NASA has picked three companies to develop new lunar landers that will carry astronauts to the surface of the moon in 2024 and beyond.
The agency announced today (April 30) that it has awarded contracts to SpaceX, a Blue Origin-led team and Dynetics to design and build a human landing system for the Artemis program, which aims to establish a sustainable, long-term human presence on and around the moon by the late 2020s.
"With these contract awards, America is moving forward with the final step needed to land astronauts on the moon by 2024, including the incredible moment when we will see the first woman set foot on the lunar surface," NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine said in a statement.
"This is the first time since the Apollo era that NASA has direct funding for a human landing system, and now we have companies on contract to do the work for the Artemis program," Bridenstine added.
Related: NASA unveils plan for Artemis 'base camp' on the moon beyond 2024
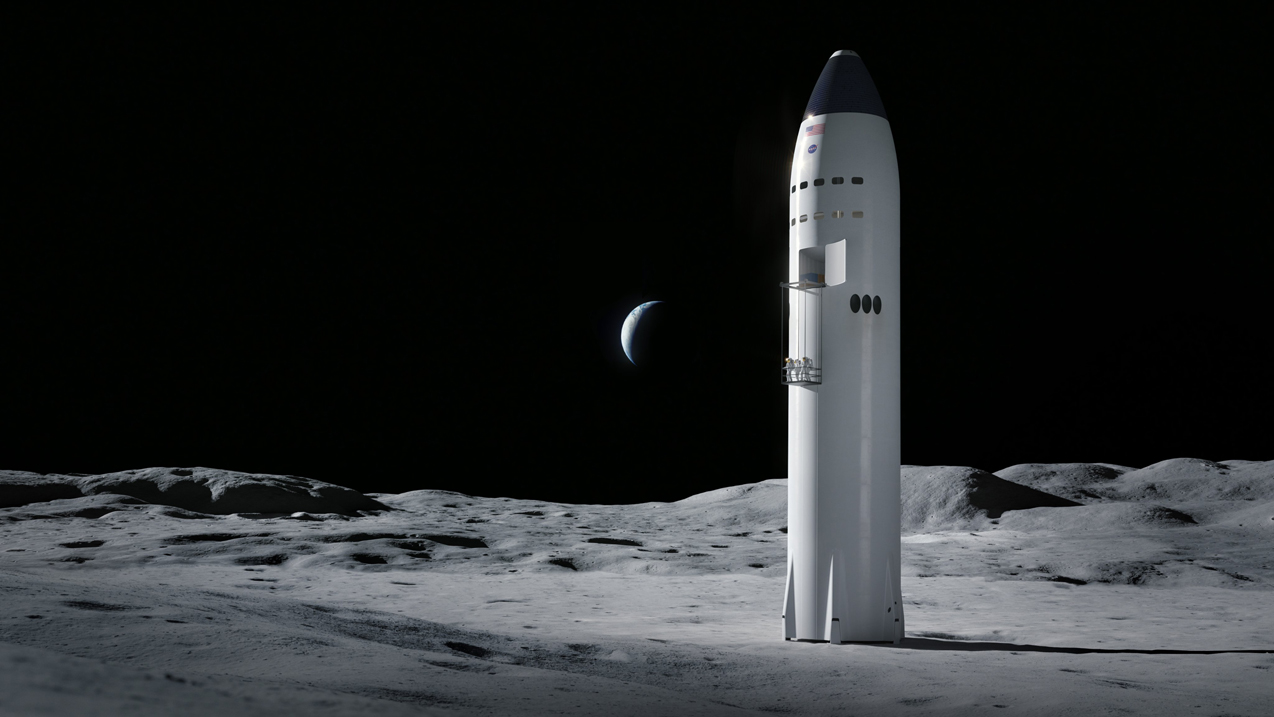


The awards, which were granted under NASA's Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships (NextSTEP-2) program, are fixed-price contracts worth a total of $967 million for 10 months of work, agency officials said. NASA issued a call for proposals in September 2019, and submissions were due in early November of that year.
