Found! NASA Spots Crash Site and Debris from India's Lost Moon Lander
Scientists and amateurs alike have spent months combing through images from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter looking for the remains of India's moon lander — and that search has paid off.
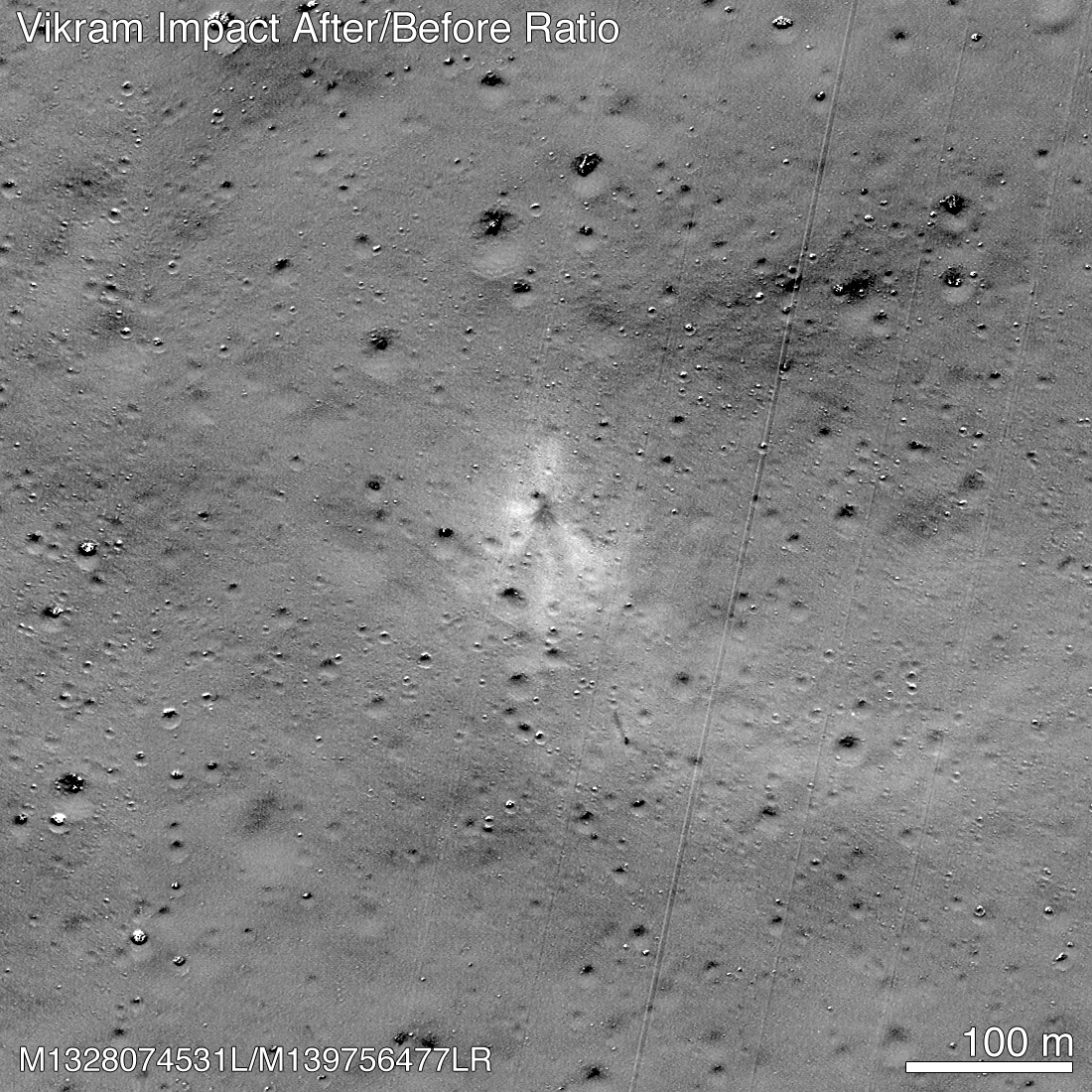
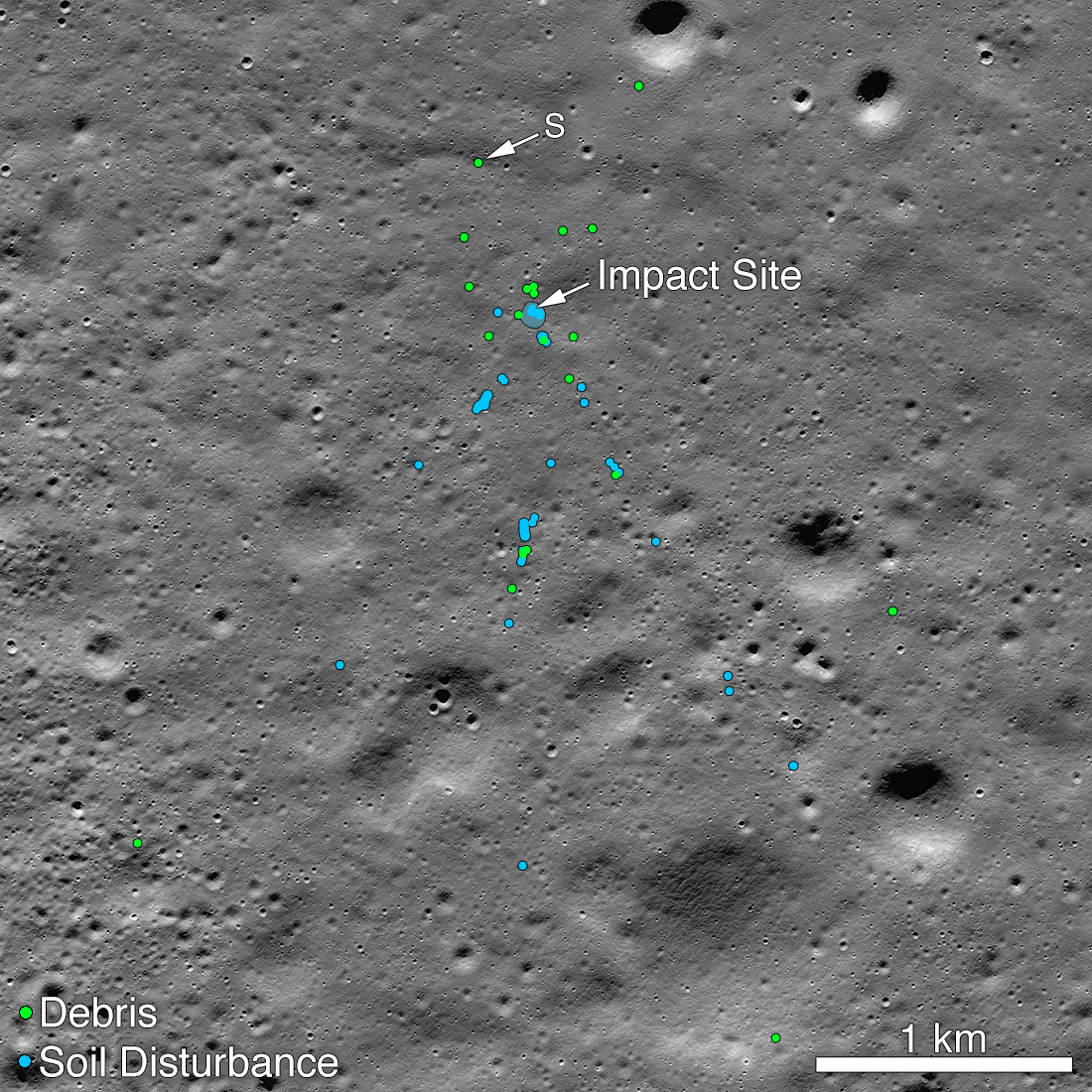
Today (Dec. 2), the team that runs the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) instrument released images taken on Nov. 11 that show how the spacecraft has changed the surface of the moon. Imaging experts have spotted extensive evidence of the crash, including both debris from the craft and places where the collision seems to have stirred up the moon's regolith.
India's Chandrayaan-2 mission to the moon included a lander called Vikram, which was meant to gently land on the lunar surface near the south pole on Sept. 6. But near the end of the touchdown maneuver, Vikram went silent. India's space agency said it spotted the lander soon after, via the orbiter component of the mission, but the agency has not released those images, and NASA's long-standing Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter hadn't had the same luck.
Related: India's Chandrayaan-2 Mission to the Moon in Photos
Now, that last part has changed. The NASA spacecraft's first pass over the impact site occurred on Sept. 17, and the LROC team published the resulting image later that month, even though they didn't think they had found any sign of the crash. But in that image, someone named Shanmuga Subramanian spotted one extraordinarily bright pixel and reached out to the LROC team, according to a NASA statement released today.
That tipoff, plus images with better lighting and resolution taken in mid-October and on Nov. 11, gave LROC specialists the details they needed to map the full scope of the surface changes caused by the hard landing. Newly released images show the impact crater itself, dark ejecta rays and light lines marking the debris field.
According to the statement, the largest pieces of debris are each about 4.5 feet (1.5 meters) across. Vikram measured 8.3 feet (2.5 m) in its longest dimension, according to materials released by India's space agency before the landing attempt.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
- India's Chandrayaan-2 Spacecraft Snaps Its First Picture of the Moon
- Amazing Moon Photos from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
- Stunning Photos Show Earth from India's Spacecraft Headed to the Moon
Email Meghan Bartels at mbartels@space.com or follow her @meghanbartels. Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.


Meghan is a senior writer at Space.com and has more than five years' experience as a science journalist based in New York City. She joined Space.com in July 2018, with previous writing published in outlets including Newsweek and Audubon. Meghan earned an MA in science journalism from New York University and a BA in classics from Georgetown University, and in her free time she enjoys reading and visiting museums. Follow her on Twitter at @meghanbartels.

