A 'doorway' on Mars? How we see things in space that aren't there.
Spoiler alert: The "dog door" on Mars isn't proof of aliens.

This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to Space.com's Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights.
David Rothery, Professor of Planetary Geosciences, The Open University
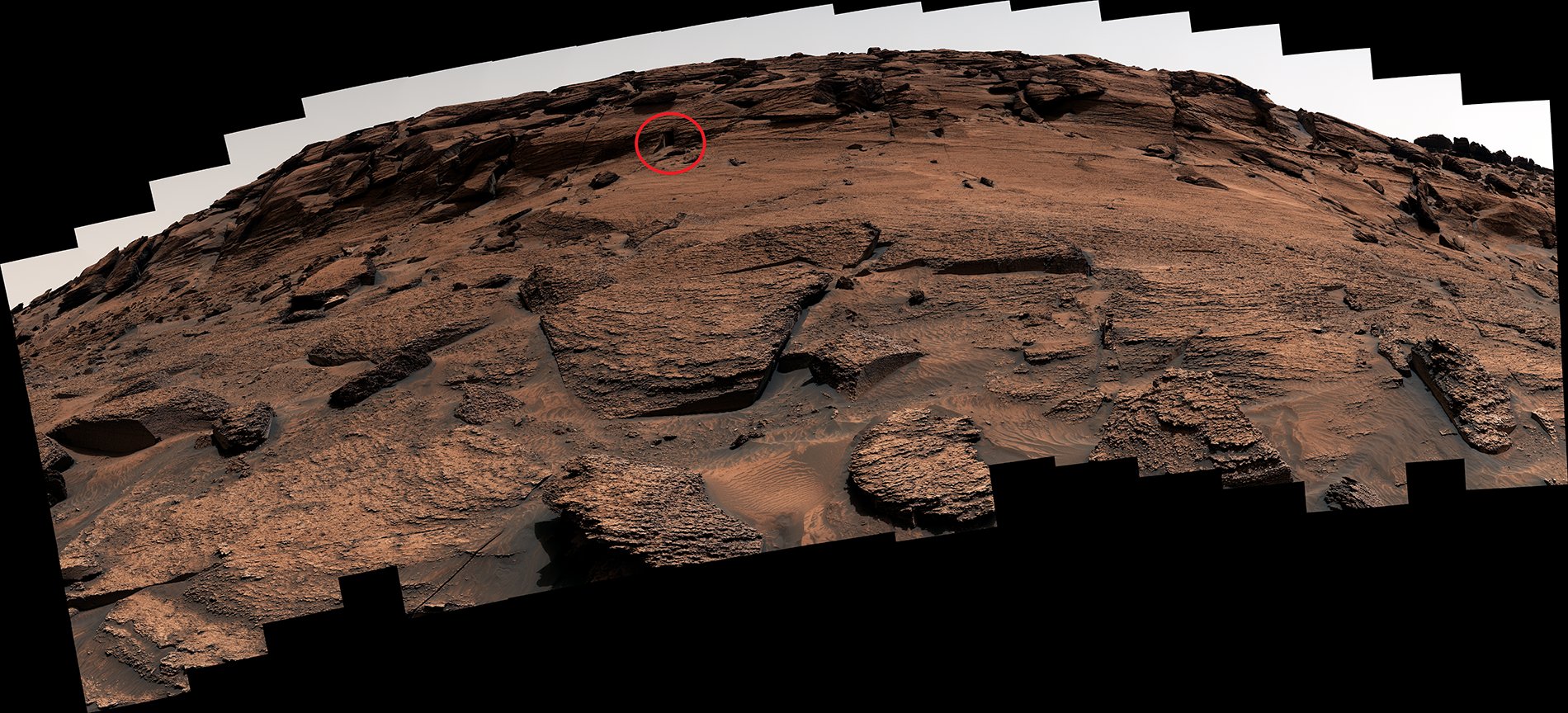
Enthusiasts lit up social media recently with images of what appeared to be a "doorway" into a hillside on Mars. Was it, some wondered, evidence that the Red Planet could be, or have been, inhabited by aliens? The "door" was imaged by NASA's Curiosity rover on May 7 on the slopes of Mount Sharp, the central massif within Gale crater, where it landed in 2012. Described on one website as a "pharaonic tomb door," because of its resemblance to some ancient Egyptian remains, it is in fact only about one foot high.
