Global Warming increase and speed-up Warming. Info about Sea level rise was published in 'Science': 'Sea Changes', years ago.Reply
Besides CO2 in the air, 'Popular Mechanics' had an article about this in 1964, the Earth Orbit swings, this has an influence on heat we get.
Not all times with same soot ppm will reach same Sea Level rises.
There are more dangers: reduced cloud cover, lower albedo, will raise Heat entry at day, Heat irradiation at night, in winther.
Temperatures will have a wider range from high to low. More moist will go up in the air in summer, meaning stronger hurricanes, heavier snowfall in winther.
If Sea temperatures go high enough, Oceans will cease being a CO2 sump, will start sending CO2 to the air.
If Sea bottom waters become hot enough, the clathrates on floor will release Methane; fires took place in harbors in recent Tsunamis, from waves stirring sediments releasing Methane.
Some sediment studies point Sea Level rise was sometimes quite fast, enough as to say it happened during European winther, meaning water came from Antarctica.
With fast CO2 release, as the Decan volcanoes in India, mass species extinction took place.
The Methane content in permafrost is huge, even if CH4 can ignite spontaneously upon entering atmosphere, lasts no more than 2 years in the air, it's a much more powerful Greenhouse effect gas than CO2.
Are your cows farting Methane? Feed it with algae.
Is a Wet Greenhouse possible? I'd say yes, but can't provide figures about chances.
Is this an Star Wars batte? Perhaps, perhaps, perhaps. (Xavier Cugat, Pérez-Prado)
Many coastal areas will drow, good for NYC, Pentagon, London, Paris, Flanders, Berlin, they bother a lot, but a human emergency in sites as Bangladesh.
There were forecasts of whole Paris going under water, except Sacre Cœur temple in Montmartre. From this, you can estimate Sea level prospectives.
The technology exists as to reduce Greenhouse effect gases emissions, just the Politics are missing; as first step, put on hold the 'programmed obsolescence', reduce taxation for energy-savings devices and procedures.
The future had an anthem: '5 feet high and risin', Johnny Cash, it fell short.
The situation is racing, time is ending.
Cool or perish!
Blessings +








