This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to Space.com's Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights.
Written by Sara Webb, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Centre for Astrophysics and Supercomputing, Swinburne University of Technology.
By far my favorite thing about my job as an astronomer is those rare moments when I get to see beautiful distant galaxies, whose light left them millions to billions of years ago. It's a combination of pure awe and scientific curiosity that excites me about "galaxy hunting."
In astronomy today, much of our work is handling enormous amounts of data by writing and running programs to work with images of the sky. A downside to this is that we don’t always have that "hands-on" experience of looking at every square inch of the universe while we study it. I'm going to show you, though, how I get my fix of wonder by looking at galaxies that only a select few people will ever have seen, until now.
In just our observable universe we estimate there are over 2 trillion galaxies!
Related: The 15 weirdest galaxies in our universe
Galaxies at your fingertips
Only a few decades ago astronomers had to tediously examine photographic plates after a long, cold and lonely night of observing. In the 21st century we have access to information any time, anywhere via the internet.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Automatic telescopes and surveys now provide us with so much data that we require machines to help us analyze it. In some cases human eyes will only ever look at what the computers have deemed is interesting! Massive amounts of data are hosted online, just waiting to be admired, for free.
Go online for a universe atlas
Aladin Lite is one of the greatest online tools available to look at our universe through the eyes of many different telescopes. Here we can scan the entire sky for hidden galaxies, and even decipher information about their stellar populations and evolution.
Let’s start our universal tour by searching for one of the most visually stunning galaxies out there, the Cartwheel Galaxy. In the Aladin interface, you can search for both the popular name of an object (like "cartwheel galaxy") or known coordinates. The location will be centered in the interface.
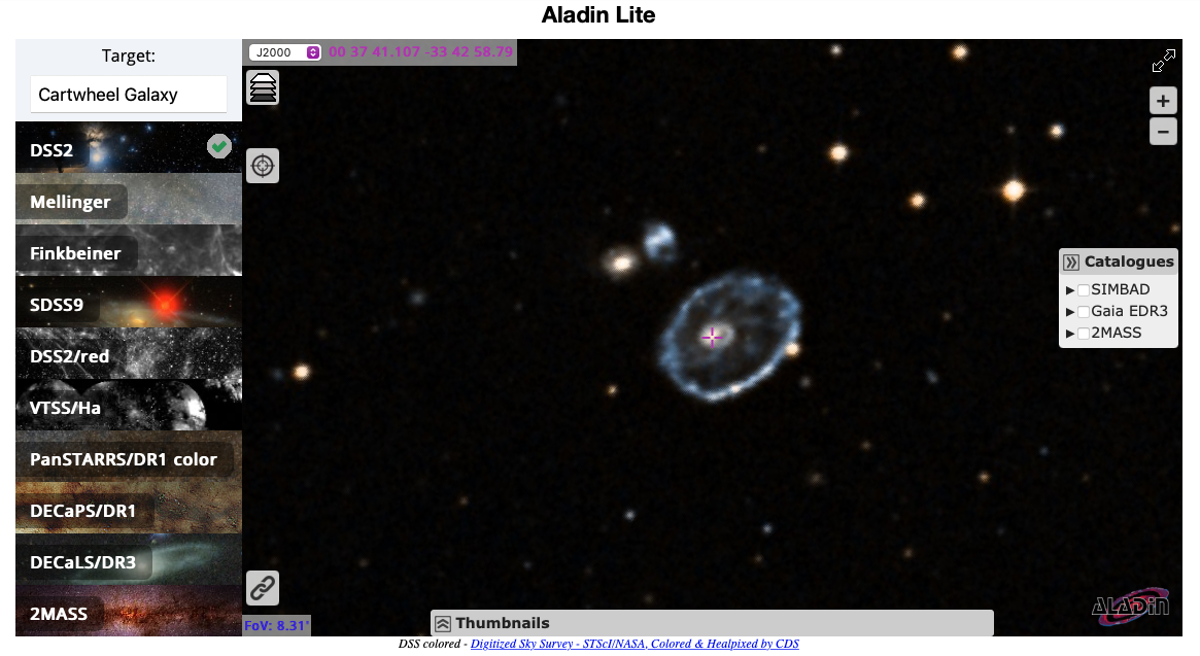
The first image of the Cartwheel Galaxy we see is from optical imaging by the Digitized Sky Survey. The colors we see represent different filters from this telescope. However, these are fairly representative of what the galaxy would look like with our own eyes.
A general rule of thumb as an astronomer is that "color" differences within galaxies are because of physically different environments. It’s important to note that things that look blue (shorter wavelengths) are generally hotter than things that look red (longer wavelengths).
In this galaxy, the outer ring appears to be more blue than the center red section. This might hint at star formation and stellar activity happening in the outer ring, but less so in the center.
To confirm our suspicions of star formation we can select to look at data from different surveys, in different wavelengths. When young stars are forming, vast amounts of ultraviolet (UV) radiation are emitted. By changing the survey to GALEXGR6/AIS, we are now looking at only UV wavelengths, and what a difference that makes!
