What is emergent gravity, and will it rewrite physics?
The idea is still new and requires a lot of assumptions in its calculations to make it work. Over the years, experimental results have been mixed.

In 2009, theoretical physicist Erik Verlinde proposed a radical reformulation of gravity. In his theory, gravity is not a fundamental force but rather a manifestation of deeper hidden processes. But in the 15 years since then, there hasn't been much experimental support for the idea. So where do we go next?
Emergence is common throughout physics. The property of temperature, for example, isn't an intrinsic property of gases. Instead, it's the emergent result of countless microscopic collisions. We have the tools to match those microscopic collisions to temperature; indeed, there is an entire branch of physics, known as statistical mechanics, that makes these connections known.
In other areas, the connections between microscopic behaviors and emergent properties aren't so clear. For example, while we understand the simple mechanisms behind superconductivity, we do not know how microscopic interactions lead to the emergence of high-temperature superconductors.
Related: Why Einstein must be wrong: In search of the theory of gravity
Verlinde's theory is based on what Stephen Hawking and Jacob Bekenstein observed in the 1970s: Many properties of black holes can be expressed in terms of the laws of thermodynamics. However, the laws of thermodynamics are themselves emergent from microscopic processes. To Verlinde, this was more than a mere coincidence and indicated that what we perceive as gravity may be emerging from some deeper physical process.
In 2009, he published the first version of his theory. Crucially, we do not need to know what those deeper processes are, since we already have the tool kit — statistical mechanics — for describing emergent properties. So Verlinde applied these techniques to gravity and arrived at an alternate formulation of gravity. And because gravity is also tied to our concepts of motion, inertia, space and time, this means our entire universe is also emergent from those same deeper processes.
At first, not much came of this; rewriting a known law of physics, while interesting, doesn't necessarily provide deeper insights. But in 2016, Verlinde expanded his theory by discovering that a universe containing dark energy naturally leads to a new emergent property of space, thus allowing it to push inward on itself in regions of low density.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
This discovery led to a flurry of excitement, as it provided an alternative explanation for dark matter. Currently, astronomers believe that dark matter is a mysterious, invisible substance that makes up the bulk of all the mass of every galaxy. While that hypothesis has been able to explain a vast wealth of observations, from the rotation rates of stars within galaxies to the evolution of the largest structures in the cosmos, we have yet to identify the mysterious particle.
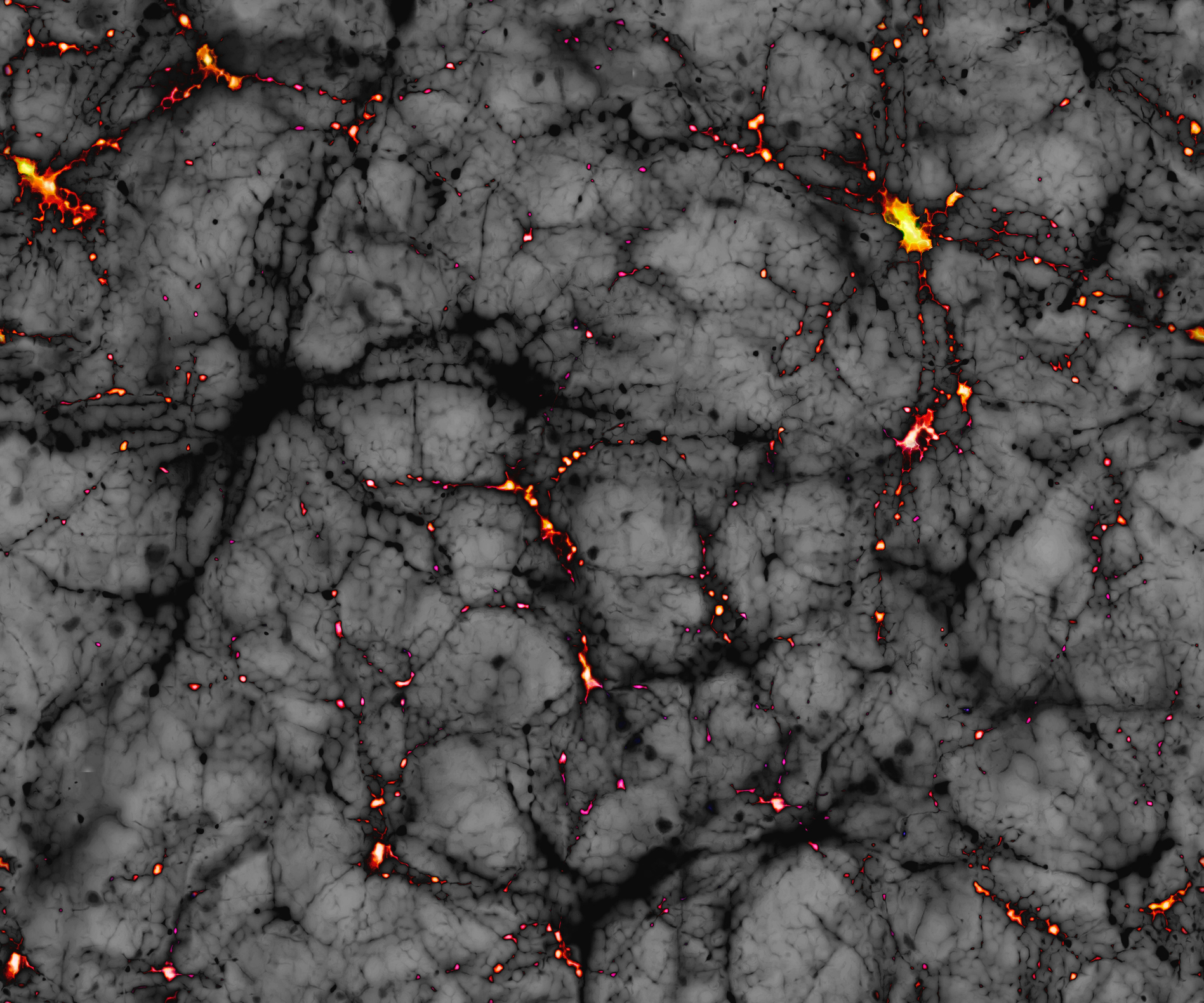
In Verlinde's picture of emergent gravity, as soon as you enter low-density regions — basically, anything outside the solar system — gravity behaves differently than we would expect from Einstein's theory of general relativity. At large scales, there is a natural inward pull to space itself, which forces matter to clump up more tightly than it otherwise would.