It is hard to spot on the panoramic image mosaic of the hillside above, but it leaps out at the eye if you see the individual frame where it occurs, seen below. It does look like a doorway until you realize how small it is. And if you boost the contrast in the dark parts of the image, the picture just about reveals a solid rock face at the back of the shadowed interior. So as a gateway into the hollow hills of Mars, it doesn't lead very far.
Related: Curiosity's "dog door" on Mars a rocky gate to the ancient past
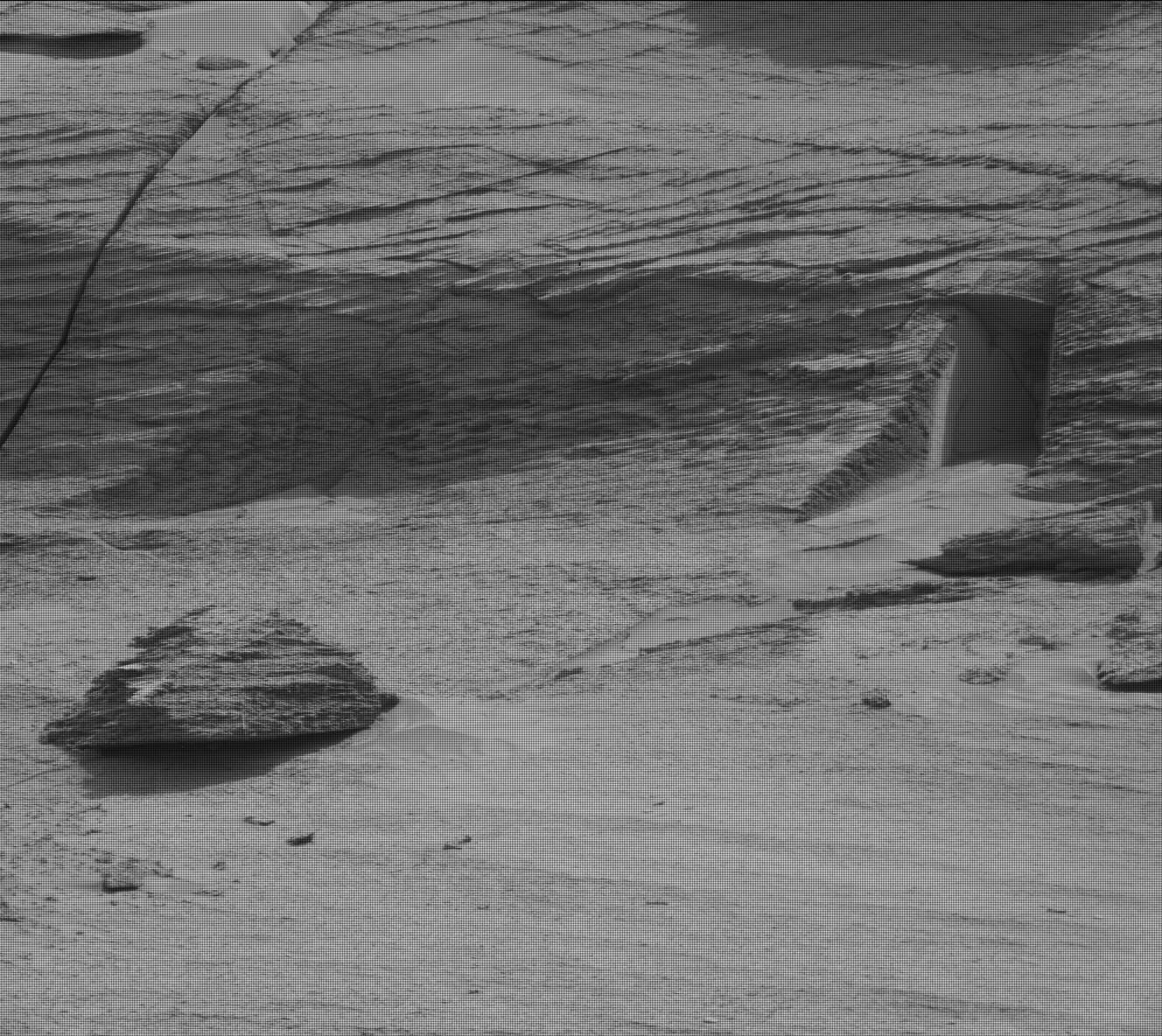

What the "door" really is
Nobody with even a little geological experience is likely to mistake the feature as a "door." A geologist would note the thin and slightly sloping repeated layers of sandstone making up the whole of the rock face, and would immediately expect that they were looking at the eroded remains of hardened sand dunes. These once covered the stream and lake sediments that Curiosity examined earlier in its gradual climb up through the layers of sedimentary rock making up Mount Sharp.
