Northrop Grumman names Cygnus spacecraft for first African American astronaut
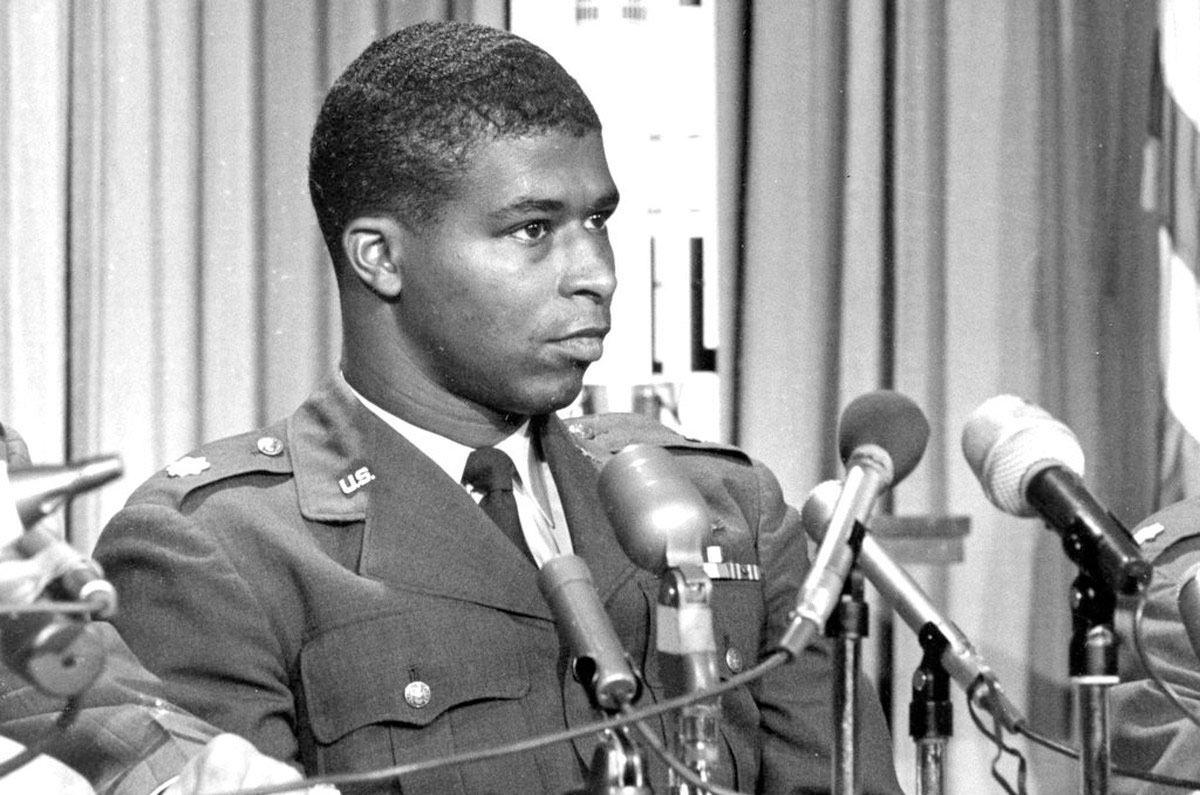

The first African American to be selected as an astronaut is being remembered with the naming of a space station cargo capsule set to launch during Black History Month.