This idea was exciting because it allowed astronomers to find a way to test this new theory. Observers could take this new theory of gravity and put it in models of galaxy structure and evolution to find differences between it and models of dark matter.
Over the years, however, the experimental results have been mixed. Some early tests favored emergent gravity over dark matter when it came to the rotation rates of stars. But more recent observations haven't found an advantage. And dark matter can also explain much more than galaxy rotation rates; tests within galaxy clusters have found emergent gravity coming up short.
This isn't the end of emergent gravity. The idea is still new and requires a lot of assumptions in its calculations to make it work. Without a fully realized theory, it's hard to tell if the predictions it makes for the behavior of galaxies and clusters accurately represent what emergent gravity would tell us. And astronomers are still trying to develop more stringent tests, like using data from the cosmic microwave background, to really put the theory through its paces.
Emergent gravity remains an intriguing idea. If it's correct, we would have to radically reshape our understanding of the natural world and see gravity and motion — and even more fundamental concepts, like time and space — through a lens of emergence from deeper, more complicated interactions. But for right now, it remains simply an intriguing idea. Only time and extensive observational testing will tell us if we're on the right track.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.

Paul M. Sutter is an astrophysicist at SUNY Stony Brook and the Flatiron Institute in New York City. Paul received his PhD in Physics from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign in 2011, and spent three years at the Paris Institute of Astrophysics, followed by a research fellowship in Trieste, Italy, His research focuses on many diverse topics, from the emptiest regions of the universe to the earliest moments of the Big Bang to the hunt for the first stars. As an "Agent to the Stars," Paul has passionately engaged the public in science outreach for several years. He is the host of the popular "Ask a Spaceman!" podcast, author of "Your Place in the Universe" and "How to Die in Space" and he frequently appears on TV — including on The Weather Channel, for which he serves as Official Space Specialist.
-
Rod Mack The ideas of Theory Z0 using the density of energy to drive the acceleration seen as gravity have applications to this view.Reply
The Z0 Theory is a new idea about gravity, simplifying the complex ideas developed over the last century. Instead of thinking of gravity as a force pulling things together, it suggests a connection to acceleration. This means gravity is linked to electromagnetic energy, not mass, as traditionally believed.
At its core, Z0 challenges traditional notions by proposing that gravity is not a force of attraction but rather an 'equivalence' related to acceleration. This unique perspective links gravity to electromagnetic energy, departing from the conventional association with mass, as famously expressed in Einstein's E=mc².
Maxwell's equations play a crucial role. The speed of light (c) and the admittance of free space (Y0) are interconnected, revealing that alterations in these parameters impact the rate of energy flow. Changes in the speed of light, representing energy, are then identified as the acceleration attributed to gravity.
The gravitational constant in this framework denoted as Gv, where Gv = -Δx/Δ√ε0μ0, is intricately tied to the rate of change in the speed of energy. This theory not only offers a mechanism for gravity compatible with existing mathematical frameworks but also provides explanations for phenomena like black holes, and cosmic microwave background structures, and even postulates the existence of impedance bubbles as barrier structures.
Entropy, accounting for energy changes such as redshift and signal delays, becomes a key element in this quantum view of gravity based on energy. Z0 introduces a concept of 'quantum gravity,' emphasizing a connection between the complex admittance of energy into space.
Z0 presents a compelling framework where gravity is intricately tied to energy dynamics. This theory, akin to relativity, introduces the idea of a constant time and a variable speed of energy, explaining force as 'equivalent' gravity due to slight changes in energy density. It's a paradigm shift that seeks simplicity in explaining the profound mysteries of our universe.