A geologist would also spot the steep and fairly straight cracks running up the rock face, and recognize these as "joints." These are fractures that typically open up when the weight of overlying rock layers is removed by erosion. There is a particularly obvious joint in the left of the "door" image, but several others can be made out — including one that forms the smooth wall that lines up with the left side of the "door" itself. There's another joint that forms the right side of the feature.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Related: Mars Illusion Photos: The 'Face on Mars' and Other Martian Tricks
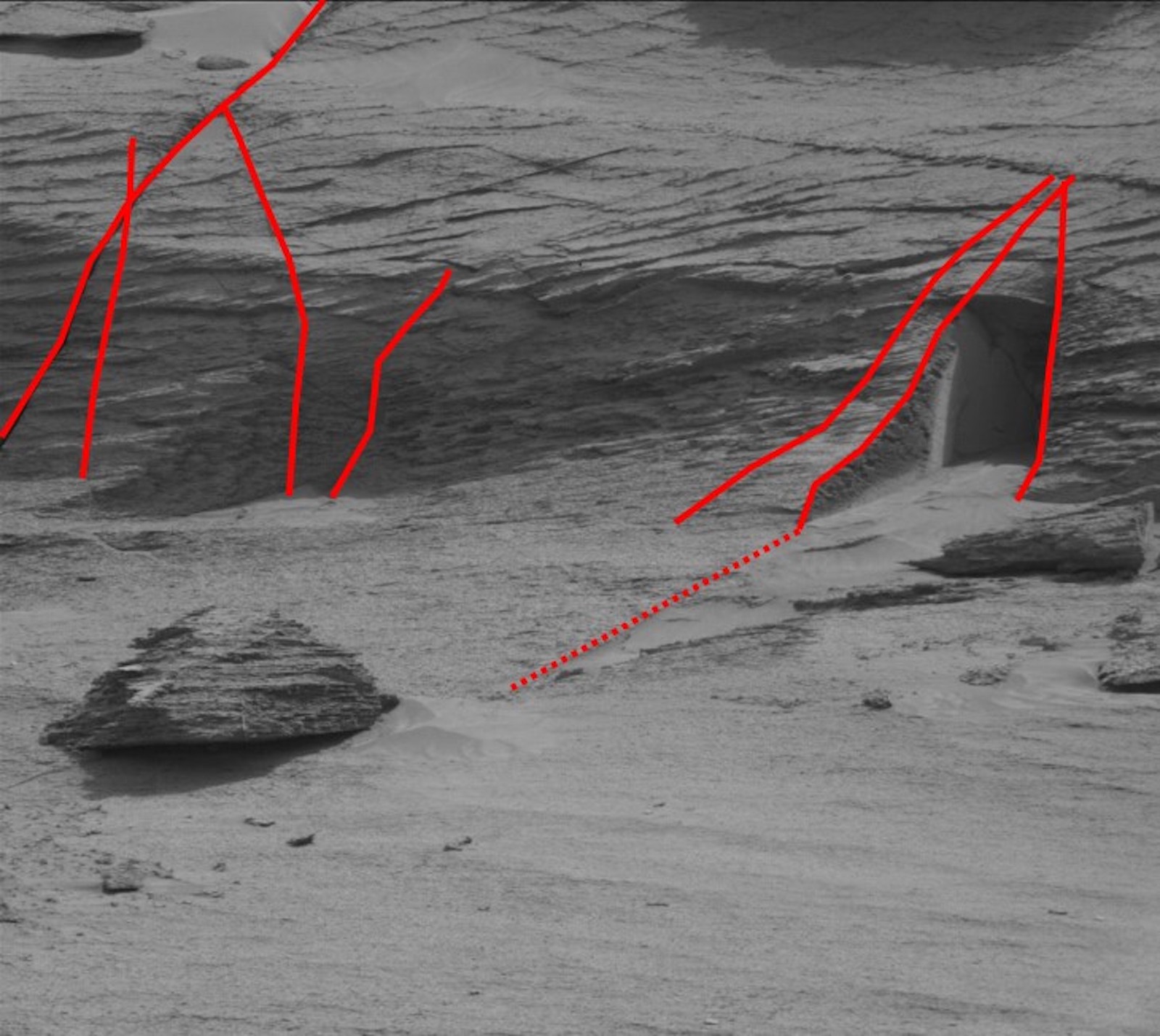

The whole hillside has been eroded back. The "doorway" is simply a place where the wind has been able to scour out the poorly consolidated sand and dust from the rock face a little more effectively, in an area bounded by the joints on either side. The base of an overlying bed of sandstone is the "door lintel," and the sloping top of a bed of sandstone forms the gentle ramp that leads up to the door.