Star facts: The basics of star names and stellar evolution
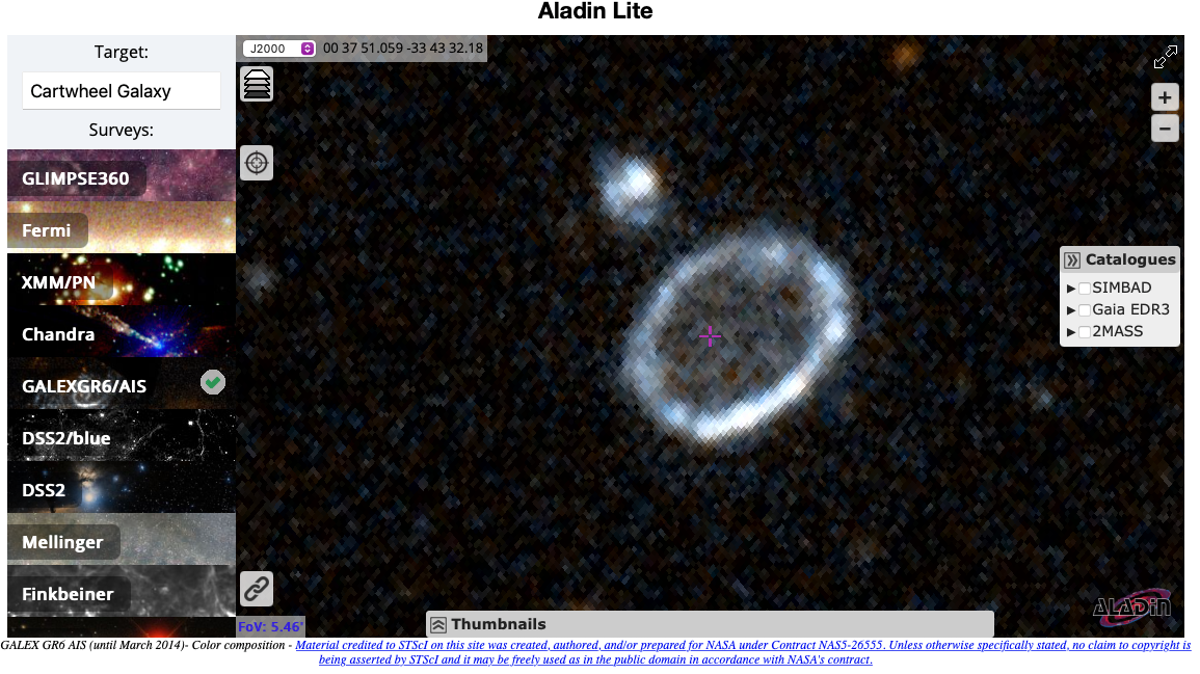
The whole center section of the galaxy seems to “disappear” from our image. This suggests that section is likely home to older stars, with less active stellar nurseries.
Aladin is home to 20 different surveys. They provide imaging of the sky from optical, UV, infrared, X-rays and gamma rays.
When I am wandering the universe looking for interesting galaxies here, I generally start out in optical and find ones that look interesting to me. I then use the different surveys to see how the images change when looking at specific wavelengths.
Universal 'Where's Waldo'
Now that you've had a crash course in galaxy hunting, let the game begin! You can spend hours exploring the incredible images and finding interesting-looking galaxies. I recommend looking at images from DECalS/DR3 for the highest resolution and detail when zooming further in.
The best method is to just drag the sky atlas around. If you find something interesting, you can find out any information we have on it by selecting the target icon and clicking on the object.
To help you on your galactic expedition, here are my favorite finds of the different types of objects you might see.
Spiral galaxies typically have a central rotating disc with large spiral "arms" curving out from the denser central regions. They are incredibly beautiful. Our own Milky Way is a spiral galaxy.
Elliptical galaxies are largely featureless and less "flat" than spirals, with stars occupying almost a 3D ellipse at times. These type of galaxies tend to have older stars and less active star-forming regions compared to spiral galaxies.
Lenticular galaxies appear like cosmic pancakes, fairly flat and featureless in the night sky. These galaxies can be thought of as the "in-between" of spiral and elliptical galaxies. The majority of star formation has stopped, but lenticular galaxies can still have significant amounts of dust in them.
There are also other amazing types of galaxies, including mergers and lenses, which are just waiting for you to find them. I’d love to see what amazing things you find over on Twitter at @sarawebbscience.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Follow all of the Expert Voices issues and debates — and become part of the discussion — on Facebook and Twitter. The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the publisher.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Sara Webb is an Astrophysics/ML postdoctoral researcher and science communicator based at Swinburne University. She spends her days solving data challenges with machine learning and coordinating student-led research projects to the International Space Station. In her PhD she was chasing the fastest bursts in the Universe, caused by the most energetic stellar events. This research took her in many amazing directions, from hunting gravitational wave counterparts to investigating the largest stellar flares.