NASA did not name the submitters at the time, though some of the companies identified themselves. For example, Boeing announced in November that it had put in a proposal, which ended up being unsuccessful.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
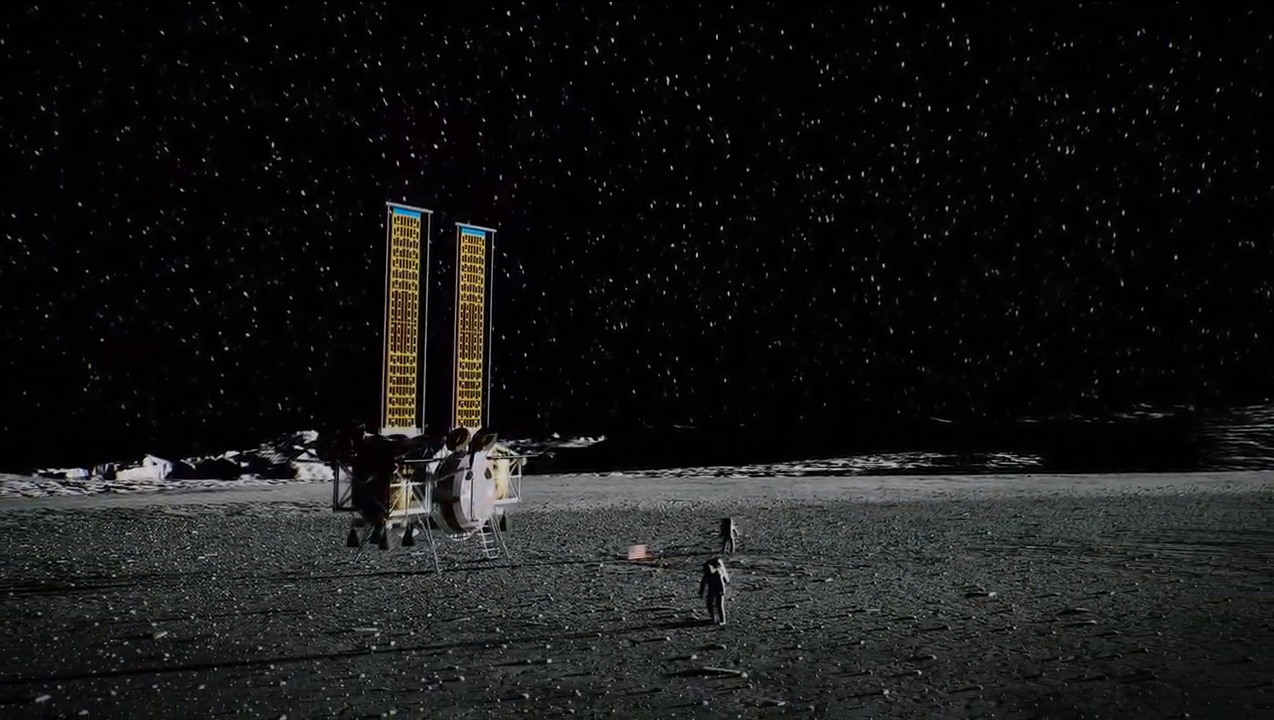
SpaceX's funded proposal centers on its huge Starship vehicle, which the company is already developing to help colonize Mars and enable a variety of other ambitious exploration feats. Starship will launch off Earth atop a huge rocket called Super Heavy, but the spacecraft will land on, and launch off, the moon and Mars on its own, without the need for any other vehicles.
Blue Origin will lead a so-called "National Team" that includes partners Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman and Draper. These companies together will build a three-stage system that includes a descent vehicle, an ascent vehicle and a transfer stage, NASA officials said.
Alabama-based Dynetics will build a two-stage system consisting of an ascent stage and a descent stage.
The variety of approaches represented by these three proposals is a major plus, providing significant design redundancy, Lisa Watson-Morgan, Human Landing System program manager at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, said during a teleconference with reporters today.
NASA will work with the three commercial teams over the next 10 months, assessing their progress all the while. The agency will determine during that period which team(s) will perform initial demonstration missions. NASA will then tap one or more companies to mature their systems and fly additional test missions, officials said. The agency will procure operational flights, as a commercial transportation service, from the firms that made it through the development gauntlet.
The Artemis architecture relies on NASA's Orion crew capsule and huge Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, which will launch astronauts off Earth. NASA also plans to build a small space station in lunar orbit called Gateway, which will serve as a staging point for crewed and uncrewed missions to the lunar surface.
The landing system is the final major Artemis piece, so getting development work going on it soon is a big priority for the agency if it hopes to meet the 2024 touchdown goal, which was set by the Trump Administration in March 2019.
"We are on our way," Douglas Loverro, NASA's associate administrator for Human Explorations and Operations Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C., said in the same statement.
"With these awards, we begin an exciting partnership with the best of industry to accomplish the nation's goals," Loverro added. "We have much work ahead, especially over these next critical 10 months. I have high confidence that working with these teammates, we will succeed."
While Gateway is a big part of the long-term Artemis plan, it probably won't be involved in the 2024 crewed landing, Bridenstine said during today's telecon.
Artemis' vision doesn't end at the moon, by the way. NASA views the program as a steppingstone, teaching the agency skills and techniques that will be required to get astronauts to Mars in the 2030s.
- NASA unveils plan for Artemis 'base camp' on the moon beyond 2024
- Blue Moon: Here's how Blue Origin's new lunar lander works
- Boeing's 1st Starliner flight test in photos
This story was updated with additional details at 3 p.m. EDT on April 30.
Mike Wall is the author of "Out There" (Grand Central Publishing, 2018; illustrated by Karl Tate), a book about the search for alien life. Follow him on Twitter @michaeldwall. Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom or Facebook.
OFFER: Save 45% on 'All About Space' 'How it Works' and 'All About History'!
For a limited time, you can take out a digital subscription to any of our best-selling science magazines for just $2.38 per month, or 45% off the standard price for the first three months.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Michael Wall is a Senior Space Writer with Space.com and joined the team in 2010. He primarily covers exoplanets, spaceflight and military space, but has been known to dabble in the space art beat. His book about the search for alien life, "Out There," was published on Nov. 13, 2018. Before becoming a science writer, Michael worked as a herpetologist and wildlife biologist. He has a Ph.D. in evolutionary biology from the University of Sydney, Australia, a bachelor's degree from the University of Arizona, and a graduate certificate in science writing from the University of California, Santa Cruz. To find out what his latest project is, you can follow Michael on Twitter.
-
newtons_laws As Space X's proposal uses their starship design which is launched on their Super Heavy launcher presumably in their case the astronaut crew could launch directly from Earth on the starship, directly land on the Moon and then take off again, either then to rendezvous with the Lunar Gateway or return directly to Earth (as the starship is designed to be able to re-enter the Earth's atmosphere). In that case then a manned mission to the Moon's surface wouldn't actually require NASA's Orion capsule or NASA's expensive SLS launcher. Being a cynic that might just count against Space X at the next contract award decision point....Reply -
Mr_Bill Using the Space X Starship would be a significant change in direction from what NASA currently has planned for the moon missions. I can't imagine that they will simply throw away the years of development, and billions already spent on the SLS, and select the Space X lander and Super Heavy launcher.Reply