Artifacts on Mars
It doesn't take much searching on the internet to find images taken by Mars rovers that show rock formations that resemble other familiar objects, even though all are implausibly out of place. We should not be surprised that some of the innumerable rocks on Mars have weird shapes, because many have been sandblasted by wind erosion for billions of years.

Apart from "doors" and bits of "hardware" ranging from wrecked "spaceships" and a "jet engine" to individual items of "cutlery," images have also captured "pyramids," numerous "humanoid heads," "dinosaurs," various "bones" and even a "squirrel." Only a few of these strange objects are real, and those are all junk that humans put there. The others lose their visual distinctiveness if seen at closer range or from a different perspective.

Weirdness beyond Mars
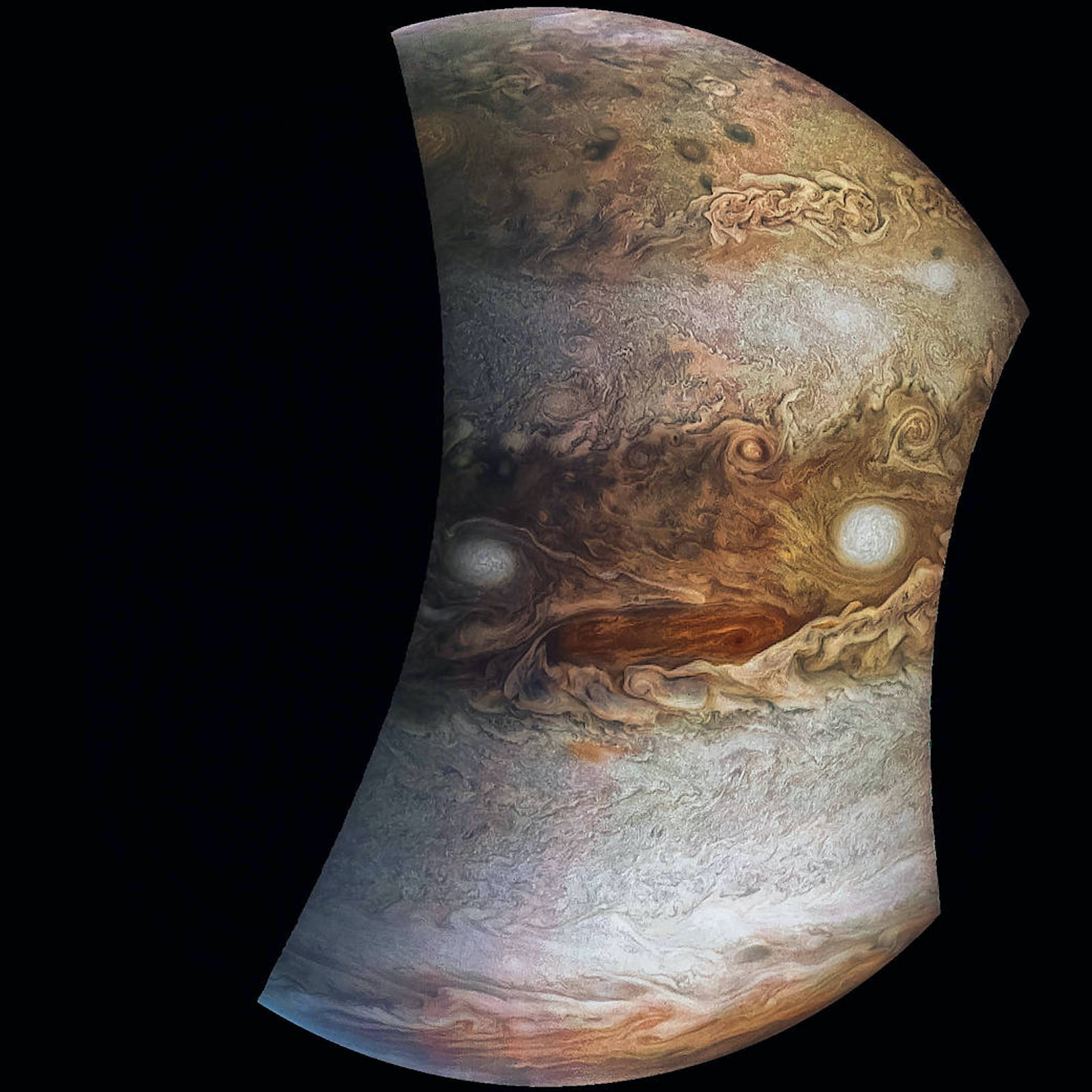
