James Webb Space Telescope spots rare red spiral galaxies in the early universe
The most powerful space telescope ever created has been "seeing red."
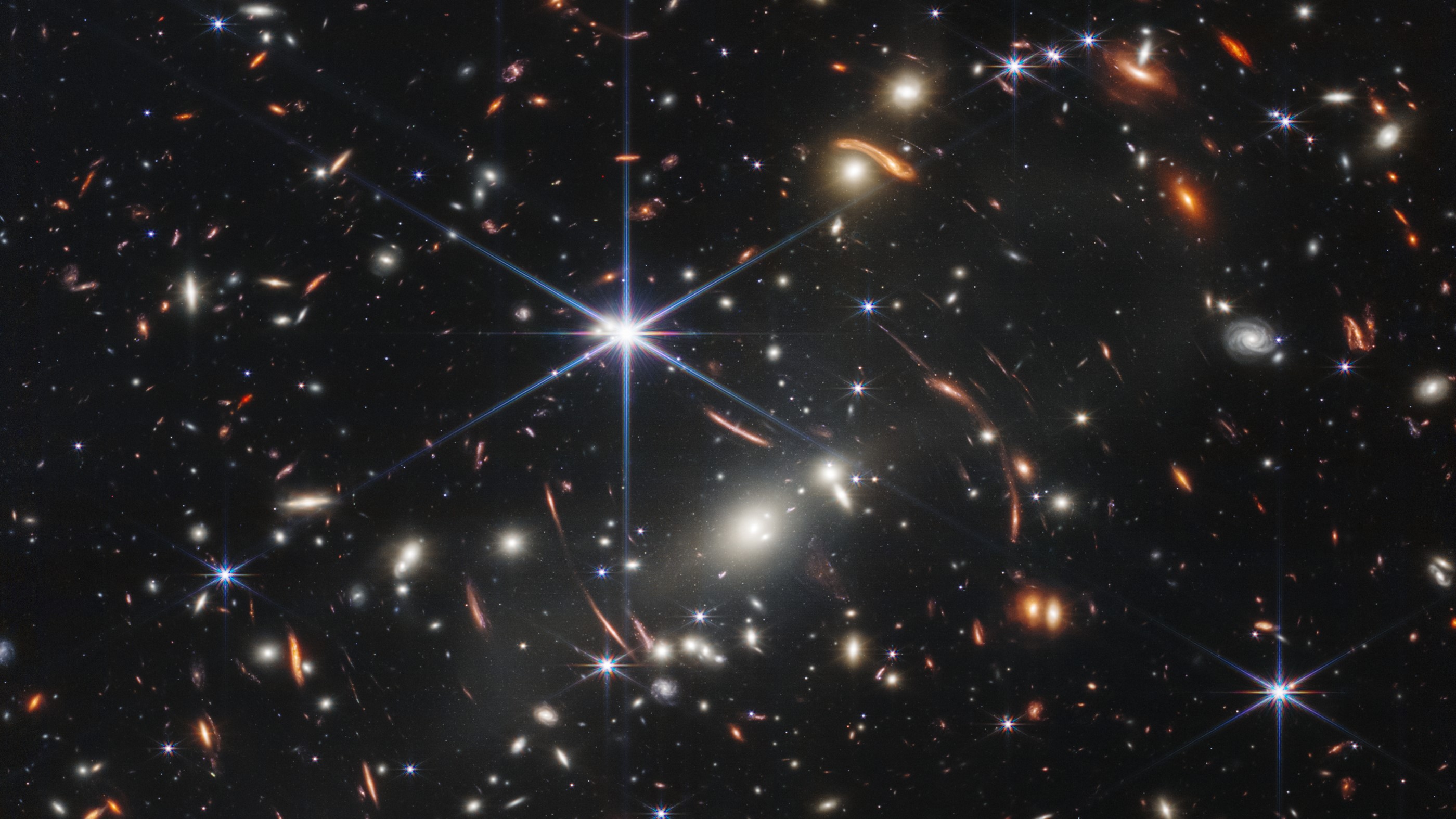

The James Webb Space Telescope (Webb or JWST) has spotted several rare red spiral galaxies, giving astronomers a new view of the early universe.
Astronomers analyzed red spiral galaxies in one of the James Webb Space Telescope's first images, that of the galaxy cluster SMACS J0723.3–7327. Seen through the eyes of JWST, the most powerful telescope ever placed into orbit, the galaxy cluster magnifies objects seen behind it, letting astronomers see deeper into the universe. The researchers determined that some of these galaxies represent the most distant spiral galaxies ever seen.
The red spiral galaxies themselves aren't new discoveries: NASA's retired Spitzer Space Telescope imaged them in the past. But Spitzer didn't have the power of JWST and couldn't see the details of the galaxies' shape, which astronomers call morphology. The shape of galaxies tells the story of their evolution, so the intricate detail of these galaxies' morphology provided by JWST could improve our understanding of the early universe significantly.
Gallery: James Webb Space Telescope's 1st photos
Additionally, one particular galaxy hidden in the image could change our perception of the galactic population that existed during this period of cosmic history. In the image, the astronomers spotted a red spiral galaxy in the early universe that is "passive," or not forming stars. The discovery is surprising, since astronomers expected galaxies in the early universe to be actively birthing stars.
