Cosmic orcs? Scientists snap best image yet of eerie 'odd radio circles' in space
Astronomers first observed these mysterious circles in 2019.
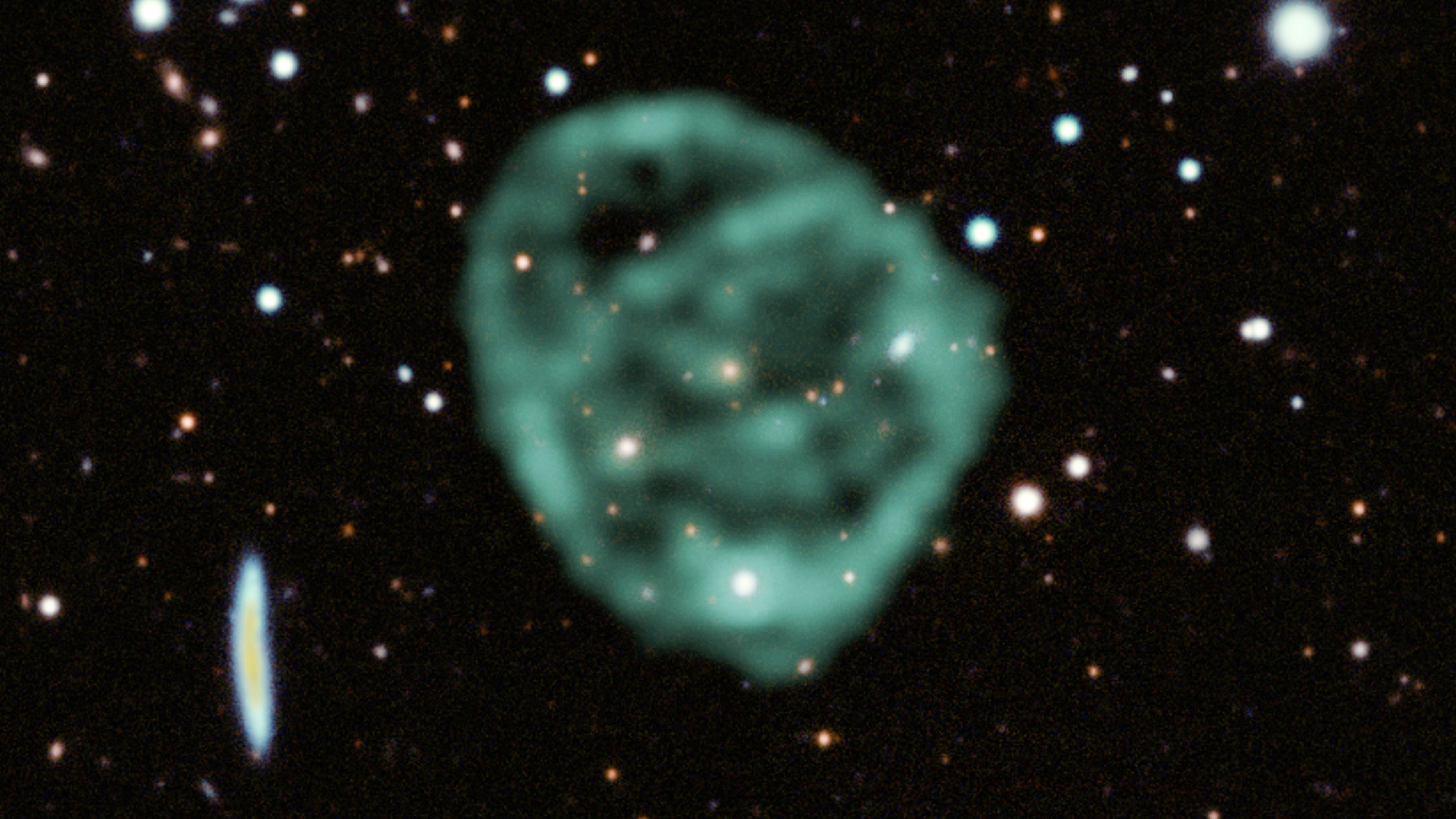

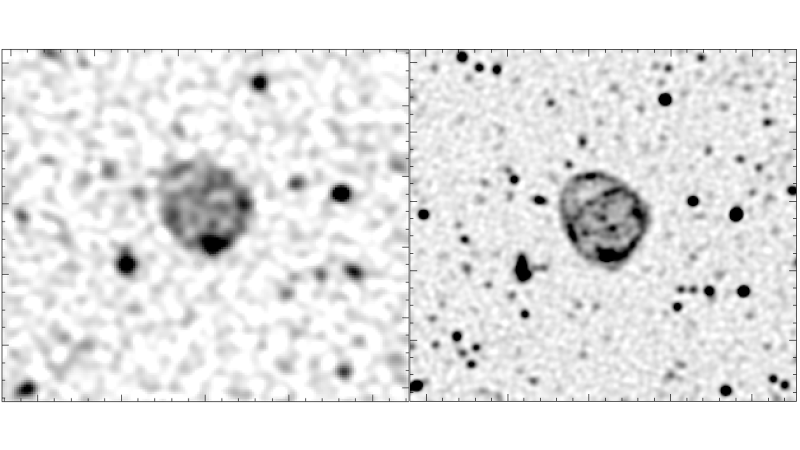
Astronomers imaged a weird circle in space in high-definition for the first time as they try to figure out how these mysterious structures form.