"Seeing" the familiar even when it isn’t there is a phenomenon called pareidolia. This denotes what happens when you see faces in the random pattern of your wallpaper, or peering out from the grain of wooden flooring, or in the clouds. The latter, for example, is what's causing Jupiter to look angry in the image below.
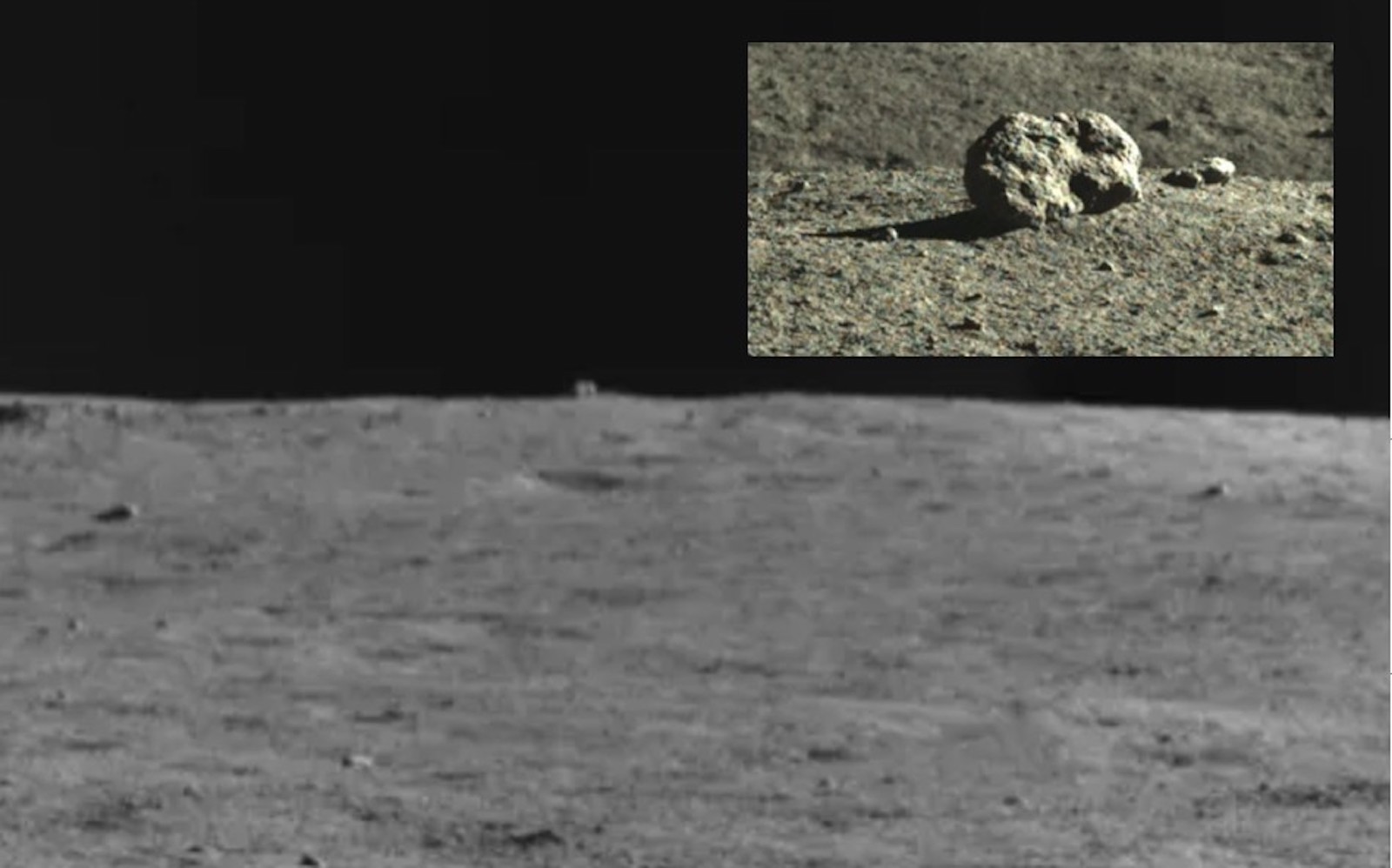
Seemingly mysterious objects don’t occur solely on Mars. In December 2021, China's Chang'e 4 rover — still doing great things on the on the lunar far side more than three years after landing — spotted a "hut shaped" object 80 meters away. It duly trundled towards it, and revealed it to be just a boulder, presumably ejected from a nearby impact crater. Some say it looks like a crouching rabbit, but I doubt anyone is claiming that it was sculpted by aliens.

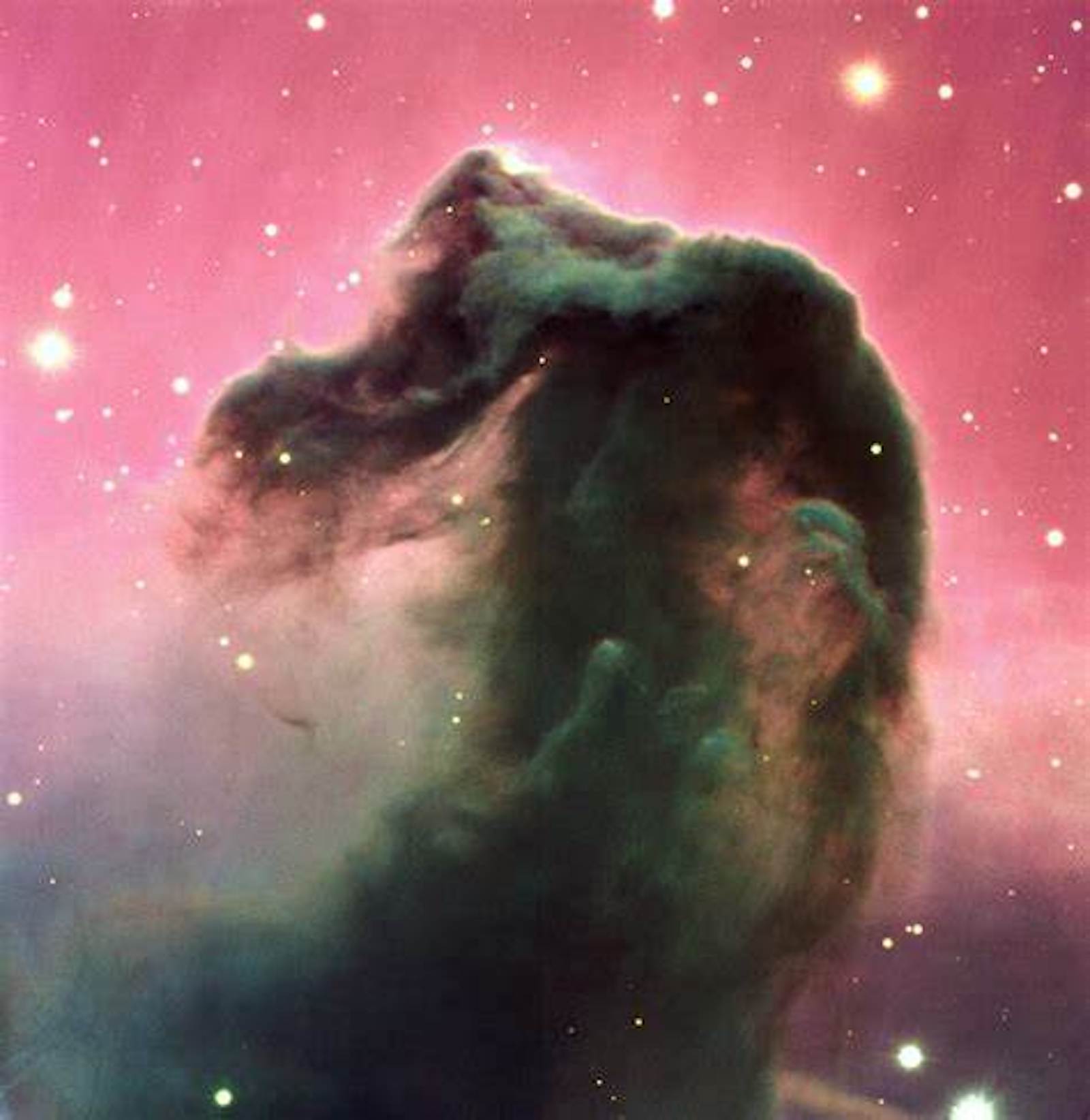
One of the most famous, and largest, examples of pareidolia is the Horsehead Nebula. This is a vast cosmic cloud of gas and dust, within which whole stellar systems are forming. An image collected in the right part of the