"While these galaxies were already detected among the previous observations using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and Spitzer Space Telescope, their limited spatial resolution and/or sensitivity did not allow us to study their detailed shapes and properties," Yoshinobu Fudamoto, a junior researcher at Waseda University in Japan and first author on the new research, said in a statement.
Spiral galaxies are extremely common in the cosmic neighborhood around the Milky Way, but red spiral galaxies are much rarer, accounting for only 2% of galaxies in the local universe. The discovery of red spiral galaxies in the early universe in observations that encompass a relatively insignificant fraction of space suggests that these rare galaxies were much more common in the early universe.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
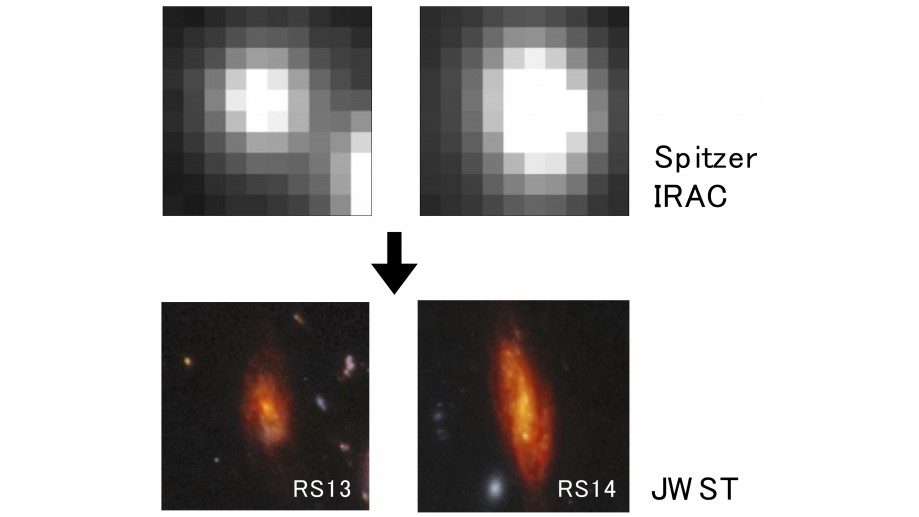
Astronomers found that the two most extremely red galaxies, RS13 and RS14, appear as they were between 8 billion and 10 billion years ago, quite early in the universe's 13.8-billion-year lifespan. The two galaxies are also the most distant and earliest known spiral galaxies to date.
And the fact that RS14 is a passive galaxy that has stopped forming stars only makes the discover more intriguing because its existence suggests that non-star-forming galaxies could be more common in the early universe than astronomers thought.
"Our study showed for the first time that passive spiral galaxies could be abundant in the early universe," Fudamoto said. "While this paper is a pilot study about spiral galaxies in the early universe, confirming and expanding upon this study would largely influence our understanding of the formation and evolution of galactic morphologies."
The team's research is published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom or on Facebook.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.’s Open University. Follow him on Twitter @sciencef1rst.
-
rod "Astronomers analyzed red spiral galaxies in one of the James Webb Space Telescope's first images, that of the galaxy cluster SMACS J0723.3–7327. Seen through the eyes of JWST, the most powerful telescope ever placed into orbit, the galaxy cluster magnifies objects seen behind it, letting astronomers see deeper into the universe. The researchers determined that some of these galaxies represent the most distant spiral galaxies ever seen."Reply
Spiral galaxies are very interesting and now reports where they show up with deep redshifts. Spiral arms last perhaps 80-100 million years, and then must be regenerated for astronomers on Earth today to see the spiral structures like the Milky Way, so modeling density waves and spiral arm recycling is required for long ages used in BB cosmology. Here are some other reports I read on this topic.
Discovering a rare red spiral galaxy population from the early universe with the James Webb Space Telescope, https://phys.org/news/2022-12-rare-red-spiral-galaxy-population.html
ref - Red Spiral Galaxies at Cosmic Noon Unveiled in the First JWST Image, https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/ac982b, 21-Oct-2022.
My notes. The report is 6-page PDF file. From the published report. "4. Results and Discussion 4.1. SED Fitting Results We found that the redshifts of extremely red spirals are in a range of zph = 1–3. In particular, RS 14 (zspec = 2.463) is one of the highest redshift spiral galaxies identified so far (Dawson et al. 2003; Law et al. 2012; Margalef-Bentabol et al. 2022; Wu et al. 2022)."
My note. Using cosmology calculators, H0=69.6 km/s/Mpc, z=2.463. Age of universe at z = 2.688 Gyr. Look back distance or light time = 11.034 Gyr. The universe radius when these early spirals appeared, about 5.56 Gly or less than 12 billion light years diameter compared to present day, about 93 billion light years diameter. The comoving radial distance for z = 2.463 is 19.224 Gly. 4D space is expanding 1.36 x c velocity. https://lambda.gsfc.nasa.gov/toolbox/calculators.html
When explaining and interpreting early spirals like this report, the cosmology parameters documented are required for the BB cosmology to work. Here is another report on JWST seeing 13.2 redshifts with discussion on various parameters required to explain and photons losing energy as they redshift traveling through 4D space expanding, even expanding faster than c velocity. https://forums.space.com/threads/confirmed-james-webb-space-telescope-has-bagged-the-oldest-known-galaxies.59123/









