The West Antarctic Ice Sheet is melting, and it's too late to stop it
Not only is this melting process "unavoidable," but its rate is also increasing.
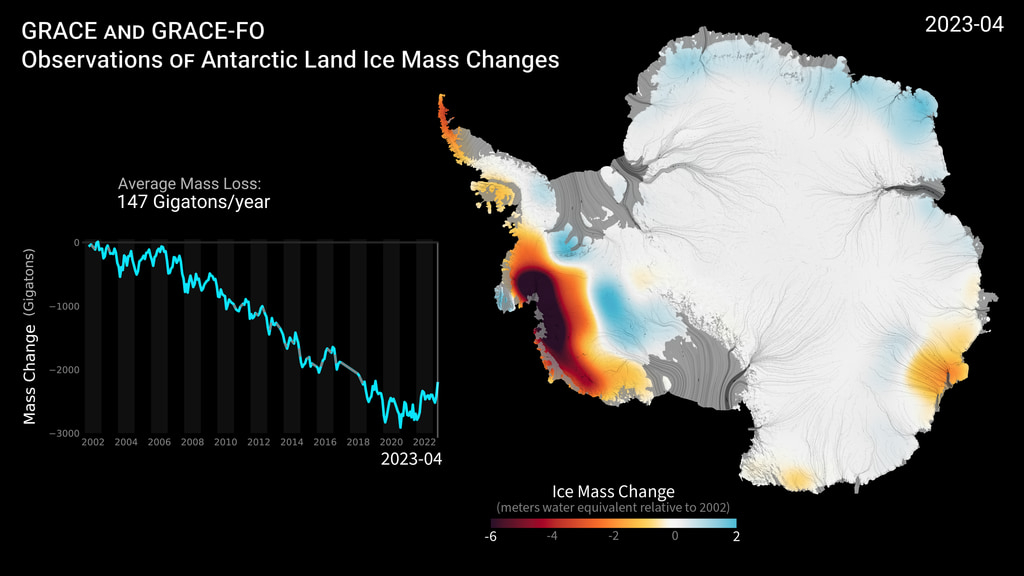
It's not looking good for the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. This body of ice is Antarctica's largest contributor to global sea-level rise, and it's only going to get worse from here. After running multiple simulations, researchers determined that increased melting of the sheet will be unavoidable throughout the rest of the century.
Scientists previously hypothesized that a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions could mitigate the warming of the Amundsen Sea, which contributes to melting of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet.
That hypothesis has now been put to the test.
Related: Antarctic sea ice hits record low, satellites reveal
Using the UK's national supercomputer, researchers have developed four future melting projections using anticipated global temperature rise data based on mid-range and best-case emission scenarios — and none of the cases are good ones. Even in the team's best-case projection that meets ambitious Paris Accord targets, the West Antarctic Ice Sheet still melts three times faster in the 21st century than it did in the 20th.
"It looks like we’ve lost control of melting of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. If we wanted to preserve it in its historical state, we would have needed action on climate change decades ago," Dr. Kaitlin Naughten, a British Antarctic Survey researcher, said in a statement.
Instead, the floating ice shelves that buttress the West Antarctic Ice Sheet will weaken over the coming decades, accelerating the flow of upstream glaciers toward the ocean, where they will eventually break off into icebergs and melt.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
"The bright side is that by recognizing this situation in advance, the world will have more time to adapt to the sea level rise that’s coming," said Naughten. "If you need to abandon or substantially re-engineer a coastal region, having 50 years lead time is going to make all the difference."
On a more positive note, the melting is projected to slow at the end of the 21st century — but we'd need to take action immediately to achieve that future. "We must not stop working to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels," said Naughten. "What we do now will help to slow the rate of sea level rise in the long term.
The team's research was published in the journal Nature Climate Change on Oct. 23.

Space.com contributing writer Stefanie Waldek is a self-taught space nerd and aviation geek who is passionate about all things spaceflight and astronomy. With a background in travel and design journalism, as well as a Bachelor of Arts degree from New York University, she specializes in the budding space tourism industry and Earth-based astrotourism. In her free time, you can find her watching rocket launches or looking up at the stars, wondering what is out there. Learn more about her work at www.stefaniewaldek.com.