spectrum and with an appropriate exposure time shows a shape that most people would recognize as a horse's head. Shift wavelengths (which we can do) or look at it from a different direction (which we can’t) and the recognizable shape will vanish.

Back on Earth, climbers high on Great Gable, a mountain in Cumbria, U.K., often look out for Cat Rock, otherwise known as Sphinx Rock. Seen from below this looks like a sitting cat, and seen side-on it resembles the profile of the Sphinx's head. So far as I know, everyone accepts this as fluke and no one claims it as evidence that aliens have left landscape clues to their visits to Earth. It beats me why people persist in making such claims for flukey rock formations on Mars.
Ultimately, although you can generally believe your eyes, you should be cautious in believing your brain’s interpretation of what your eyes see.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Follow all of the Expert Voices issues and debates — and become part of the discussion — on Facebook and Twitter. The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of the publisher.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

David Rothery is a professor of planetary geosciences at the Open University in Milton Keyes, England, where he studies volcanic activity with remote sensing, as well as volcanology and geoscience on other planets. He earned a Ph.D. on the applications of remote sensing from Open University in 1982 and has been a professor of planetary geosciences since 2013. Prior to that he had served as a senior lecturer since 1994. David is the U.K. lead co-investigator on the Mercury Imaging X-ray Spectrometer aboard the European Space Agency's BepiColombo mission to Mercury and chairs ESA's Mercury Surface and Composition Working Group. He is the author of several books on space geosciences, including his landmark Planet Mercury: From Pale Pink Dot to Dynamic World (Springer-Praxis, 2014). You can see David's latest updates by following him on Twitter.