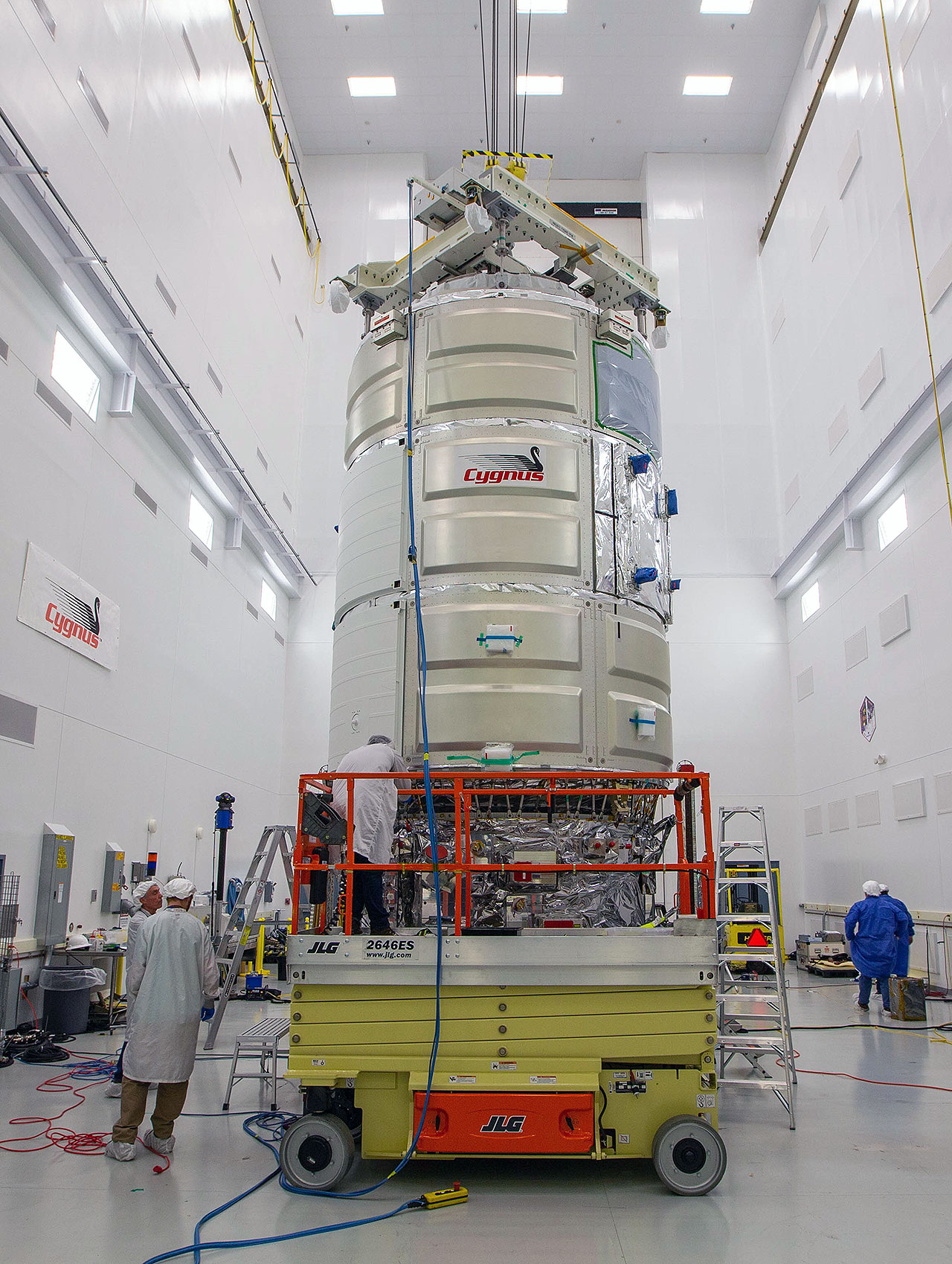
The 13th Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft has been christened for Robert Henry Lawrence, Jr., who in 1967 was chosen for the U.S. Air Force's Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) program. The "S.S. Robert H. Lawrence" is scheduled to launch to the International Space Station atop a Northrop Grumman Antares rocket from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9.
"Northrop Grumman is proud to name the NG-13 Cygnus spacecraft after former astronaut Robert Henry Lawrence Jr.," Northrop Grumman announced on its website on Martin Luther King, Jr. Day (Jan. 20). "Major Lawrence was selected in honor of his prominent place in history as the first African-American astronaut."