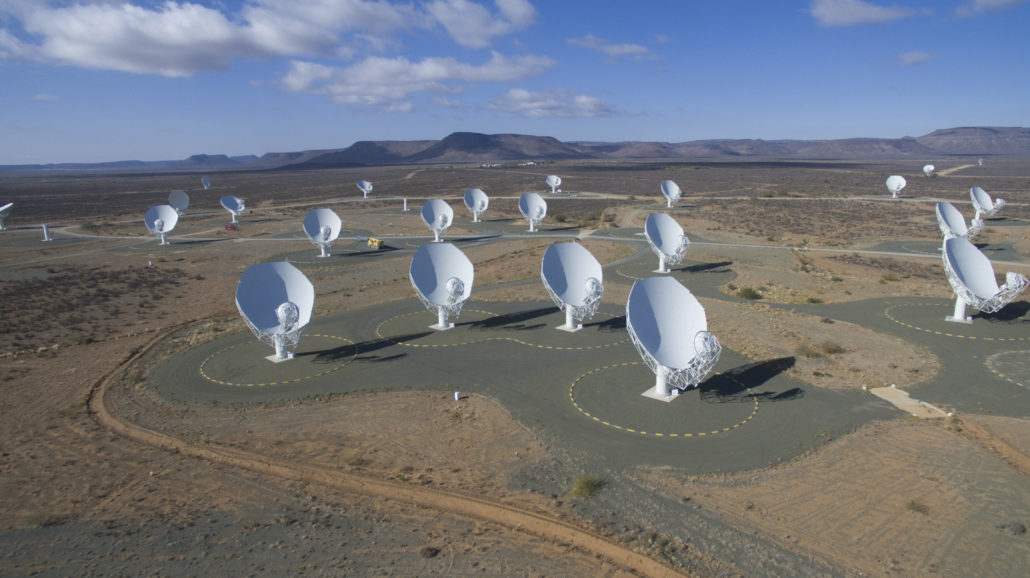
Known as "odd radio circles" (ORCs), the enigmatic shapes were first spotted in 2019 in images from the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP) radio telescope. Consisting of 36 colossal dishes located in Western Australia, ASKAP images the entire night sky in radio waves, began seeing circles in various spots.
Each circle appears to be several billion light-years away, and potentially as big as a few million light-years in diameter. Individual ORCs appear to have galaxies at their centers, but strangely, are only visible in radio waves.
Now there's more information incoming. The South African Radio Astronomy Observatory’s MeerKAT radio telescope array captured a new detailed look at one of the circles, nicknamed ORC 1 ("Odd Radio Circle 1.") The image was shared in a statement Tuesday (March 22.)
While research is still ongoing, the astronomers say that such imagery will eventually allow them to narrow down how these radio structures are formed, and to better fit in ORC evolution with the universe at large.
Astronomers have only found the ORCs in radio wavelengths, making them even more mysterious as the objects do not show up in other investigations using optical, X-ray or infrared telescopes.
At present, there are three theories as to how ORCs form. One is they could represent a gigantic explosion in the middle of their host galaxy, on the scale of two supermassive black holes merging.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Other possibilities include ORCs being jets of energetic particles emanating from the galaxy's center, or a starburst "termination shock" produced as stars are formed.
The team admitted in a statement that more detailed radio surveys are required to learn more, but added they are excited to spot something novel in the sky.
"We know ORCs are rings of faint radio emissions surrounding a galaxy with a highly active black hole at its center, but we don't yet know what causes them, or why they are so rare," stated lead author Ray Norris, a data scientist and astrophysicist from Western Sydney University and Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation.
The team said they hope to obtain access to "even more sensitive radio telescopes", such as the Square Kilometer Array (SKA) Observatory. Construction on the world's largest radio observatory began in 2021. First light is expected in 2027.
The array of dishes is positioned at two sites. The SKA-Mid array, in the Karoo desert in South Africa, will use 197 dishes for middle frequency bands. The SKA-Low array, includes 131,072 antennas located north of Perth, Australia to listen for lower-frequency bands.
A paper based on the research is expected to be uploaded shortly to the Royal Notices of the Astronomical Society. A preprint version of the paper is available on Arxiv.
Follow Elizabeth Howell on Twitter @howellspace. Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom or Facebook.

Elizabeth Howell (she/her), Ph.D., was a staff writer in the spaceflight channel between 2022 and 2024 specializing in Canadian space news. She was contributing writer for Space.com for 10 years from 2012 to 2024. Elizabeth's reporting includes multiple exclusives with the White House, leading world coverage about a lost-and-found space tomato on the International Space Station, witnessing five human spaceflight launches on two continents, flying parabolic, working inside a spacesuit, and participating in a simulated Mars mission. Her latest book, "Why Am I Taller?" (ECW Press, 2022) is co-written with astronaut Dave Williams.