Related: Private Antares rocket & Cygnus spacecraft explained (infographic)

An experienced pilot with a doctorate in physical chemistry, Lawrence flew test flights that later helped to inform the landing performance of NASA's space shuttle orbiters. On June 30, 1967, he was chosen as a member of the third group of Air Force aerospace research pilots in preparation for the Manned Orbiting Lab (MOL), which was then planned as a crew-tended, reconnaissance platform in Earth orbit.
Six months later, on Dec. 8, 1967, Lawrence, 32, was tragically killed in the crash of an F-104 Starfighter supersonic jet.
Had Lawrence lived, he may have transferred with other MOL candidates to NASA's astronaut corps after the Air Force program was canceled two years later. The move could have led to him being the first African American to fly into space, a distinction that fell to Guion "Guy" Bluford in 1983, launching aboard the eighth flight of the space shuttle.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"Lawrence made the ultimate sacrifice in service to the space program," Northrop Grumman described on its website. "Although his career was cut short, he paved the way for future generations of aerospace pioneers of all races highlighting the need for diversity and inclusion across the industry."
In 1997, Lawrence was honored by the Astronauts Memorial Foundation with the addition of his name to the Space Mirror Memorial at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In 2018, artist Tavares Strachan and the Los Angeles County Museum of Art strove to raise awareness about Lawrence's life by launching ENOCH, a small sculpture-satellite that featured a gold bust of the late MOL candidate.
Flying the second of at least five missions under Northrop Grumman's Commercial Resupply Services-2 (CRS) contract with NASA, the S.S. Robert Lawrence will deliver science, supplies and equipment for the space station's Expedition 61 and 62 crews. Among the payloads launching on the NG-13 Cygnus will be a tissue and cell culture facility and the seeds needed to cultivate radishes in the station's Advanced Plant Habitat facility.
The S.S. Robert Lawrence will also support combustion experiments after being unloaded of its cargo and departing the station, prior to its own fiery demise during its re-entry into Earth's atmosphere.
The christening of the S.S. Robert Lawrence carries forward a custom that began in 2013. "It is the company's tradition to name each Cygnus after an individual who has played a pivotal part in the legacy of human spaceflight," Northrop Grumman explained.
Other astronaut namesakes have been David Low, Gordon Fullerton, Janice Voss, Deke Slayton, Rick Husband, Alan Poindexter, John Glenn, Gene Cernan, John Young and Roger Chaffee. The most recent Cygnus, which launched in November and is scheduled to depart the space station on Jan. 31, was named the S.S. Alan Bean after the Apollo 12 moonwalker and Skylab commander.
An additional Cygnus was named the S.S. J.R. Thompson after a former company executive.
Click through to collectSPACE to see Northrop Grumman's mission patch for the S.S. Robert H. Lawrence's NG-13 flight to the space station.
- SpaceX launches artist's satellite memorializing first black astronaut
- In photos: Antares rocket launches Cygnus NG-12 cargo craft to space station
- Cygnus cargo ship arrives at space station with cookie dough, mice and more
Follow collectSPACE.com on Facebook and on Twitter at @collectSPACE. Copyright 2020 collectSPACE.com. All rights reserved.

Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Robert Pearlman is a space historian, journalist and the founder and editor of collectSPACE.com, a daily news publication and community devoted to space history with a particular focus on how and where space exploration intersects with pop culture. Pearlman is also a contributing writer for Space.com and co-author of "Space Stations: The Art, Science, and Reality of Working in Space” published by Smithsonian Books in 2018.In 2009, he was inducted into the U.S. Space Camp Hall of Fame in Huntsville, Alabama. In 2021, he was honored by the American Astronautical Society with the Ordway Award for Sustained Excellence in Spaceflight History. In 2023, the National Space Club Florida Committee recognized Pearlman with the Kolcum News and Communications Award for excellence in telling the space story along the Space Coast and throughout the world.